
How to get URL link on X (Twitter) App


 A provocative claim from physicists in Copenhagen is reigniting deep questions about the nature of time, causality, and human decision making. According to their interpretation of quantum experiments, reality may not flow strictly forward as we experience it.
A provocative claim from physicists in Copenhagen is reigniting deep questions about the nature of time, causality, and human decision making. According to their interpretation of quantum experiments, reality may not flow strictly forward as we experience it.

 By applying the mathematical elegance of the Fibonacci sequence to quantum hardware, researchers have created a new phase of matter that preserves data four times longer.
By applying the mathematical elegance of the Fibonacci sequence to quantum hardware, researchers have created a new phase of matter that preserves data four times longer.

 Quantum physics suggests that what we often call “luck” may follow underlying patterns rather than being completely random. Some researchers argue that at the quantum level, events are influenced by probabilities and hidden structures that shape outcomes in ways we’re only beginning to understand.
Quantum physics suggests that what we often call “luck” may follow underlying patterns rather than being completely random. Some researchers argue that at the quantum level, events are influenced by probabilities and hidden structures that shape outcomes in ways we’re only beginning to understand.

 Its trajectory shows non-gravitational acceleration, meaning forces other than gravity are influencing it—likely outgassing, but possibly something more exotic.
Its trajectory shows non-gravitational acceleration, meaning forces other than gravity are influencing it—likely outgassing, but possibly something more exotic.

 On October 21, 2025 (00:12 UTC), independent trackers comparing live sky data with JPL’s official Horizons predictions noticed a clear mismatch.
On October 21, 2025 (00:12 UTC), independent trackers comparing live sky data with JPL’s official Horizons predictions noticed a clear mismatch. 
 Trillions of tons of hidden hydrogen have been discovered beneath Earth’s surface, and it could change everything. 🌍⚡ Scientists have found massive underground reserves of naturally occurring “gold hydrogen”, a clean and carbon-free fuel source powerful enough to meet global energy needs for over 1,000 years.
Trillions of tons of hidden hydrogen have been discovered beneath Earth’s surface, and it could change everything. 🌍⚡ Scientists have found massive underground reserves of naturally occurring “gold hydrogen”, a clean and carbon-free fuel source powerful enough to meet global energy needs for over 1,000 years.
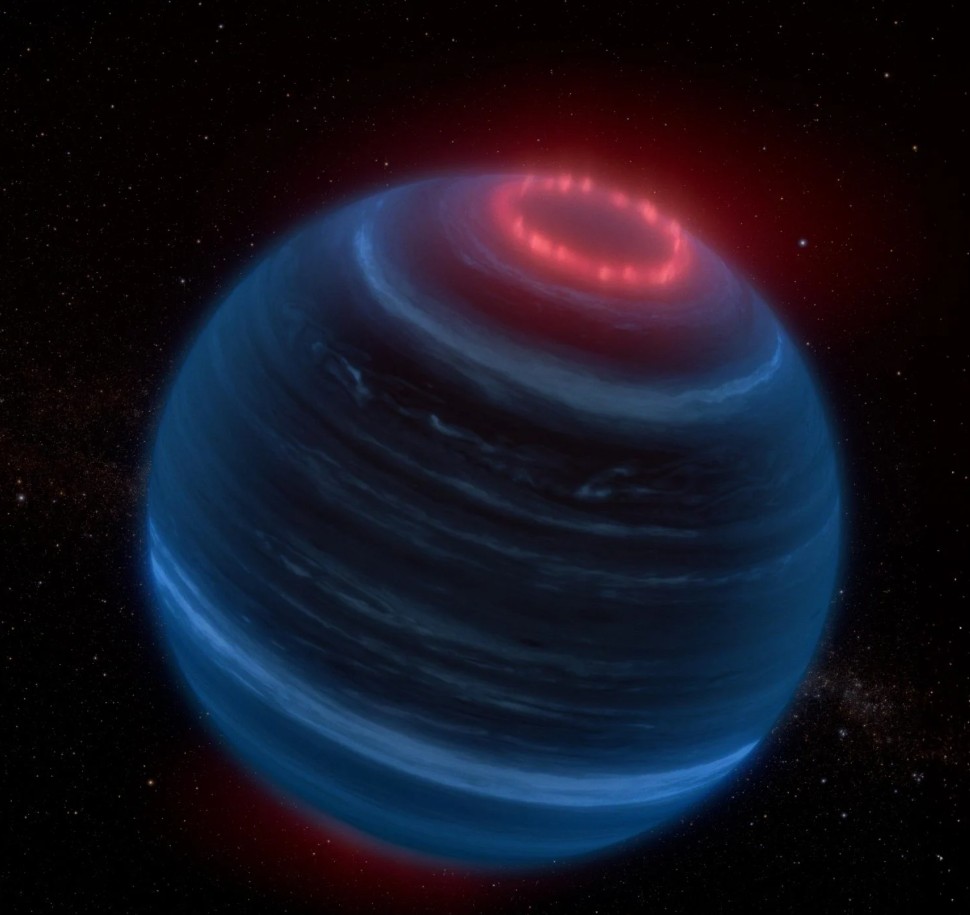

