
The Soviet Exploration of Venus, Bossart: America's Forgotten Rocket Scientist. Bell Labs, Princeton University, Microsoft Research.
How to get URL link on X (Twitter) App



 The core of RDS-1, the first Soviet A-bomb, a 22 kiloton fission device. Russian physicists were hoping to play a more creative role, but Beria ordered them to build copies of the American bombs, whose plans had been delivered by the Rosenberg spy ring.
The core of RDS-1, the first Soviet A-bomb, a 22 kiloton fission device. Russian physicists were hoping to play a more creative role, but Beria ordered them to build copies of the American bombs, whose plans had been delivered by the Rosenberg spy ring. 

 The rover's batteries were charged by gallium arsenide solar panels. It had four cycloramic cameras that scanned panoramic images, and two television cameras in front used for navigation. The wheel and motor assembly, and the cycloramic camera shown here.
The rover's batteries were charged by gallium arsenide solar panels. It had four cycloramic cameras that scanned panoramic images, and two television cameras in front used for navigation. The wheel and motor assembly, and the cycloramic camera shown here. 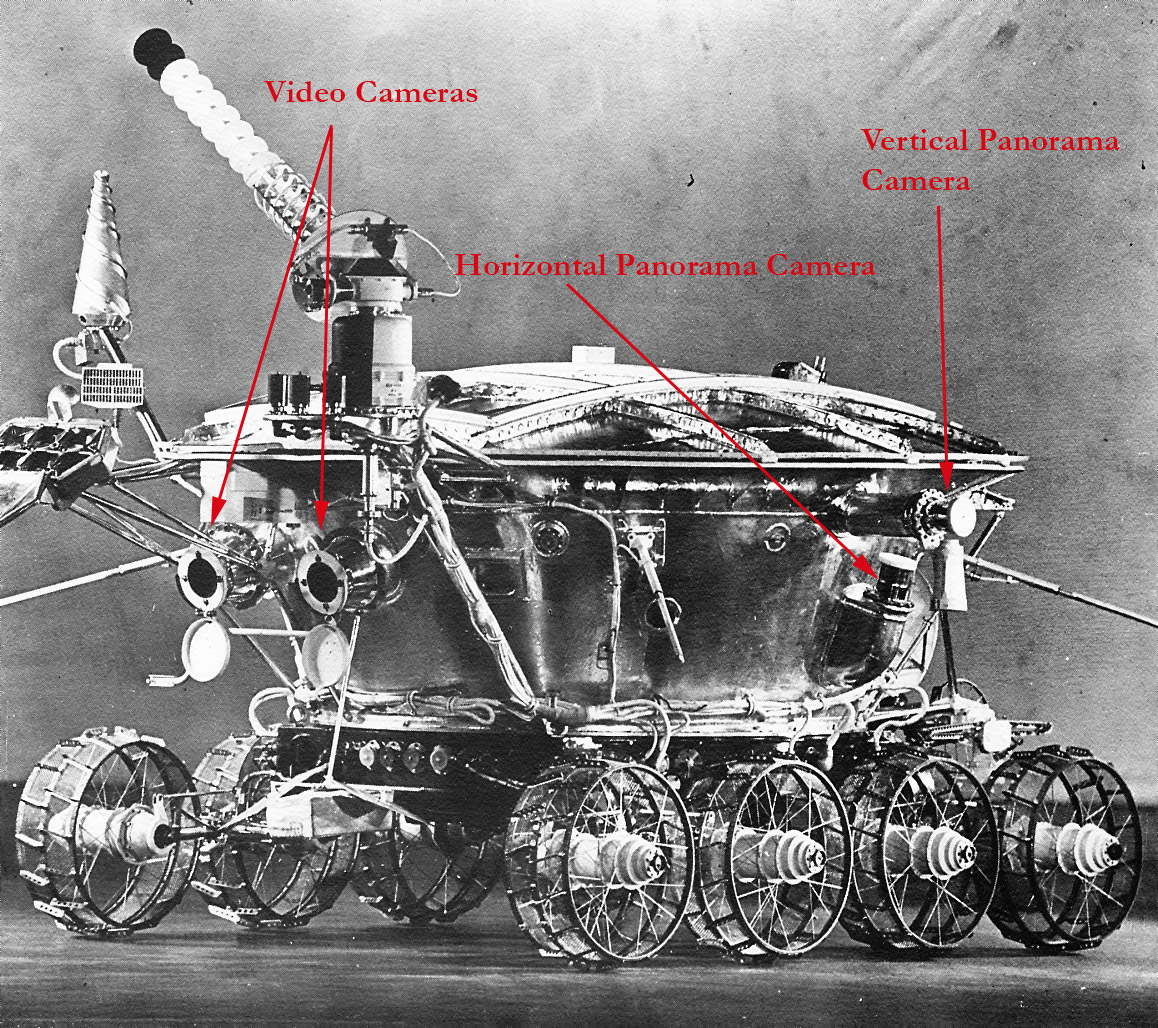
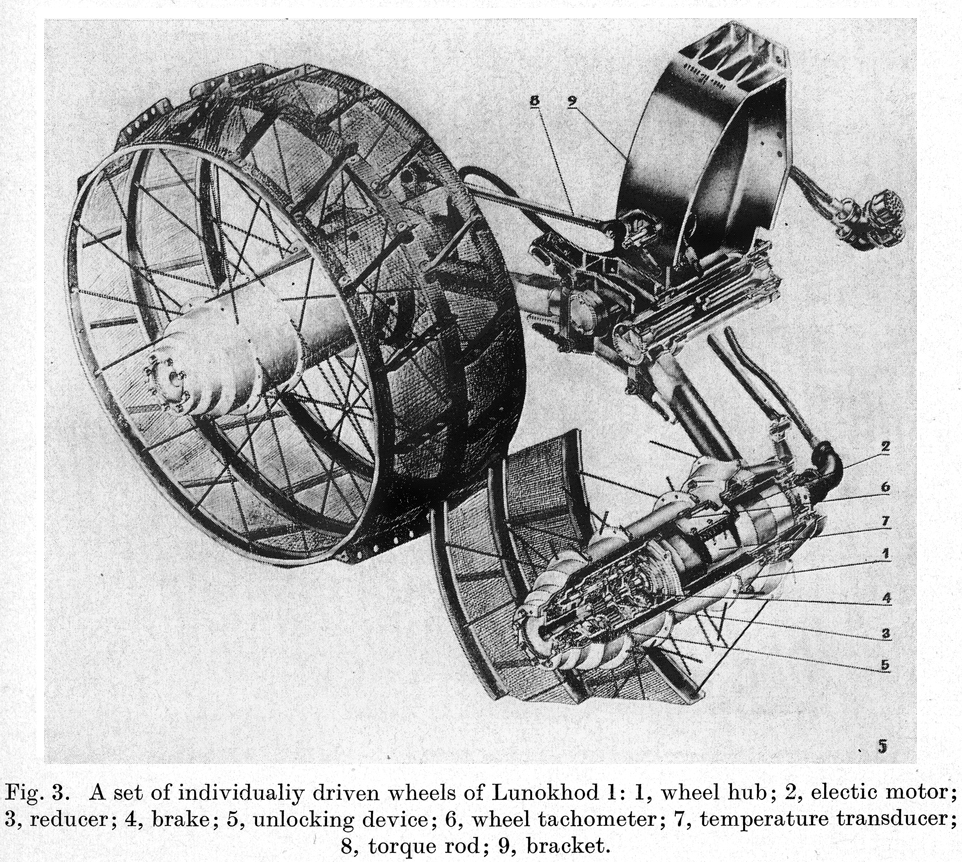
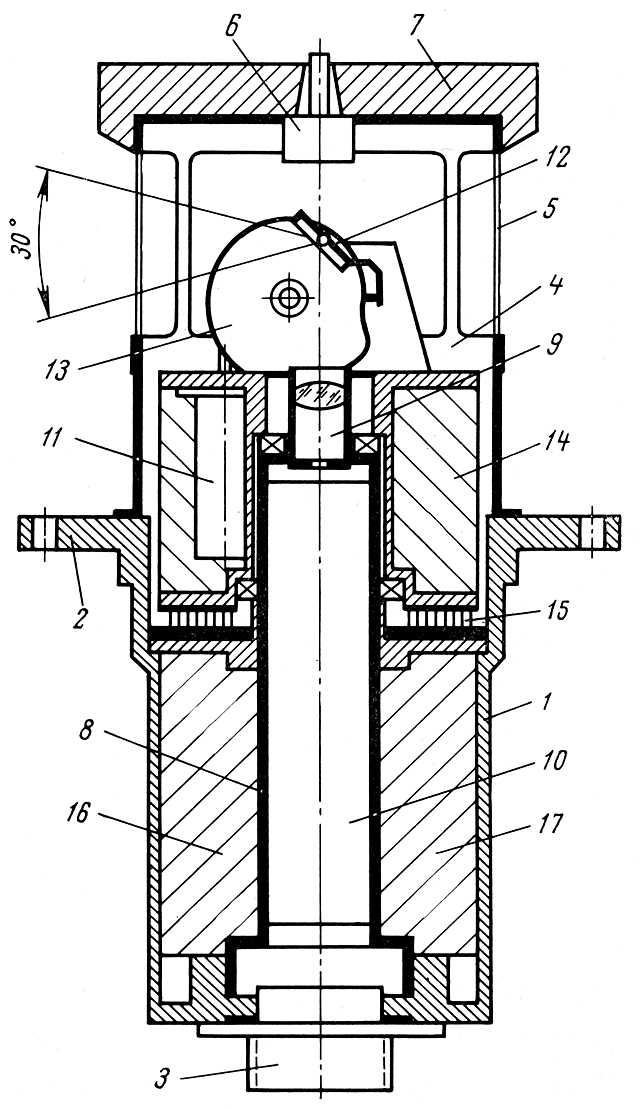

 For redundancy, the radio system used two completely different schemes: pulse code modulation at decimeter wavelength, and an old system of pulse-position modulation at centimeter wavelength (with orthogonal coding).
For redundancy, the radio system used two completely different schemes: pulse code modulation at decimeter wavelength, and an old system of pulse-position modulation at centimeter wavelength (with orthogonal coding). 
