
Quant Finance Education| GenAI Backed Algo Trading Platform https://t.co/eUs8f0t1dO| Daily Thread on Quant Trading/Research/Dev | Linkedin 130k+
How to get URL link on X (Twitter) App

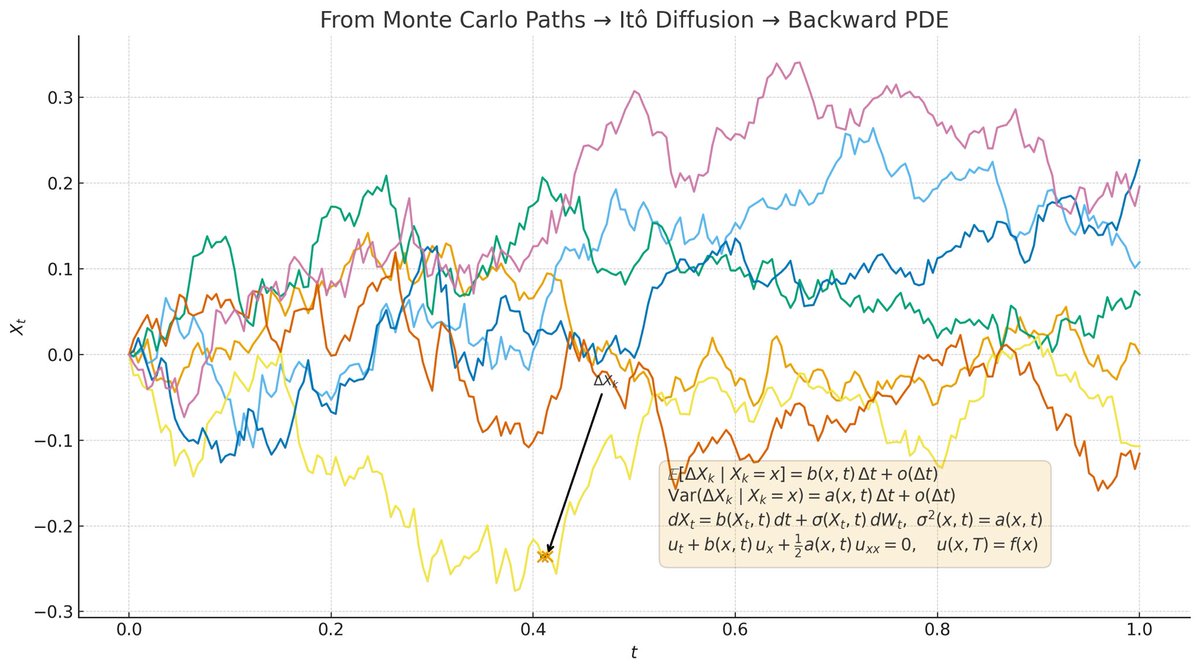
 From Monte Carlo Paths to a PDE: Why Drift & Vol Alone Define the Limit
From Monte Carlo Paths to a PDE: Why Drift & Vol Alone Define the Limit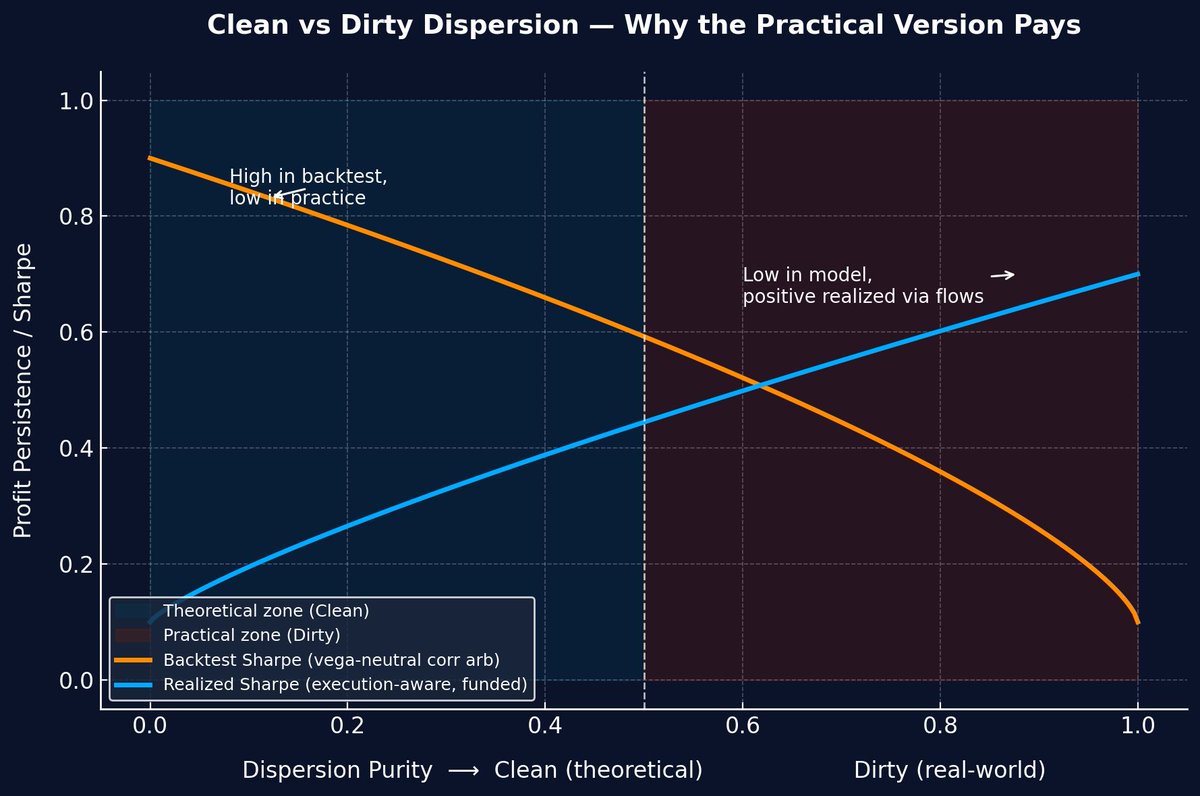
 In theory, dispersion trading isolates the correlation risk embedded in index options.
