
How to get URL link on X (Twitter) App


 - Prior studies on cardiac remodelling associated with exercise have relied on self-reported data of uncertain accuracy.
- Prior studies on cardiac remodelling associated with exercise have relied on self-reported data of uncertain accuracy.
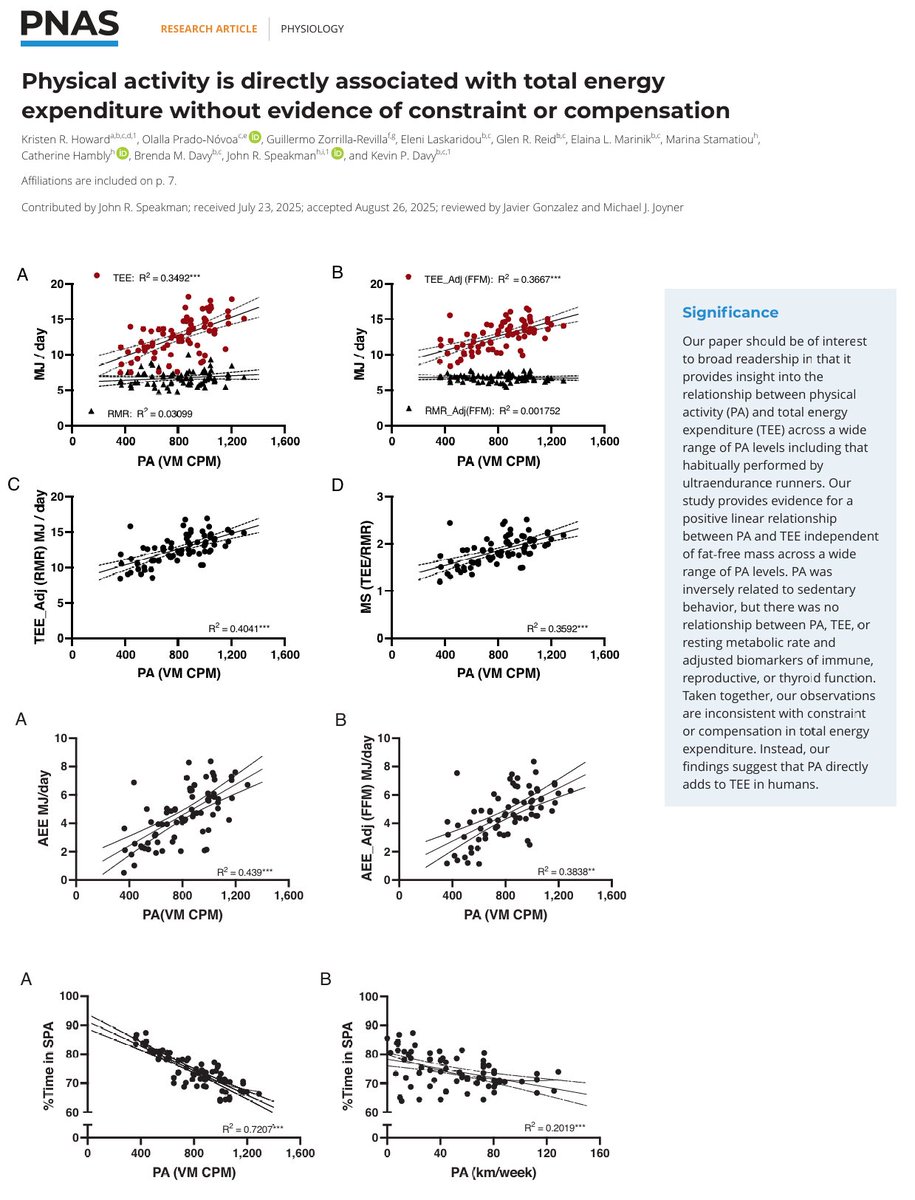
 - The health benefits of increasing energy expenditure with physical activity are well documented, but how physical activity influences the energy budget remains controversial.
- The health benefits of increasing energy expenditure with physical activity are well documented, but how physical activity influences the energy budget remains controversial.

 - In 20 young (18 to 39 years) and 20 older (> 65 years) adults, this study documented the echocardiography assessed left-ventricular responses to a very hot and dry (47°C and 15% relative humidity, reflective of the peak conditions during the Pacific Northwest 2021 heat wave) and hot humid (41°C and 40% relative humidity, reflective of the 1995 Chicago heat wave) 3-hour heat exposure, with intermittent bouts of light physical activity throughout (7 x 5 min bouts of physical activity at 3 METS).
- In 20 young (18 to 39 years) and 20 older (> 65 years) adults, this study documented the echocardiography assessed left-ventricular responses to a very hot and dry (47°C and 15% relative humidity, reflective of the peak conditions during the Pacific Northwest 2021 heat wave) and hot humid (41°C and 40% relative humidity, reflective of the 1995 Chicago heat wave) 3-hour heat exposure, with intermittent bouts of light physical activity throughout (7 x 5 min bouts of physical activity at 3 METS).