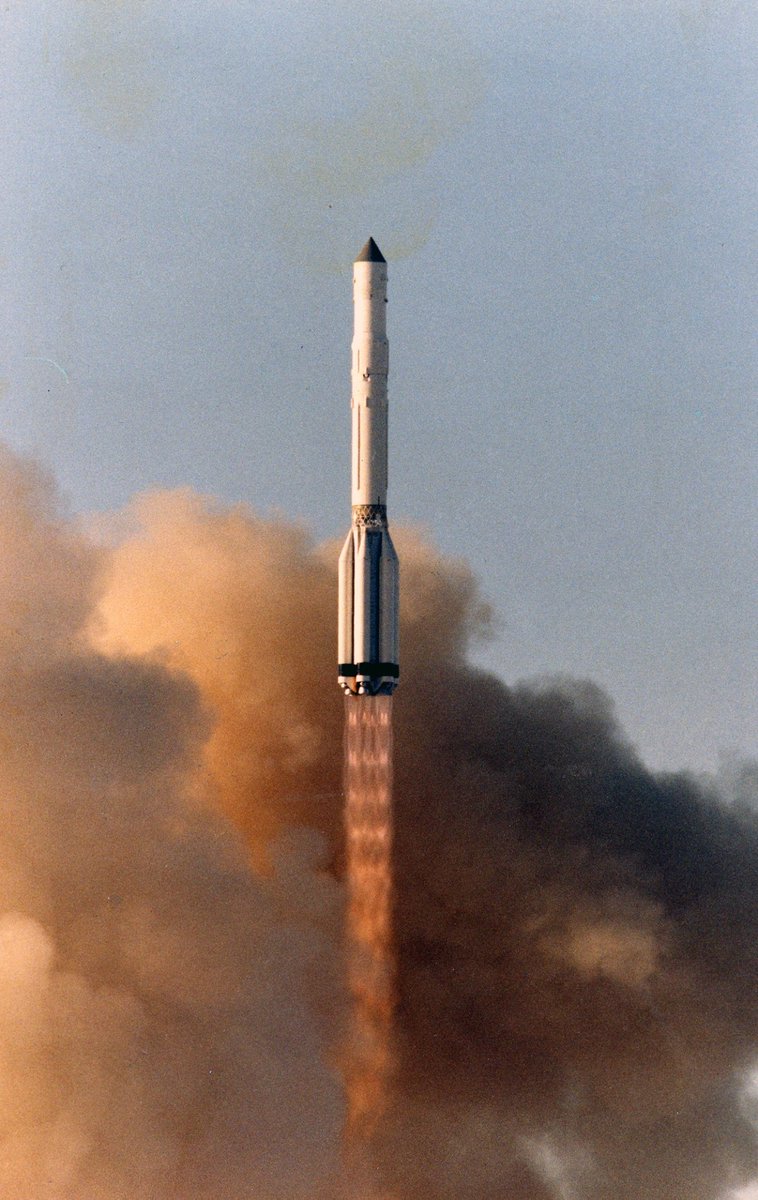


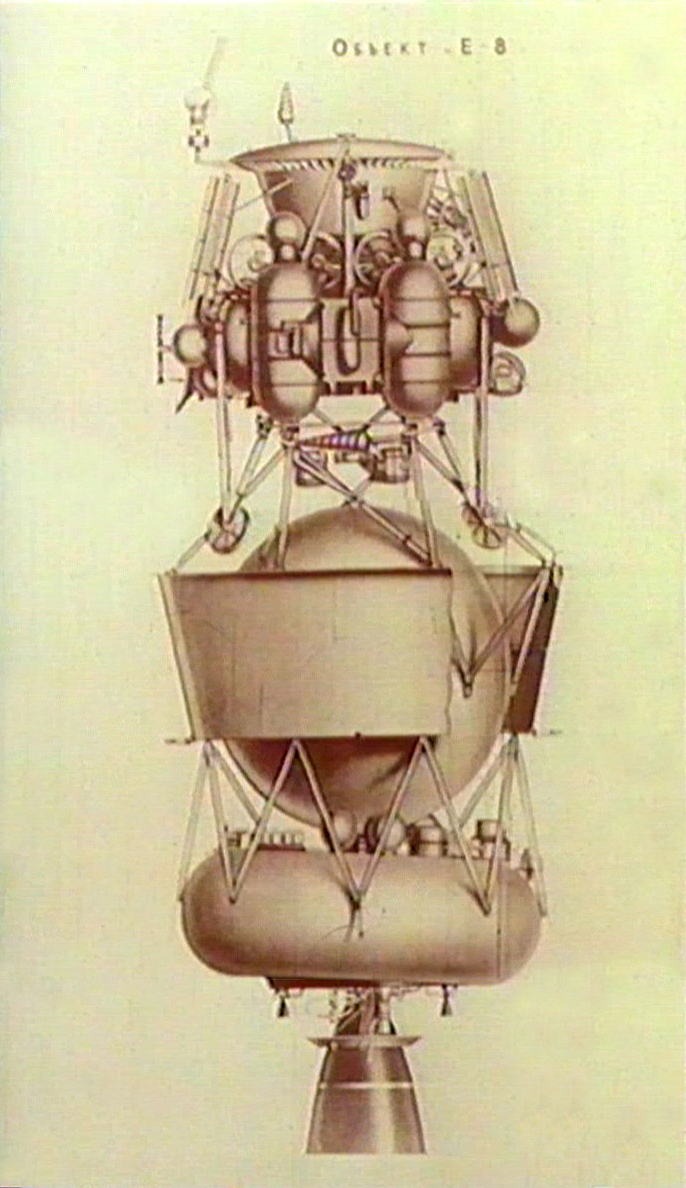
 The lander housed a number of scientific experiments in a spherical titanium pressure vessel, surrounded by silica insulation. Temperature inside was also controlled by a phase change material that absorbed heat as it melted.
The lander housed a number of scientific experiments in a spherical titanium pressure vessel, surrounded by silica insulation. Temperature inside was also controlled by a phase change material that absorbed heat as it melted. 



 The Internet was starting to spread rapidly in the 1980s. Finland was buying CISCO routers like crazy. In the USA, TCP/IP was taking over as the preferred network protocol. But in Europe and Japan, there was a decision to define their own data network standard.
The Internet was starting to spread rapidly in the 1980s. Finland was buying CISCO routers like crazy. In the USA, TCP/IP was taking over as the preferred network protocol. But in Europe and Japan, there was a decision to define their own data network standard.

 8K of 20-bit micro-program instruction ROM was implemented as core-rope memory. Wires threaded thru or around sensors represented rows of 1's and 0's. The large power transistors driving it were the cause of failure in Mars-4,5,6, and 7 in 1973.
8K of 20-bit micro-program instruction ROM was implemented as core-rope memory. Wires threaded thru or around sensors represented rows of 1's and 0's. The large power transistors driving it were the cause of failure in Mars-4,5,6, and 7 in 1973. 