In theory, dispersion trading isolates the correlation risk embedded in index options.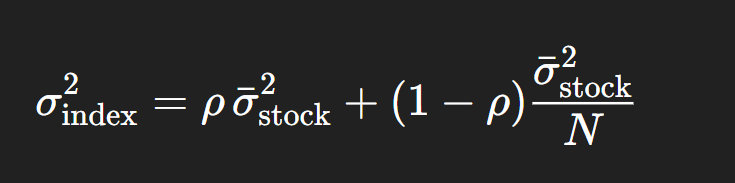
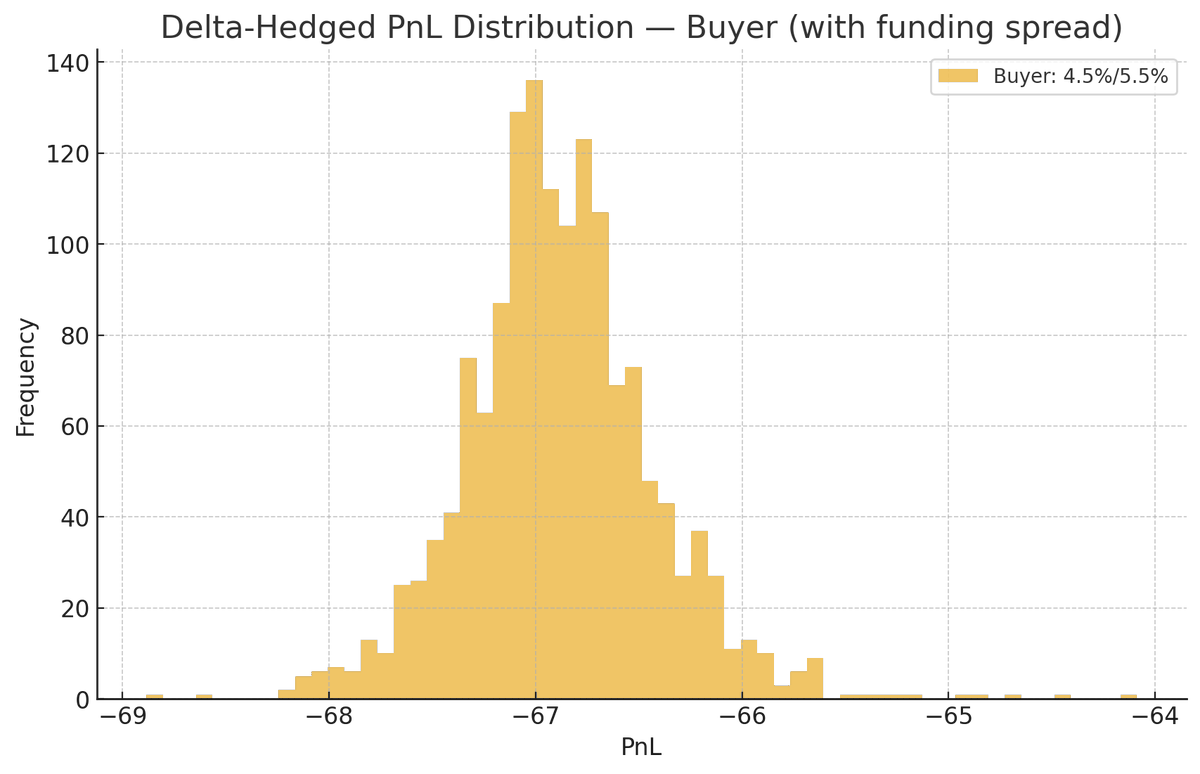