 Astronomers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope have found a brown dwarf (an object more massive than Jupiter but smaller than a star) that may display possible aurorae, like the familiar Northern Lights on our world. This is an unexpected mystery because the brown dwarf, known as W1935, is an isolated object in space, with no nearby star to create an aurora.
Astronomers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope have found a brown dwarf (an object more massive than Jupiter but smaller than a star) that may display possible aurorae, like the familiar Northern Lights on our world. This is an unexpected mystery because the brown dwarf, known as W1935, is an isolated object in space, with no nearby star to create an aurora.
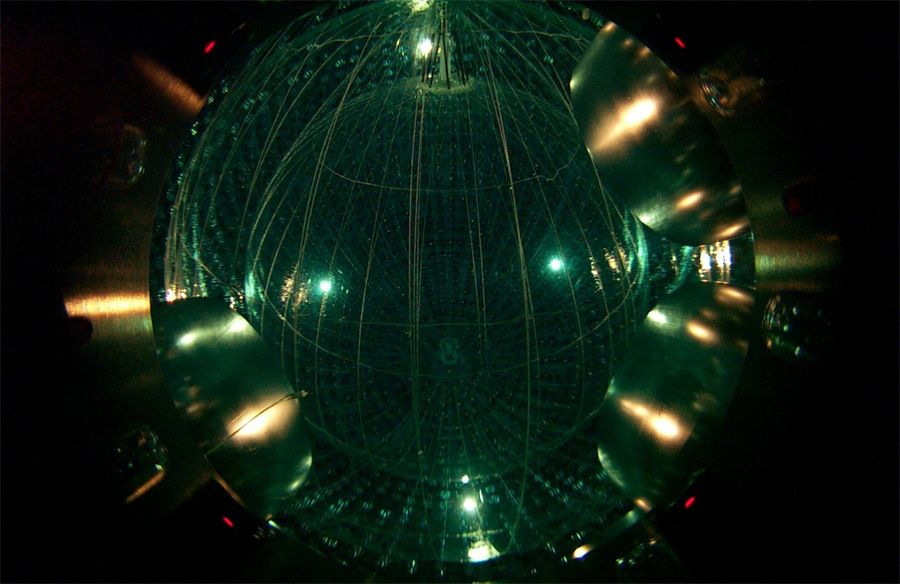

 Imagine a giant sphere, buried 700 feet underground, capable of catching the nearly invisible footprints of the cosmos’ most elusive particles: neutrinos, also called ghost particles. That sphere already exists and just "woke up" in China. His name is JUNO, and he promises to open a new window into the deepest mysteries of the universe.
Imagine a giant sphere, buried 700 feet underground, capable of catching the nearly invisible footprints of the cosmos’ most elusive particles: neutrinos, also called ghost particles. That sphere already exists and just "woke up" in China. His name is JUNO, and he promises to open a new window into the deepest mysteries of the universe.

