
Molecular Genetics, U.C. Berkeley Alumnus; Private sector; Opinions are my own; Posted studies ≠ Endorsement; Not medical advice;
4 subscribers
How to get URL link on X (Twitter) App


 (2/3) FDA Frequently Asked Questions on Potassium Iodide (KI): In December 2001, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a final Guidance on Potassium Iodide as a Thyroid Blocking Agent in Radiation Emergencies)...
(2/3) FDA Frequently Asked Questions on Potassium Iodide (KI): In December 2001, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a final Guidance on Potassium Iodide as a Thyroid Blocking Agent in Radiation Emergencies)...




https://twitter.com/RolandBakerIII/status/1791150547564888522


https://twitter.com/thelonevirologi/status/1790865158778044889
 Red tailed hawk
Red tailed hawk
 * Spread of HPAIV H5N1 from the lumen of the intestine to other organs took place via the blood and lymphatic vascular systems but not via neuronal transmission
* Spread of HPAIV H5N1 from the lumen of the intestine to other organs took place via the blood and lymphatic vascular systems but not via neuronal transmission
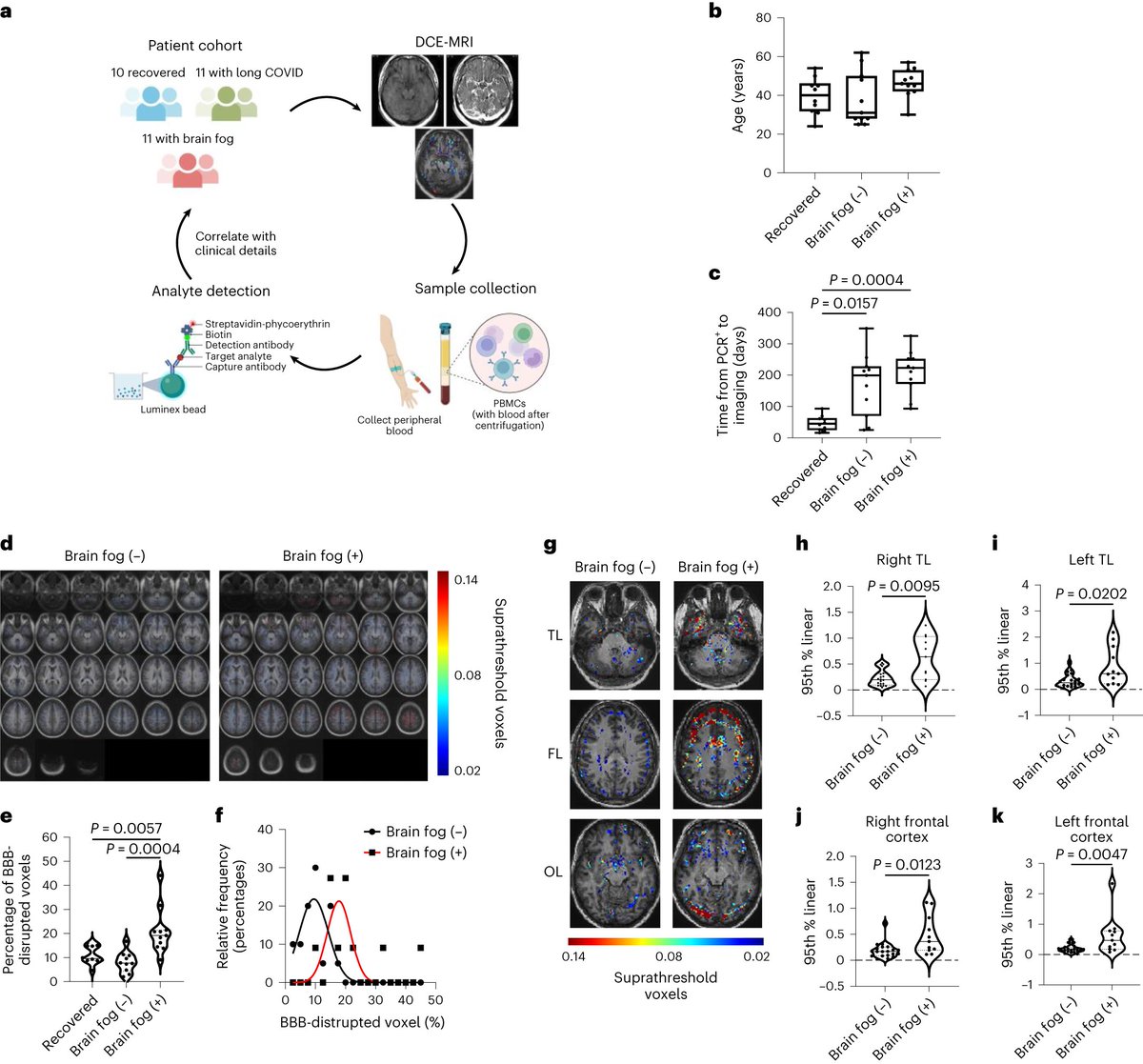

 /2 BBB disruption in the temporal lobes was associated with anosmia. BBB disfunction & sustained systemic inflammation was associated with increased astrocytic protein S100β, IL-6, bFGF and IL-13.
/2 BBB disruption in the temporal lobes was associated with anosmia. BBB disfunction & sustained systemic inflammation was associated with increased astrocytic protein S100β, IL-6, bFGF and IL-13.
https://twitter.com/BagaiDr/status/1749239589884383574


 /2 "Since March, 2020, excess mortality—the number of all-cause deaths exceeding the baseline number of expected deaths—has been observed in waves coinciding with COVID-19 outbreaks in the USA and worldwide."
/2 "Since March, 2020, excess mortality—the number of all-cause deaths exceeding the baseline number of expected deaths—has been observed in waves coinciding with COVID-19 outbreaks in the USA and worldwide."

https://twitter.com/SabiVM/status/1607915944877211651"The surprisingly higher prevalence of the IgG4 subtype might arise owing to repeated encounters with the antigen, which earlier studies on COVID-19 may not have captured. In this context, repeated infections have previously been described to elevate total IgG4 levels."