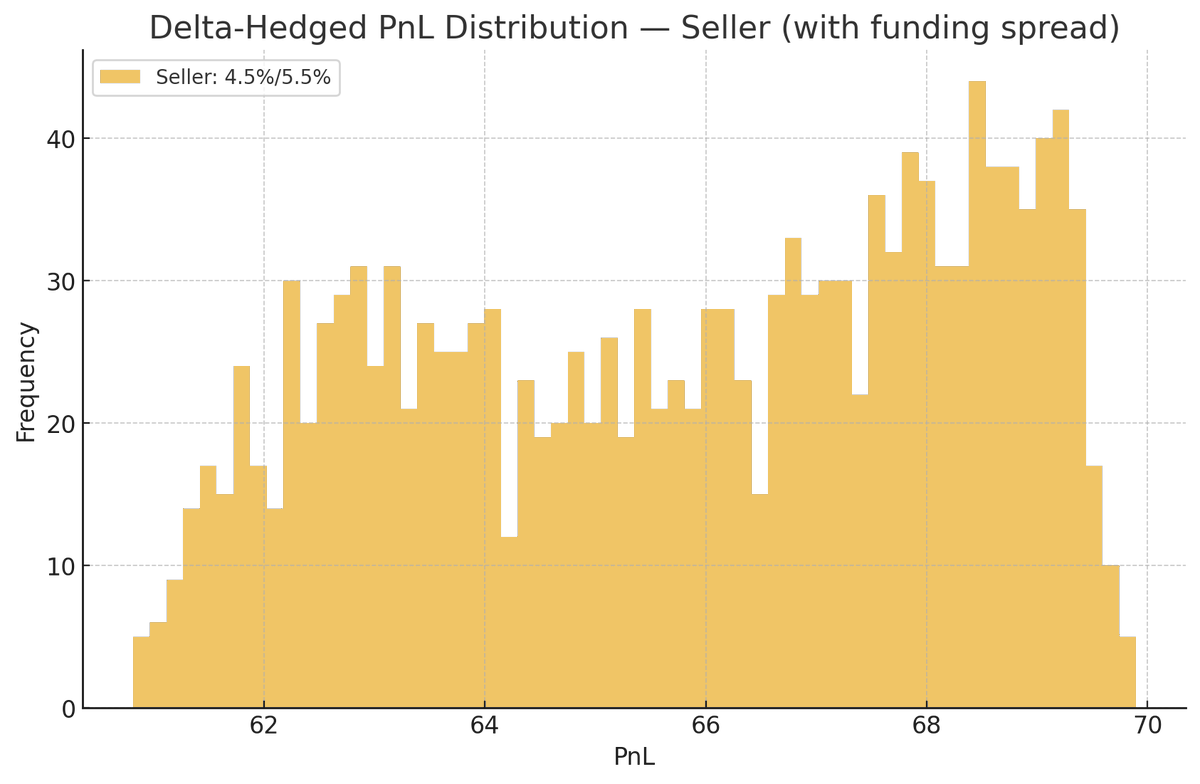 1. Option Values Depend on Funding
1. Option Values Depend on Funding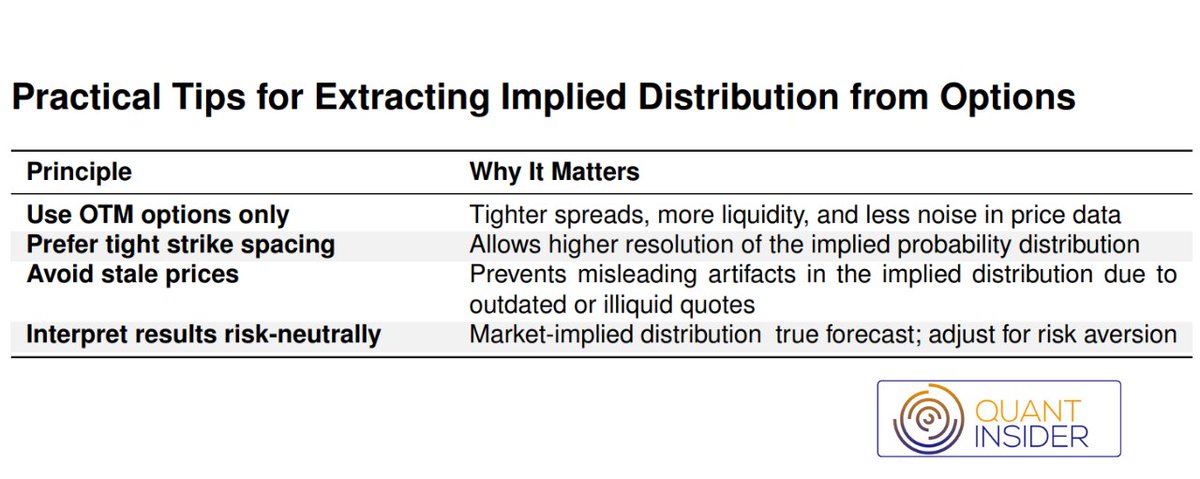
 Why Use Options to Infer Distribution?