 We’ve known that this expansion is a fact of our cosmos for a while now (we also know that expansion is speeding up, but that’s another story). But we still don’t know exactly how fast this expansion is happening—we don’t know what the Hubble constant is. And it’s not for lack of trying, either.
We’ve known that this expansion is a fact of our cosmos for a while now (we also know that expansion is speeding up, but that’s another story). But we still don’t know exactly how fast this expansion is happening—we don’t know what the Hubble constant is. And it’s not for lack of trying, either.
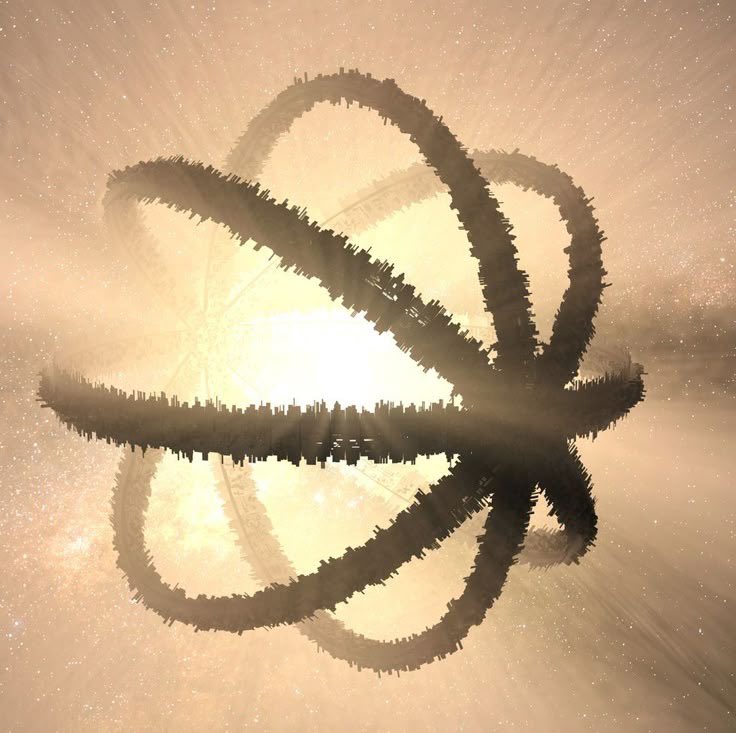

