
Dad and husband • Software Engineer for 15+ years • Algorithms, Distributed Systems, System Design, Computer Vision
13 subscribers
How to get URL link on X (Twitter) App

 1. From Passwords to Modern Approaches: sessions-cookies, tokens, API keys, OTP, and SSO.
1. From Passwords to Modern Approaches: sessions-cookies, tokens, API keys, OTP, and SSO.
 1. From theory to production: cache performance, architecture, and deployment strategies.
1. From theory to production: cache performance, architecture, and deployment strategies.
 1. A 7 steps bulletproof framework to ace your next technical interview round
1. A 7 steps bulletproof framework to ace your next technical interview round 
 1. The evolution of a web application architecture when going from serving hundreds to millions of users.
1. The evolution of a web application architecture when going from serving hundreds to millions of users. 
 Database indexes have the same functionality as textbook indexes.
Database indexes have the same functionality as textbook indexes.
 1. How to become a better writer as a software engineer.
1. How to become a better writer as a software engineer. 
 1. Application-level Universal Unique Identifiers (UUIDs).
1. Application-level Universal Unique Identifiers (UUIDs).
 1. A taxonomy of the most used types of database available on the market: relational, NoSQL, time-series and NewSQL.
1. A taxonomy of the most used types of database available on the market: relational, NoSQL, time-series and NewSQL.
 1. Learn a programming language
1. Learn a programming language
 1. How to answer this popular system design question: from a simple concept to a scalable system.
1. How to answer this popular system design question: from a simple concept to a scalable system. 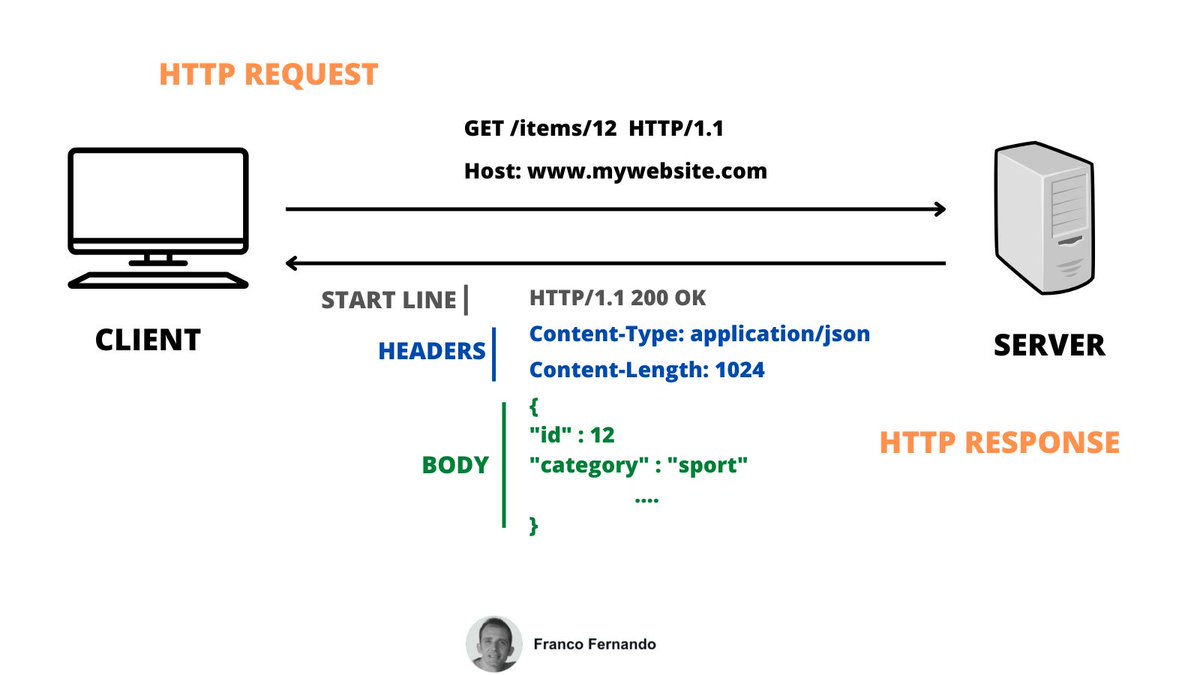
 1. What is HTTP
1. What is HTTP
 1. How RAFT solves the consensus problem in distributed systems: a step-by-step breakdown that every engineer can understand.
1. How RAFT solves the consensus problem in distributed systems: a step-by-step breakdown that every engineer can understand.
 1. Offset-Based
1. Offset-Based
 1. How to use the two-pointer method to efficiently solving array and string problems (with code templates).
1. How to use the two-pointer method to efficiently solving array and string problems (with code templates). 
 1. Breadth-first search
1. Breadth-first search 
 1. Common mistakes software engineers make during system design interviews and how to avoid them.
1. Common mistakes software engineers make during system design interviews and how to avoid them. 
 1. How to boost your career as a software engineer by communicating better with your peers, manager, and partners.
1. How to boost your career as a software engineer by communicating better with your peers, manager, and partners.
 1. Brute Force
1. Brute Force