
Author/Editor: “Clinical Arrhythmology and Electrophysiology: A Companion to Braunwald’s Heart Disease” #IssaTweetorials
How to get URL link on X (Twitter) App


 2/9
2/9

 2/9
2/9


 2/8
2/8

 2/8
2/8

 2/4
2/4


 2/7
2/7
 2/9
2/9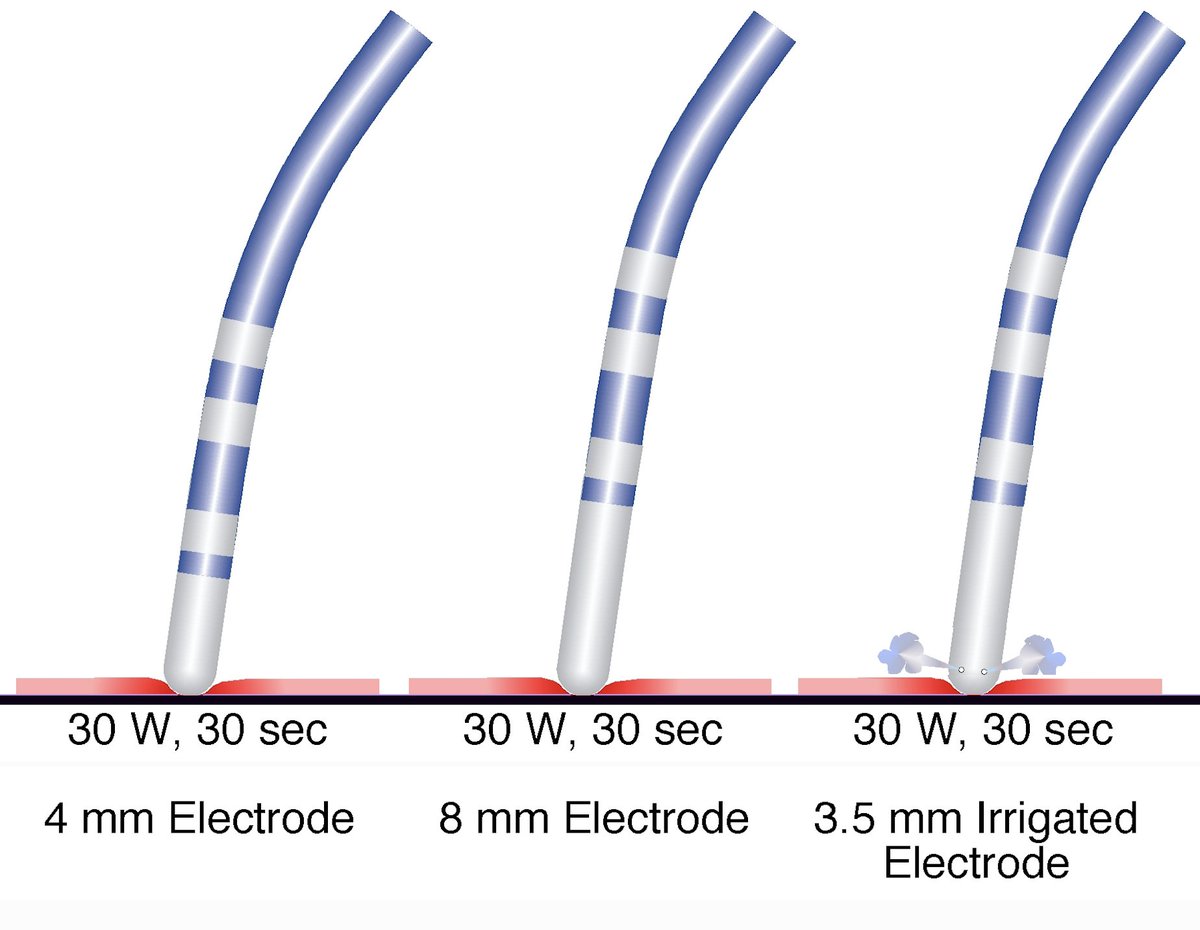
 2/10
2/10

 2/8
2/8

 2/
2/