Why Use Options to Infer Distribution?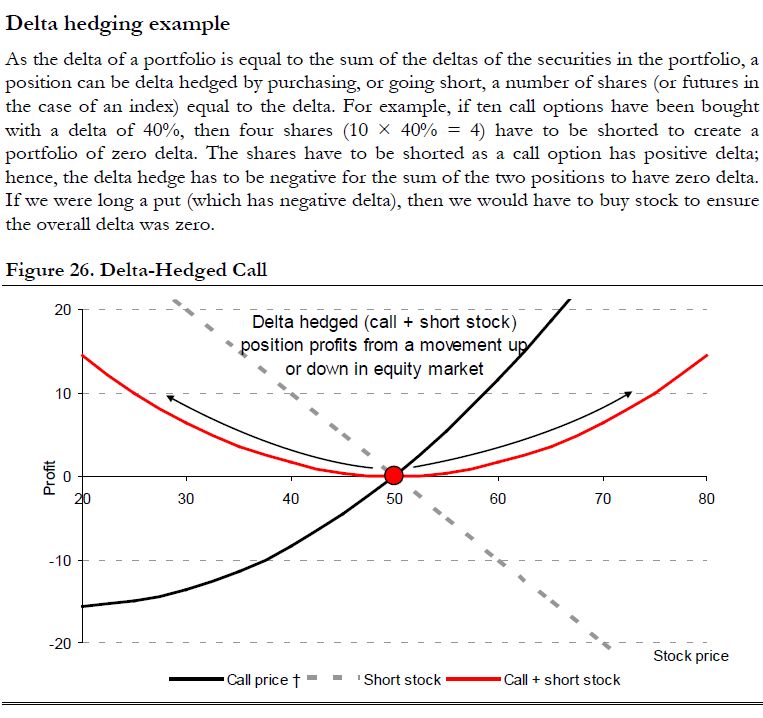
 2/n
2/n
 Stock Characteristics and Implied Volatility
Stock Characteristics and Implied Volatility 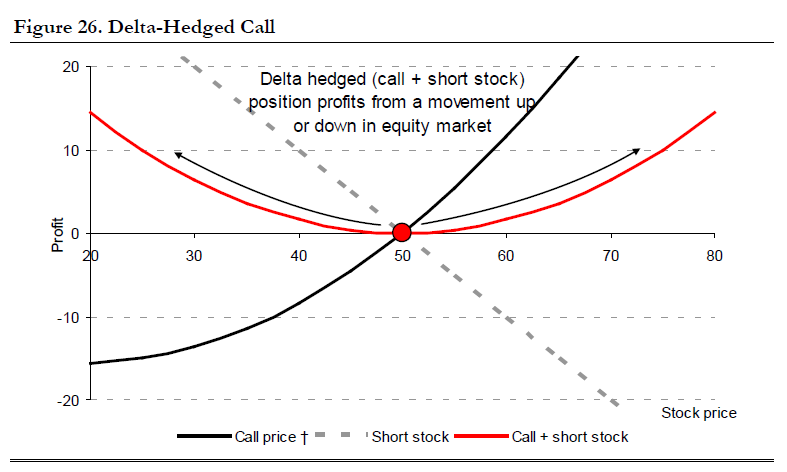
 Delta Hedging and Matching Maturity
Delta Hedging and Matching Maturity 
