
Mission Operations Center for NASA's Webb Space Telescope (#NASAWebb). Science operations for the Hubble Space Telescope and upcoming Roman Space Telescope.
How to get URL link on X (Twitter) App


 START: Your story begins with two stars orbiting each other. The more massive star is super-hot and nearing the end of its lifecycle. Strong winds from the stars collide and cool, and you find yourself surrounded by sibling grains of dust swirling.
START: Your story begins with two stars orbiting each other. The more massive star is super-hot and nearing the end of its lifecycle. Strong winds from the stars collide and cool, and you find yourself surrounded by sibling grains of dust swirling. 


 Stars 1 and 2 are the only stars we see in the sixth and final panel above—and in #NASAWebb’s images. The remaining “guests” are stars 3, 4, and 5. They are all much less massive, or far smaller and dimmer, than stars 1 and 2. (2/9)
Stars 1 and 2 are the only stars we see in the sixth and final panel above—and in #NASAWebb’s images. The remaining “guests” are stars 3, 4, and 5. They are all much less massive, or far smaller and dimmer, than stars 1 and 2. (2/9) 

 After years of preparation and anticipation, exoplanet researchers are ecstatic! The James Webb Space Telescope has captured an astonishingly detailed rainbow of near-infrared starlight filtered through the atmosphere of a hot gas giant 700 light-years away. (2/5)
After years of preparation and anticipation, exoplanet researchers are ecstatic! The James Webb Space Telescope has captured an astonishingly detailed rainbow of near-infrared starlight filtered through the atmosphere of a hot gas giant 700 light-years away. (2/5)

 Carina Nebula: One of the largest and brightest nebulae in the sky, located approximately 7,600 light-years away in the southern constellation Carina. Nebulae are stellar nurseries where stars form. The Carina Nebula is home to many massive stars. (2/8)
Carina Nebula: One of the largest and brightest nebulae in the sky, located approximately 7,600 light-years away in the southern constellation Carina. Nebulae are stellar nurseries where stars form. The Carina Nebula is home to many massive stars. (2/8)

 Light—which has wave-like properties—tends to radiate from a point outward. When light waves interact, they can either become more amplified or cancel each other out. These areas of amplification and cancellation form the light and dark spots in diffraction patterns. (2/5)
Light—which has wave-like properties—tends to radiate from a point outward. When light waves interact, they can either become more amplified or cancel each other out. These areas of amplification and cancellation form the light and dark spots in diffraction patterns. (2/5) 

 With its powerful infrared sensitivity and resolution, #NASAWebb is capable of peering into star-forming regions across our entire galaxy—like R136—where previous infrared telescopes were limited to dust clouds within our own galactic neighborhood. (2/4)
With its powerful infrared sensitivity and resolution, #NASAWebb is capable of peering into star-forming regions across our entire galaxy—like R136—where previous infrared telescopes were limited to dust clouds within our own galactic neighborhood. (2/4)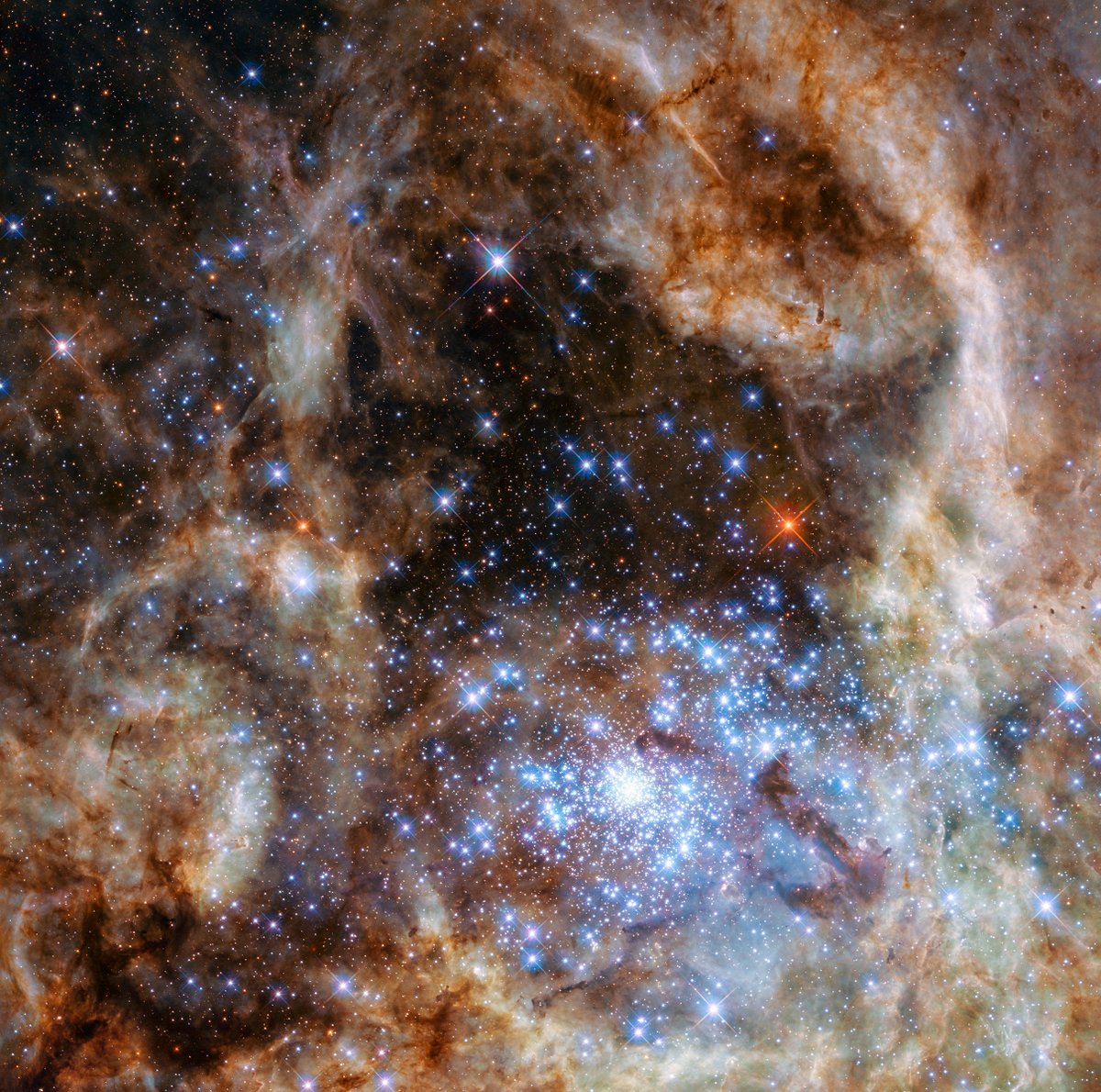 

