
@pennmedicine Heme/Onc Fellow via @UCDmedicine; @thebianchilab; @mayoMN_imres
3 subscribers
How to get URL link on X (Twitter) App


 #2: West Haven Criteria
#2: West Haven Criteria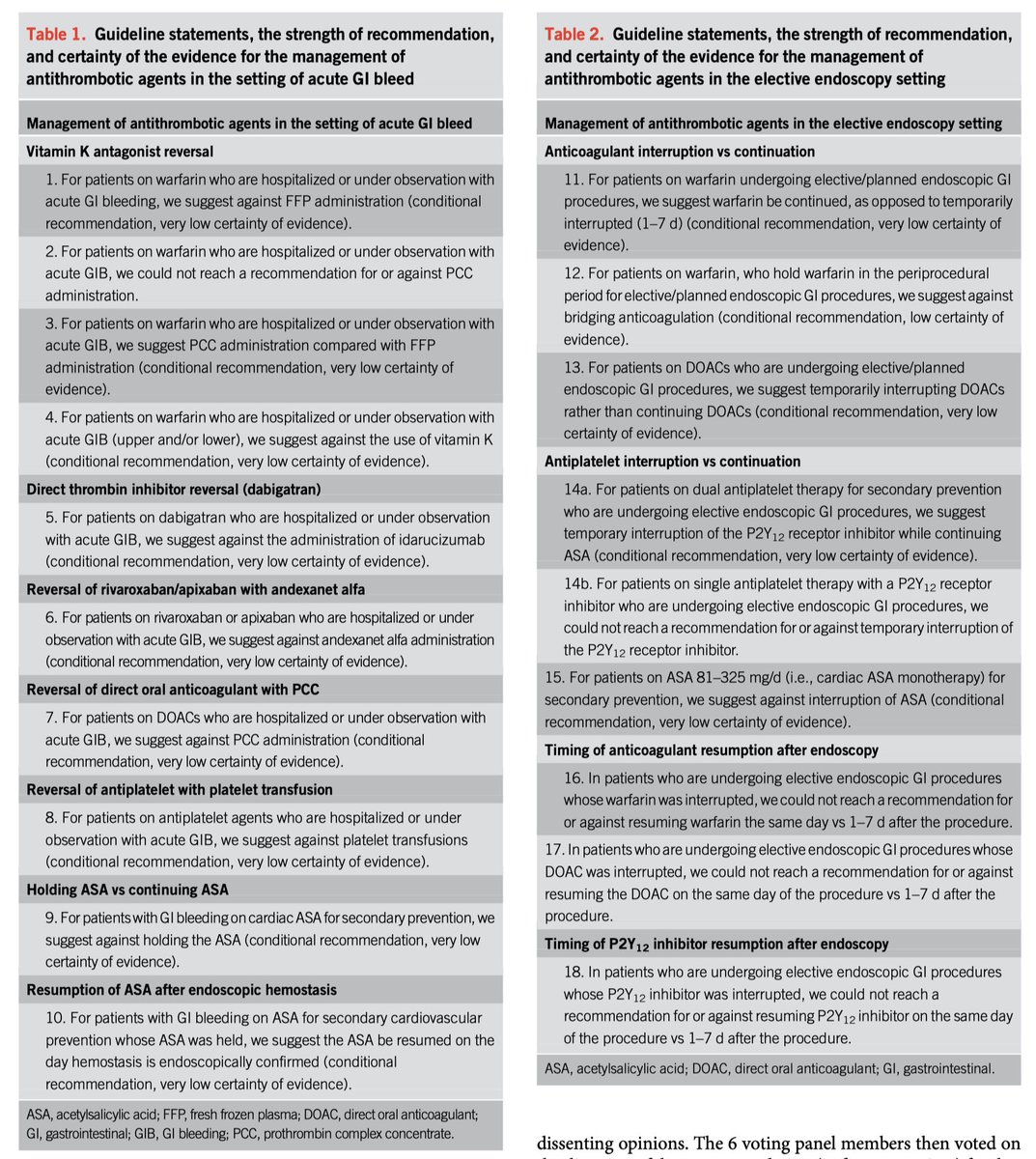
 Evidence for continuing (RCT small sample size)
Evidence for continuing (RCT small sample size)
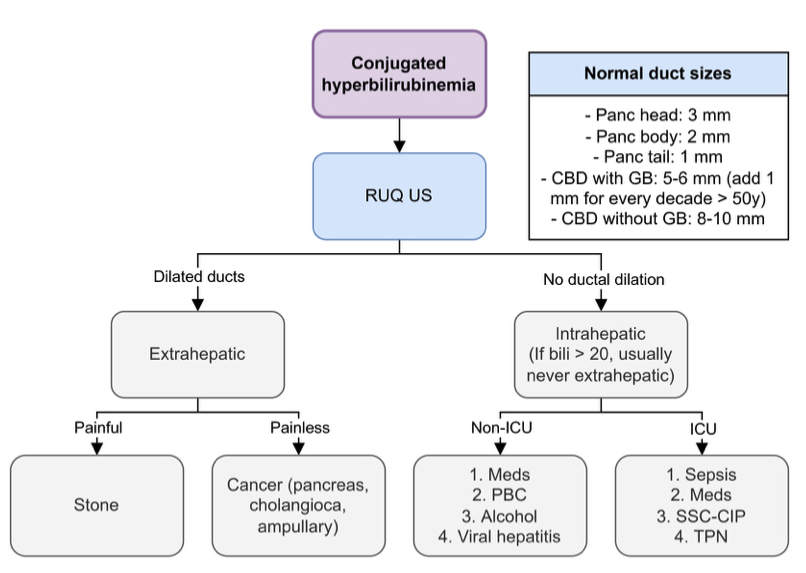

 Bilirubin thresholds:
Bilirubin thresholds: 

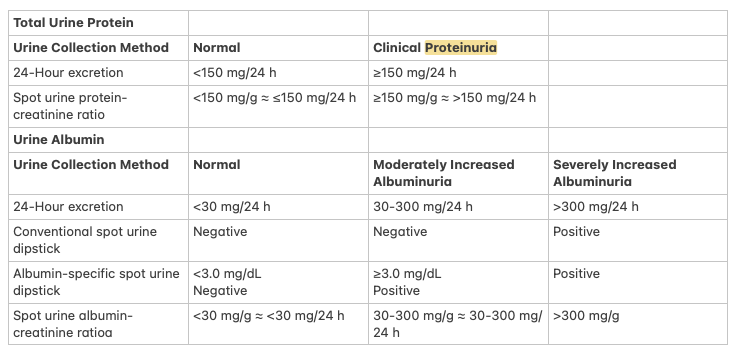

 2. Approach to iron deficiency anemia
2. Approach to iron deficiency anemia 