 1/12
1/12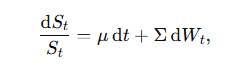
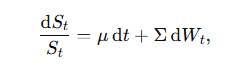
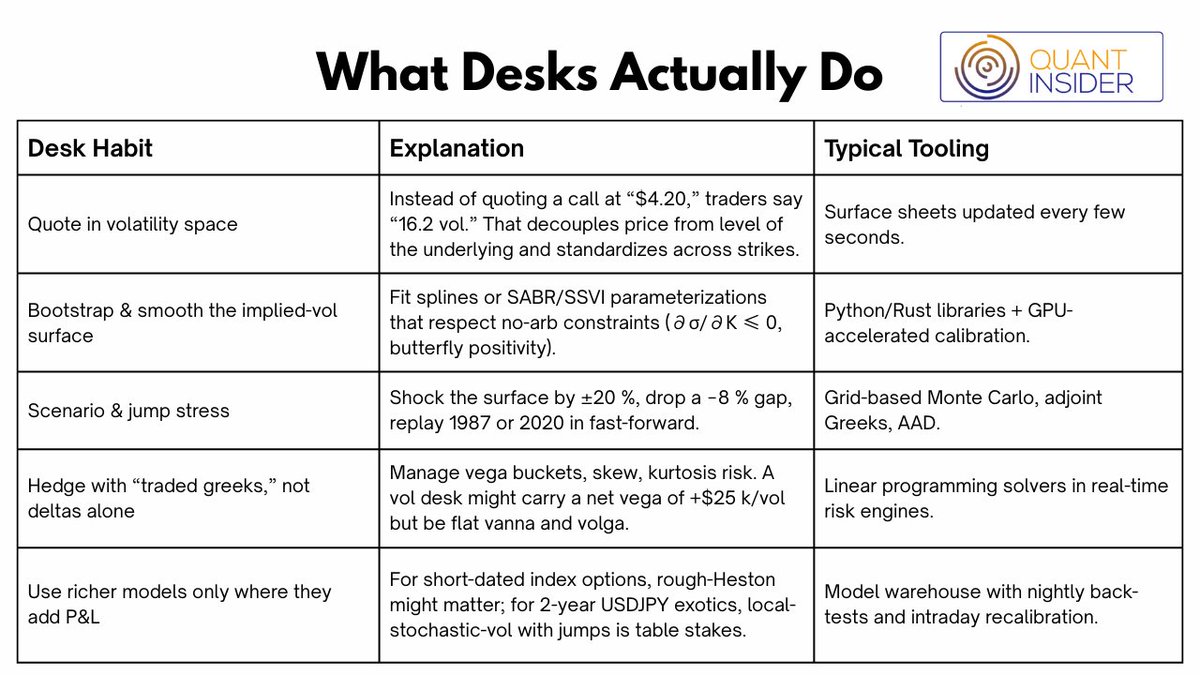
 Textbook Assumptions and How the Real World Breaks Them
Textbook Assumptions and How the Real World Breaks Them II. Supplementary Analytics Functions