 Finding a Dyson Sphere among the millions of stars observed by projects like the Gaia satellite, the Wide-Field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE), and the Two Micron All Sky Survey (2MASS) is a daunting task. However, two recent studies have taken on this challenge and identified several promising candidates.
Finding a Dyson Sphere among the millions of stars observed by projects like the Gaia satellite, the Wide-Field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE), and the Two Micron All Sky Survey (2MASS) is a daunting task. However, two recent studies have taken on this challenge and identified several promising candidates.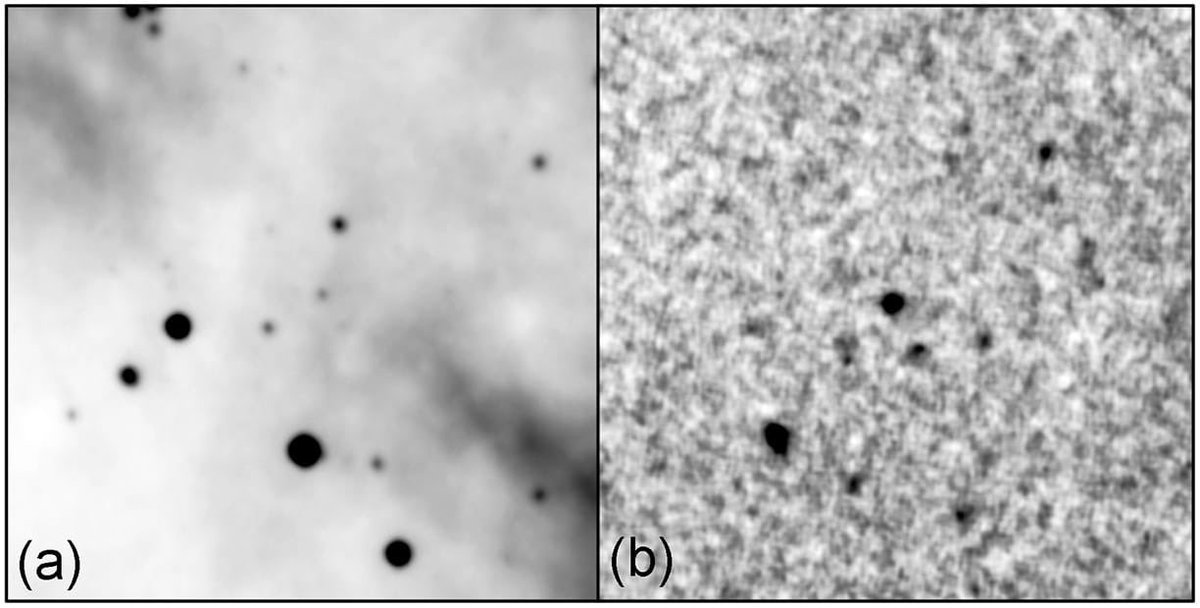
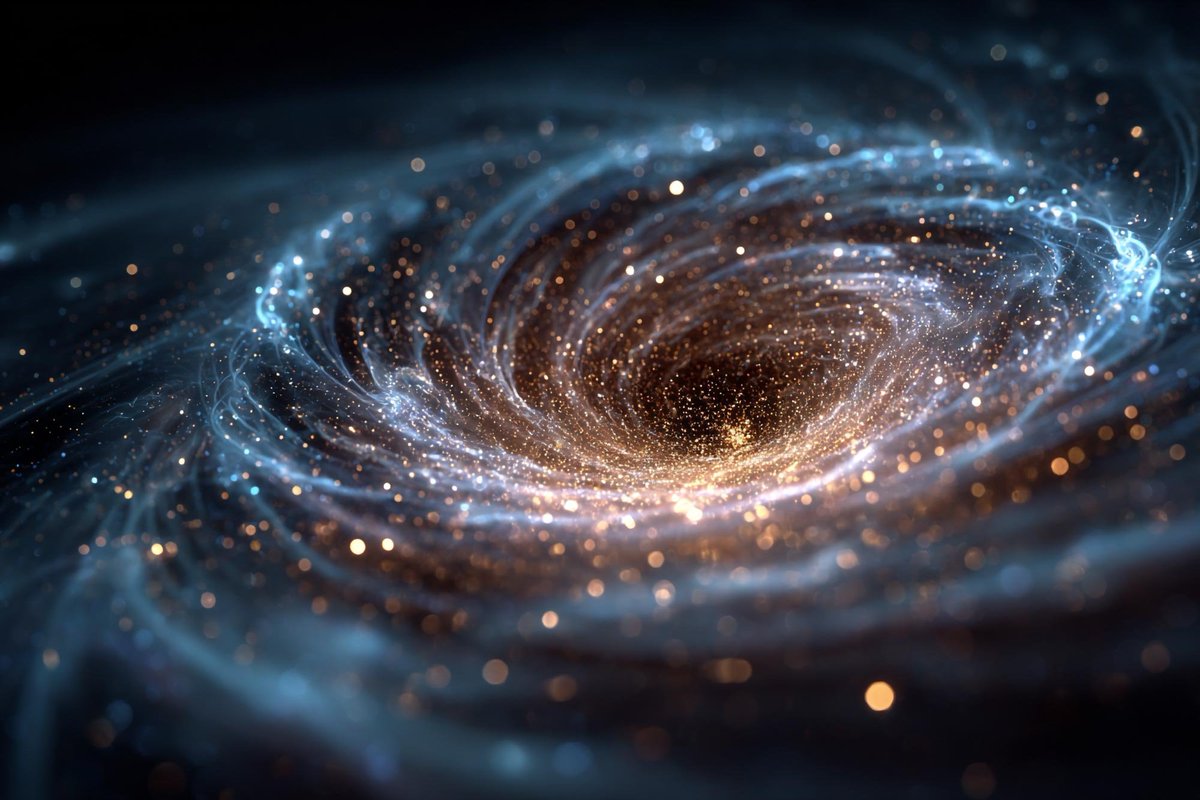