 Supermassive black holes, which lie at the centers of galaxies, are voracious! They periodically “sip” or “gulp” from COLD swirling disks of gas and dust that orbit them. Where there’s lots of very cold gas, stars can begin to form—but it also falls onto the black hole. (2/7)
Supermassive black holes, which lie at the centers of galaxies, are voracious! They periodically “sip” or “gulp” from COLD swirling disks of gas and dust that orbit them. Where there’s lots of very cold gas, stars can begin to form—but it also falls onto the black hole. (2/7) 

 DePasquale: The press release states that there is a specially designed pupil imaging lens (PIL) in one of Webb’s main imaging instruments known as NIRCam. What is a PIL anyway? <2/9>
DePasquale: The press release states that there is a specially designed pupil imaging lens (PIL) in one of Webb’s main imaging instruments known as NIRCam. What is a PIL anyway? <2/9>

 Stars don’t normally explode 💥 because they balance two forces: gravity, which wants to crush all of the gas towards the center, and pressure from fusion, which pushes outward.
Stars don’t normally explode 💥 because they balance two forces: gravity, which wants to crush all of the gas towards the center, and pressure from fusion, which pushes outward.

 Cameras: Three Webb instruments have cameras 📷 that will capture two-dimensional images of regions in space. NIRCam and NIRISS will capture images in the near-infrared, while MIRI will capture mid-infrared images. (2/8)
Cameras: Three Webb instruments have cameras 📷 that will capture two-dimensional images of regions in space. NIRCam and NIRISS will capture images in the near-infrared, while MIRI will capture mid-infrared images. (2/8)

 Mission goals for Webb include: Search for the first galaxies that formed in early universe; study the evolution of galaxies; observe star formation; and measure physical and chemical properties and investigate the potential for life in planetary systems. #AAS238 (2/9)
Mission goals for Webb include: Search for the first galaxies that formed in early universe; study the evolution of galaxies; observe star formation; and measure physical and chemical properties and investigate the potential for life in planetary systems. #AAS238 (2/9)

 Each of Webb’s four instruments is like a Swiss army knife of specialized components, with multiple ways of observing. All four can be used for investigations of the wide variety of objects that make up the universe, including planets, stars, nebulae, and galaxies. #AAS238 (2/7)
Each of Webb’s four instruments is like a Swiss army knife of specialized components, with multiple ways of observing. All four can be used for investigations of the wide variety of objects that make up the universe, including planets, stars, nebulae, and galaxies. #AAS238 (2/7)

 Webb’s key components include an enormous primary mirror to collect infrared light, a supersized sunshield to keep the telescope cold, and four scientific instruments to conduct its ambitious science operations. Credit: NASA. #AAS238 (2/10)
Webb’s key components include an enormous primary mirror to collect infrared light, a supersized sunshield to keep the telescope cold, and four scientific instruments to conduct its ambitious science operations. Credit: NASA. #AAS238 (2/10) 