II. Supplementary Analytics Functions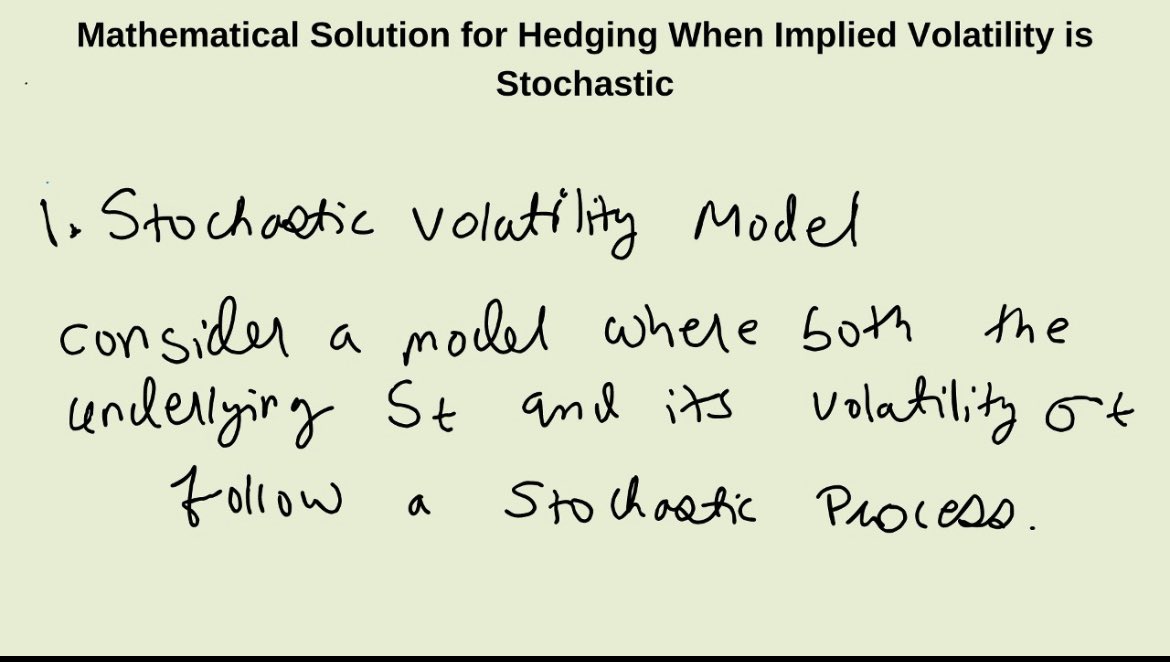

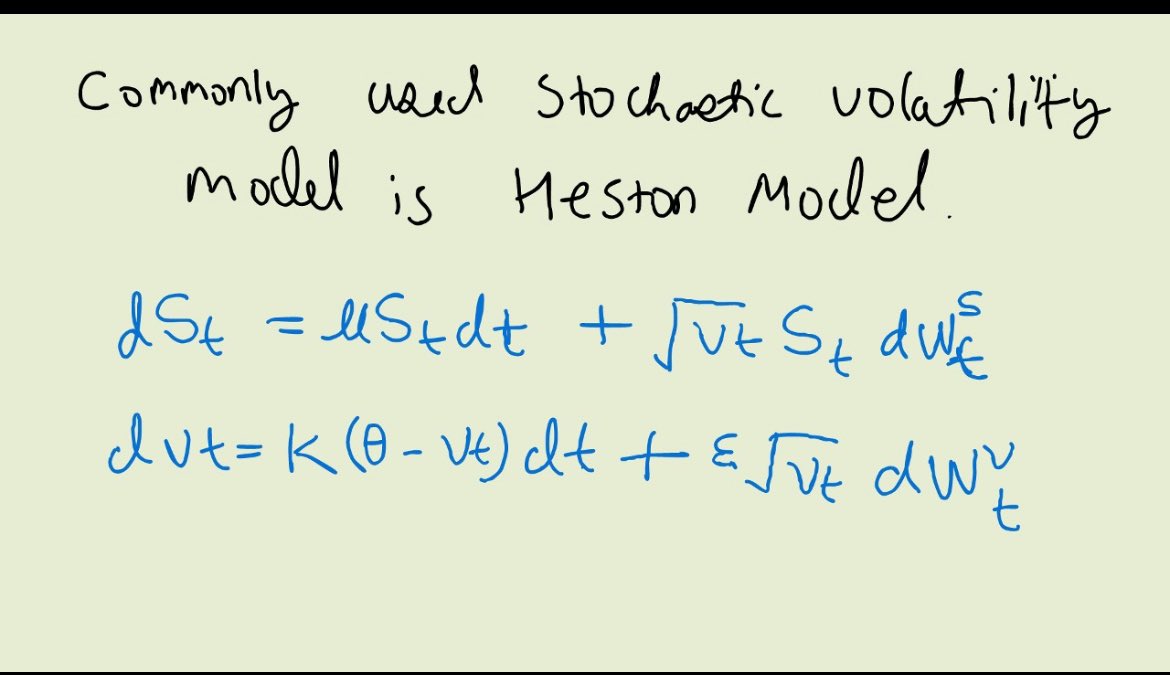
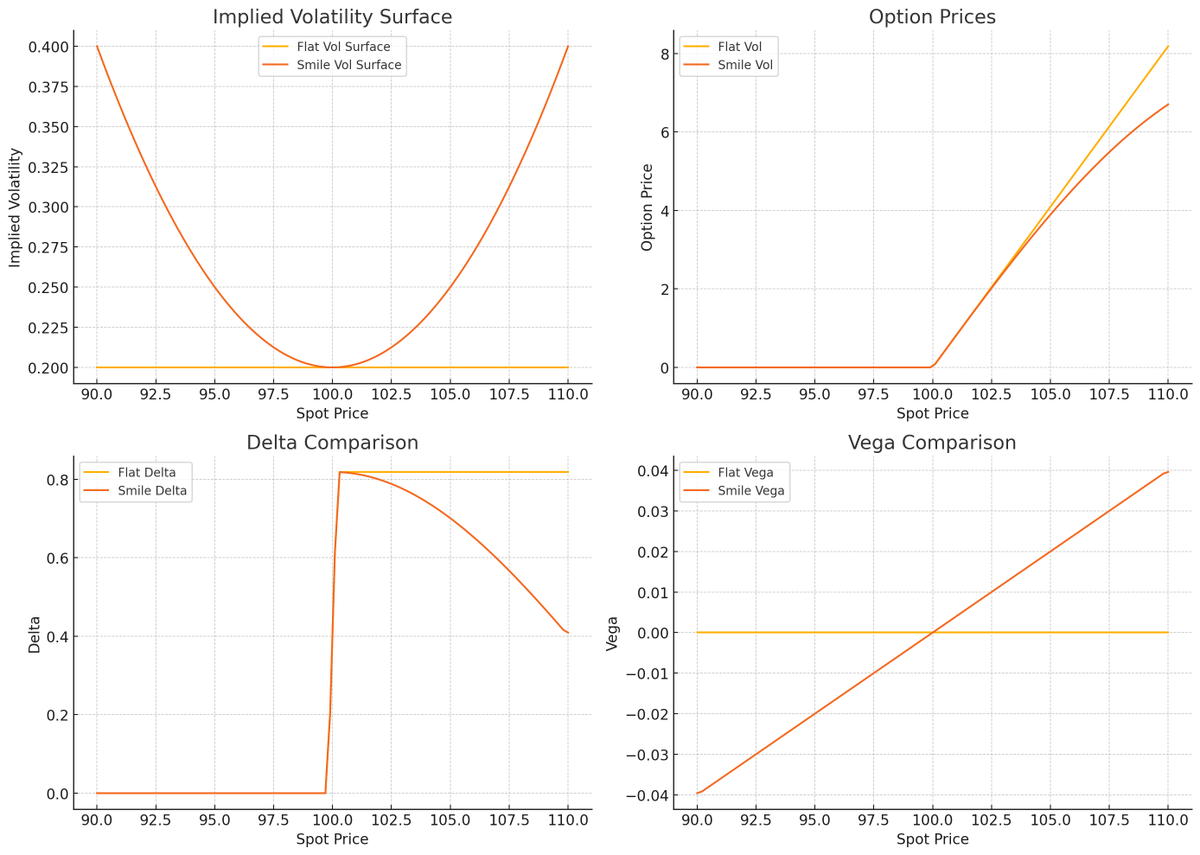
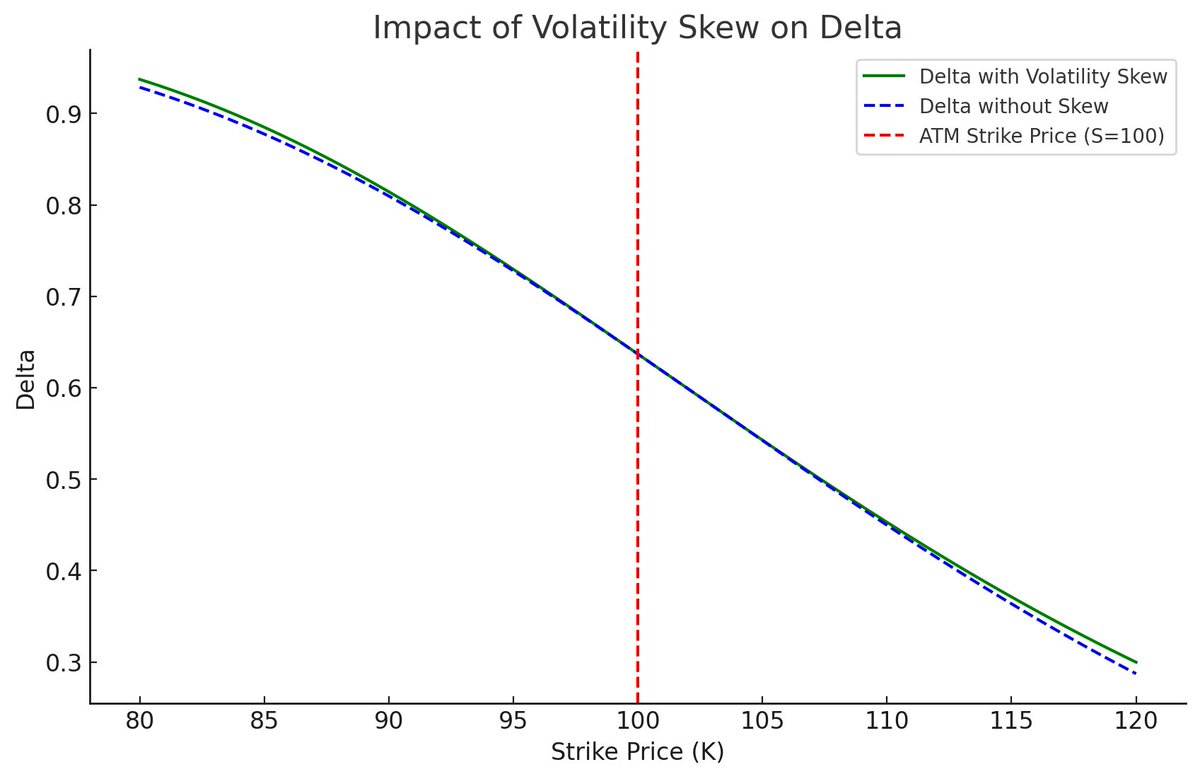
 Why Black-Scholes Delta Isn't Always Accurate?