 In 1951, Nobel Prize–winning physicist Julian Schwinger theorized that a strong enough electric field could rip pairs of matter and antimatter out of the vacuum itself, a process now known as the Schwinger effect.
In 1951, Nobel Prize–winning physicist Julian Schwinger theorized that a strong enough electric field could rip pairs of matter and antimatter out of the vacuum itself, a process now known as the Schwinger effect.
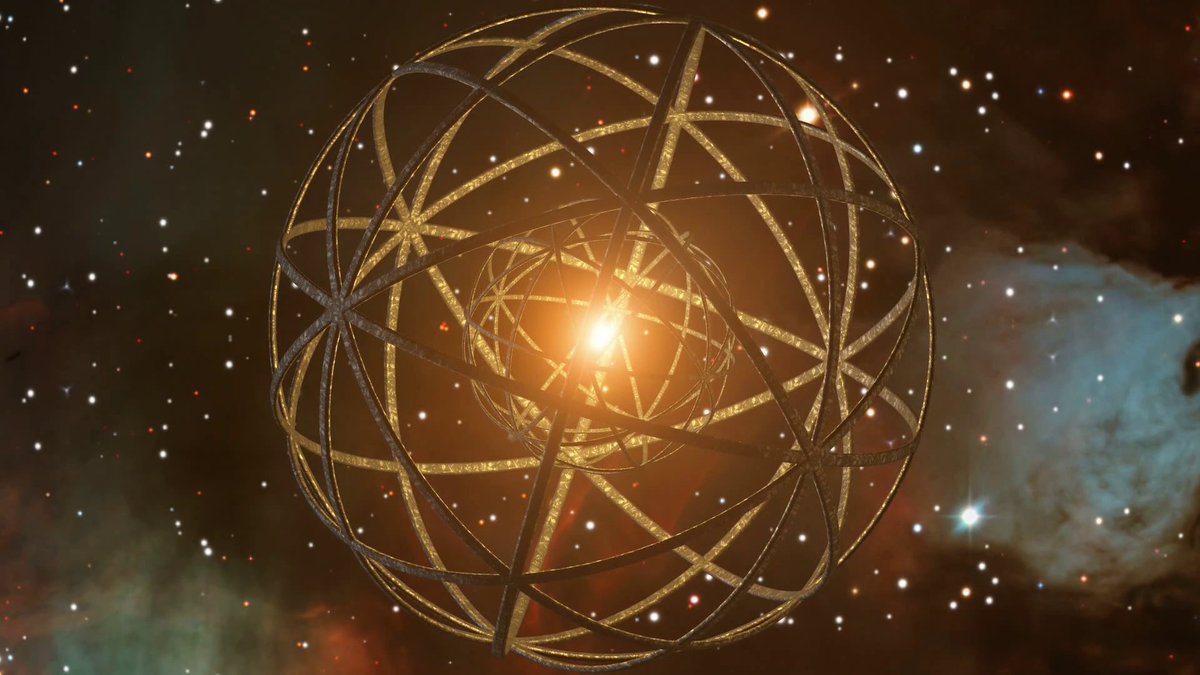

