
Jesus Christ is LORD ✝️
Evolutionism is a lie.
Pinned Post for threads of evidence for ID.
How to get URL link on X (Twitter) App

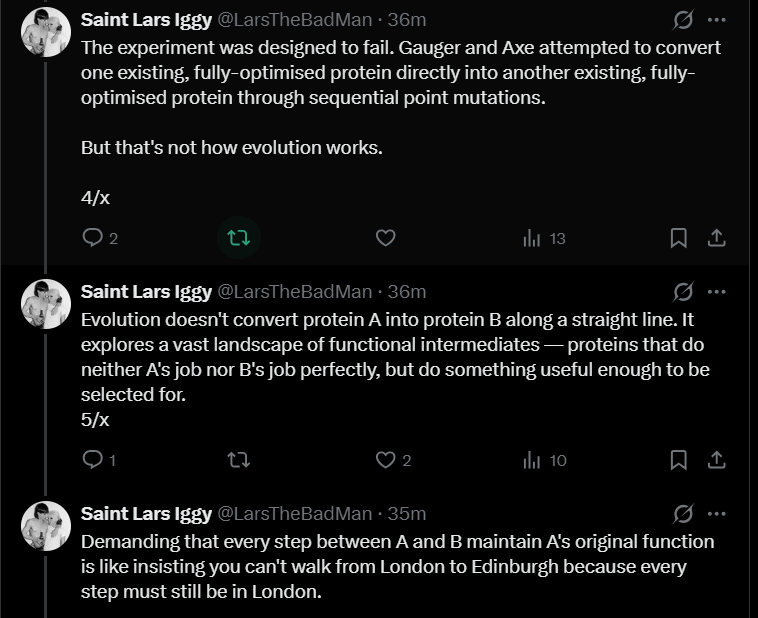
https://twitter.com/LarsTheBadMan/status/2020858596624326801Point 1: Lars claims the research I highlighted in my original post about how proteins cannot be evolved into novel forms "was designed to fail" because it doesn't reflect "how evolution works." He says evolution doesn't evolve things from A to B, but works by evolving a bit at a time, "something useful enough to be selected for."

 1. The Cambrian Explosion
1. The Cambrian Explosion

 Genetic Similarity and Homologous Genes
Genetic Similarity and Homologous Genes
 First, the background:
First, the background:
 Background:
Background:https://x.com/DivinelyDesined/status/19968812172713452551. He argues that "Hox genes are evolution's smoking gun" and that they "only make sense through common ancestry" because the same Hox clusters control development in many different organisms.

 At the moment of conception, the entire Body Plan Blueprint is already established - from that first cell all the way to full development at birth.
At the moment of conception, the entire Body Plan Blueprint is already established - from that first cell all the way to full development at birth.
 Evolutionists often claim the strongest evidence for their theory is that organisms share similar DNA content - and this similarity is best explained by common ancestry.
Evolutionists often claim the strongest evidence for their theory is that organisms share similar DNA content - and this similarity is best explained by common ancestry.
 First, let’s define multicellularity - what is it exactly?
First, let’s define multicellularity - what is it exactly?
 Even the "simplest" light sensitive cell still requires an irreducibly complex system of highly sophisticated parts, all working together, from the start, or it doesn't function.
Even the "simplest" light sensitive cell still requires an irreducibly complex system of highly sophisticated parts, all working together, from the start, or it doesn't function.https://twitter.com/DivinelyDesined/status/19752014008514071061. Genetic Data from modern humans confirms mutation rates are too fast for evolutionary timelines.

 The GULO “Pseudogene” is said to be a “shared mistake” between humans & primates, and this common mistake is best explained by common ancestry.
The GULO “Pseudogene” is said to be a “shared mistake” between humans & primates, and this common mistake is best explained by common ancestry.
 First: What exactly is Irreducible Complexity?
First: What exactly is Irreducible Complexity?
https://twitter.com/doofgeek4011/status/19584120473871689921. He starts by claiming that I misrepresented the data.

 First, a little history on the data…
First, a little history on the data…
https://twitter.com/doofgeek4011/status/1956894090844684790Let’s go through it:


 What are Orphan Genes?
What are Orphan Genes?

 The evolutionary says that modern humans evolved ~200-300,000 years ago from a large population of ~10,000-100,000 individuals.
The evolutionary says that modern humans evolved ~200-300,000 years ago from a large population of ~10,000-100,000 individuals.
 The phrase "according to its kind" is repeated in Genesis 1:1-27 TEN TIMES in total.
The phrase "according to its kind" is repeated in Genesis 1:1-27 TEN TIMES in total.