Why Black-Scholes Delta Isn't Always Accurate?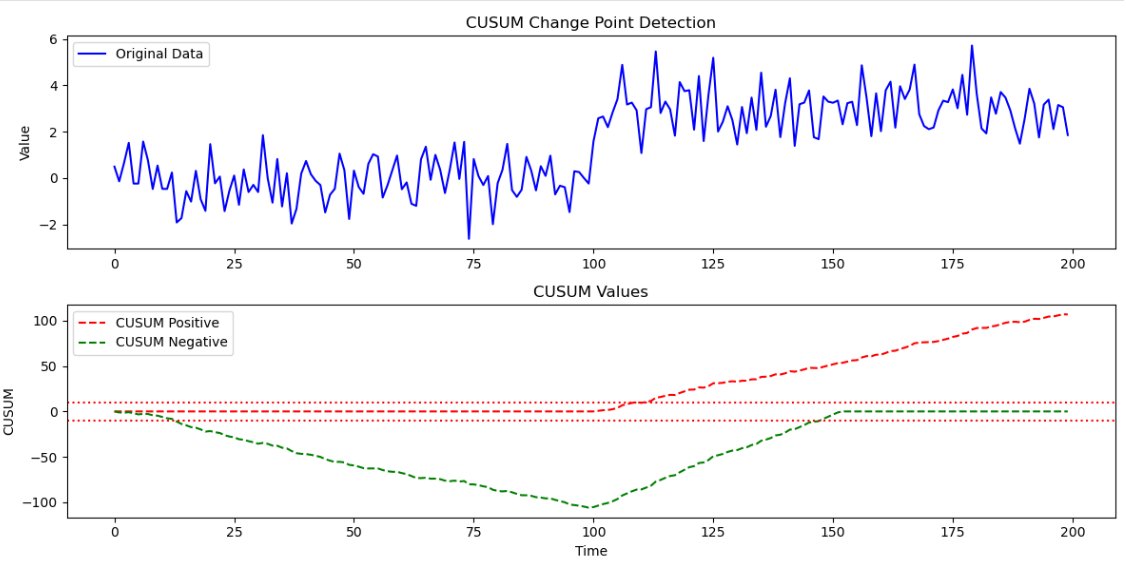
 Use Case: Quickly detects shifts in mean returns or volatility. Ideal for simple, real-time signals where efficiency is key.
Use Case: Quickly detects shifts in mean returns or volatility. Ideal for simple, real-time signals where efficiency is key. 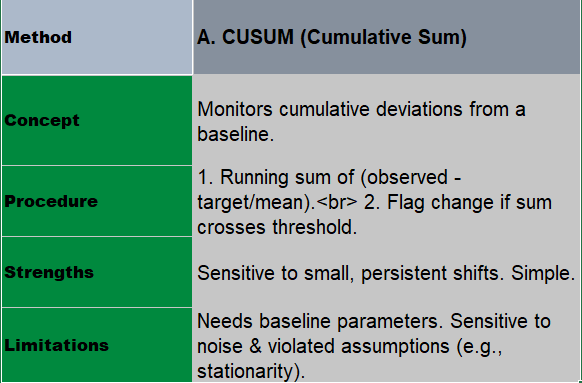
 In the Black-Scholes model:
In the Black-Scholes model: 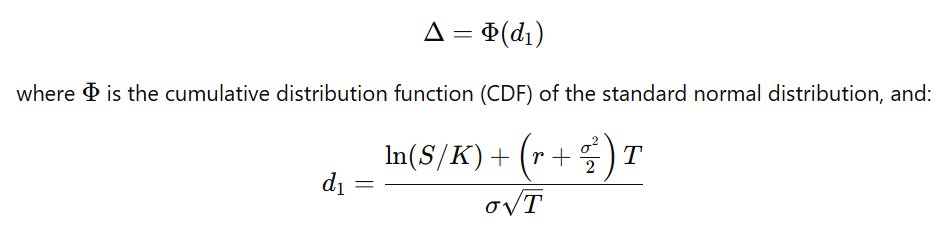

 Volatility Smile and Term Structure:
Volatility Smile and Term Structure: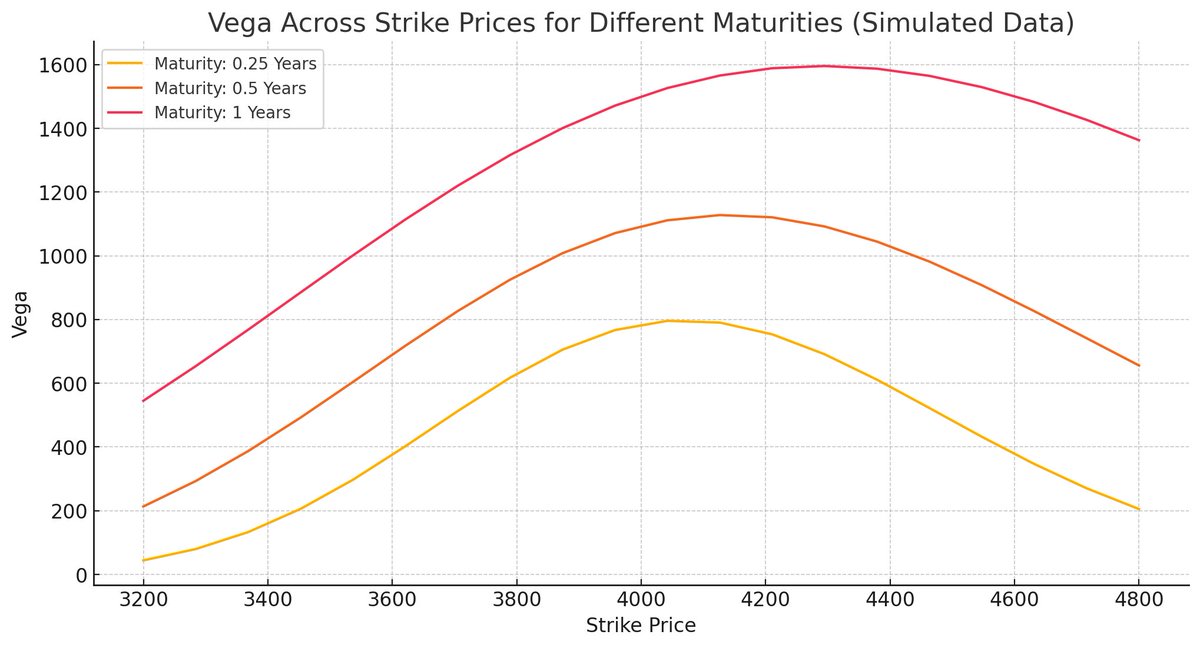

 Stock Characteristics and Implied Volatility
Stock Characteristics and Implied Volatility