 Finding a Dyson Sphere among the millions of stars observed by projects like the Gaia satellite, the Wide-Field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE), and the Two Micron All Sky Survey (2MASS) is a daunting task. However, two recent studies have taken on this challenge and identified several promising candidates.
Finding a Dyson Sphere among the millions of stars observed by projects like the Gaia satellite, the Wide-Field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE), and the Two Micron All Sky Survey (2MASS) is a daunting task. However, two recent studies have taken on this challenge and identified several promising candidates.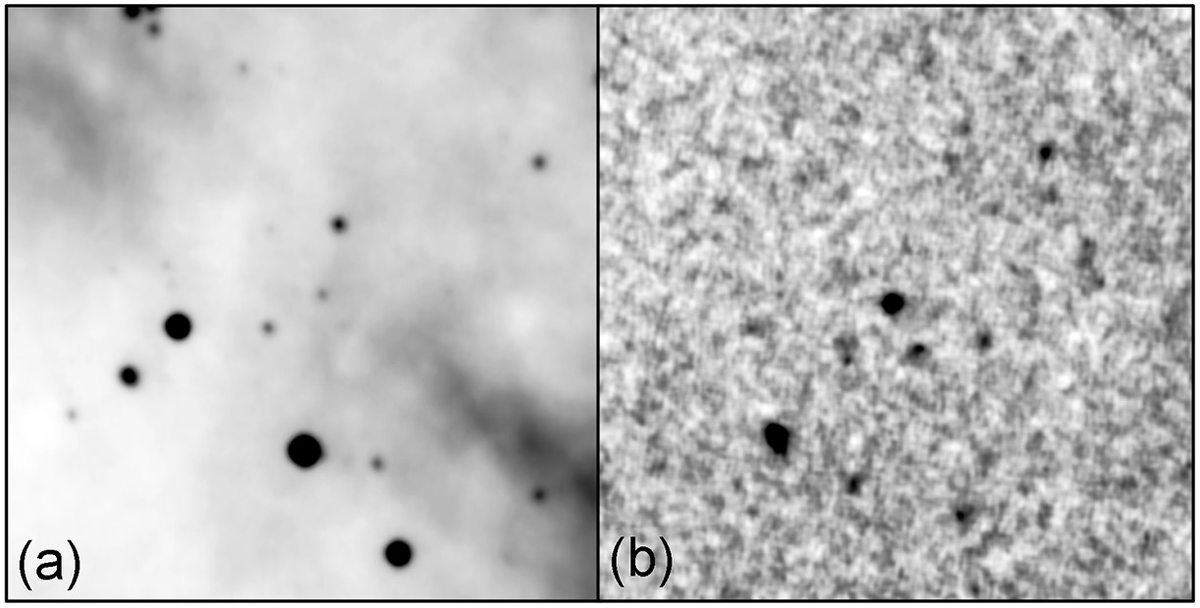
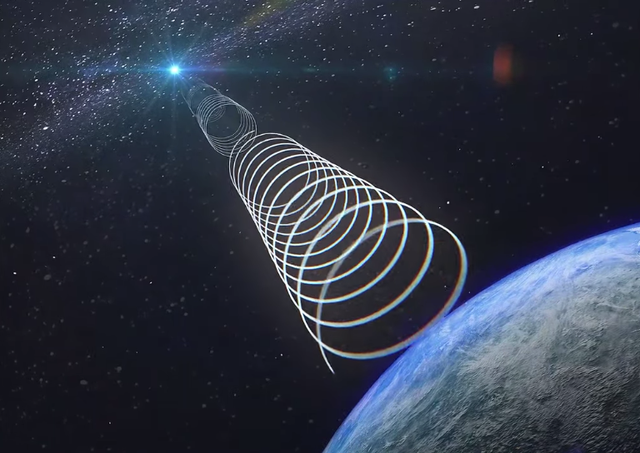
 But where did it come from, and what does it reveal about the Universe’s youth? According to a study from the University of Sydney, this is the most distant fast radio burst ever traced. Could it be a messenger from the cosmic dawn? Or one of many signals still hidden in the void?
But where did it come from, and what does it reveal about the Universe’s youth? According to a study from the University of Sydney, this is the most distant fast radio burst ever traced. Could it be a messenger from the cosmic dawn? Or one of many signals still hidden in the void?