 The derivatives market is a fundamental, "primitive" concept in finance.
The derivatives market is a fundamental, "primitive" concept in finance.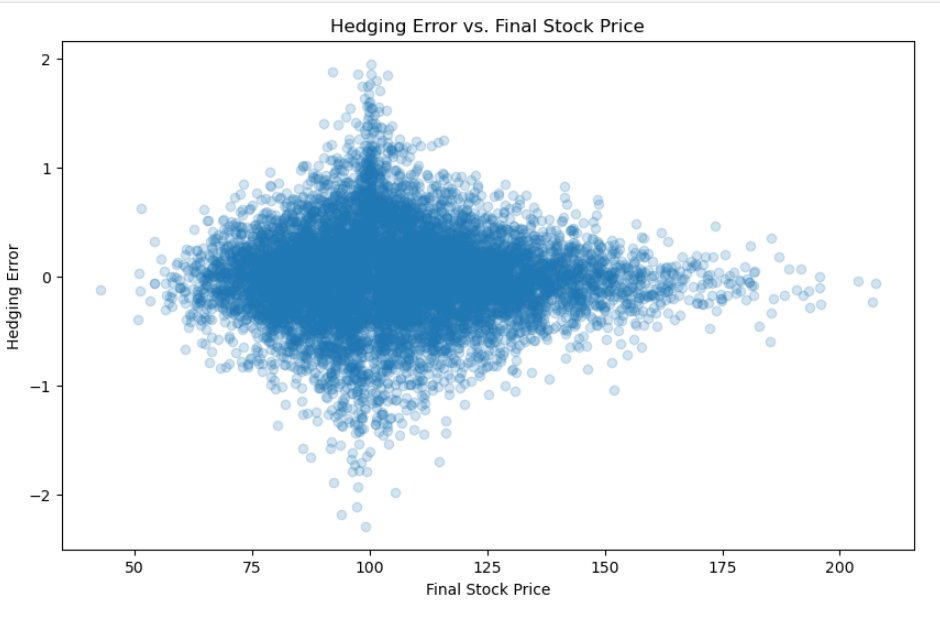
 Dynamic delta hedging is a fundamental strategy used by option traders to mitigate the risk associated with movements in the underlying asset's price.
Dynamic delta hedging is a fundamental strategy used by option traders to mitigate the risk associated with movements in the underlying asset's price.
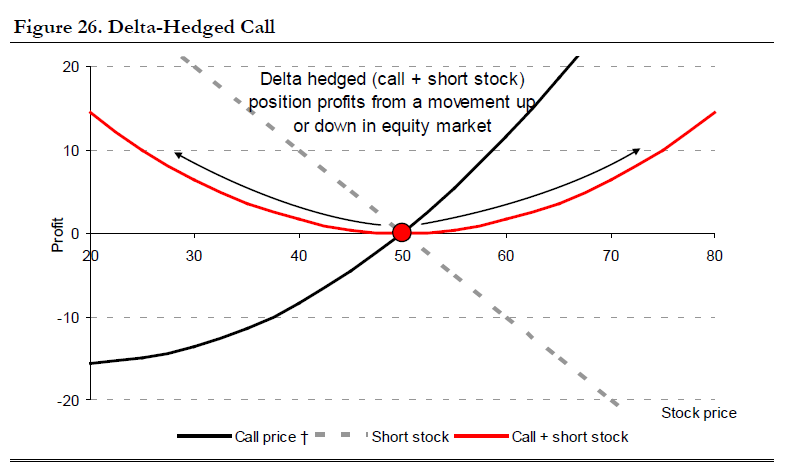
 Delta Hedging and Matching Maturity
Delta Hedging and Matching Maturity
 In the paper Three neural network models are discussed
In the paper Three neural network models are discussed