 - This study tested the overarching hypothesis that the expended rate of work above critical power during all-out whole-body exercise is related to a decline in prefrontal cortex oxygenation secondary to an organized systemic outstripping of muscle O2 supply relative to O2 demand.
- This study tested the overarching hypothesis that the expended rate of work above critical power during all-out whole-body exercise is related to a decline in prefrontal cortex oxygenation secondary to an organized systemic outstripping of muscle O2 supply relative to O2 demand.

 - Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) belongs to the family of neurotrophins and stimulates neuronal growth and differentiation, synaptogenesis, and neural plasticity.
- Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) belongs to the family of neurotrophins and stimulates neuronal growth and differentiation, synaptogenesis, and neural plasticity.
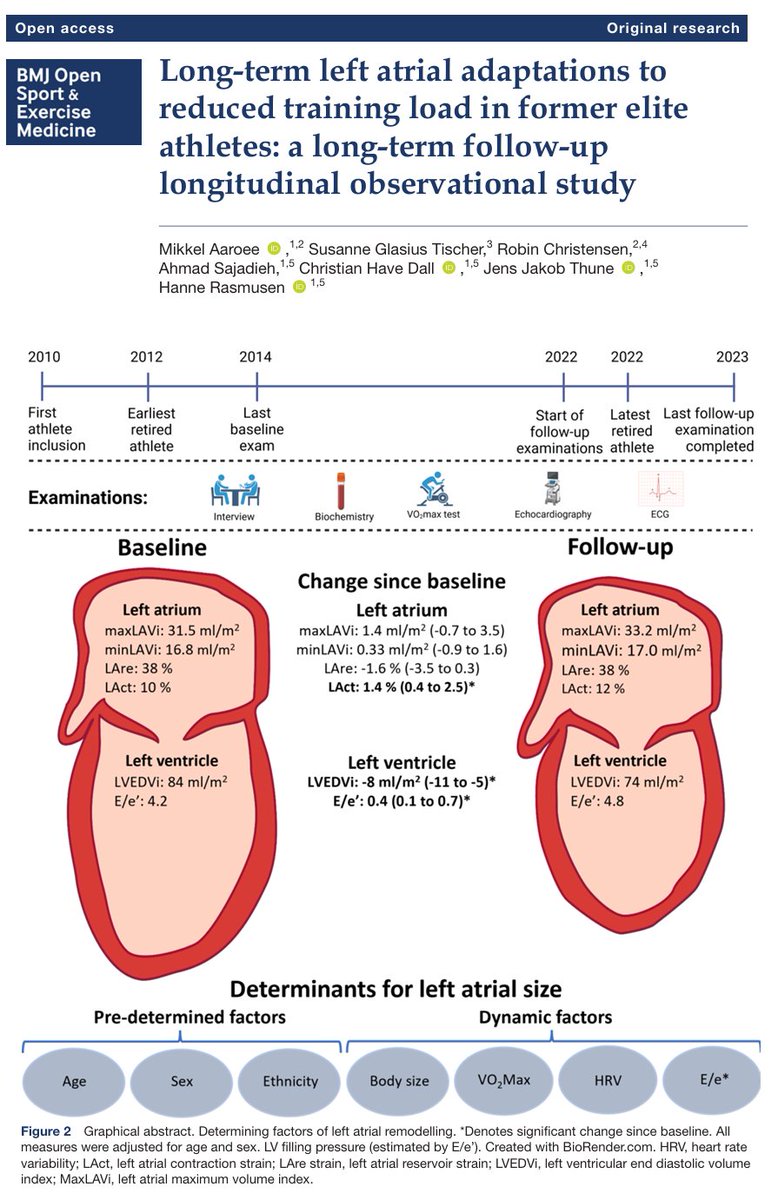
 - The objective of this study was to evaluate the effects of long-term reduced training on the left atrium in elite endurance athletes and to elucidate sex-specific differences in left atrial detraining patterns.
- The objective of this study was to evaluate the effects of long-term reduced training on the left atrium in elite endurance athletes and to elucidate sex-specific differences in left atrial detraining patterns.

 - The aim of this paper was to undertake a systematic review and meta-analysis comparing exercise-induced muscle damage (EIMD) in older and younger adults.
- The aim of this paper was to undertake a systematic review and meta-analysis comparing exercise-induced muscle damage (EIMD) in older and younger adults.

 - This study investigated the relationship between the type 2 diabetes prevalence and intensity, frequency, and metabolic equivalent of task (MET) score of physical activity in in 2,428,448 participants included in the Korea Community Health Survey.
- This study investigated the relationship between the type 2 diabetes prevalence and intensity, frequency, and metabolic equivalent of task (MET) score of physical activity in in 2,428,448 participants included in the Korea Community Health Survey.

 - Age-related deterioration in muscle volume, intramuscular fat content and muscle function can be modulated by physical activity.
- Age-related deterioration in muscle volume, intramuscular fat content and muscle function can be modulated by physical activity.

 - This prospective study used data from the UK Biobank cohort, which provided accelerometer-based physical activity data for a full week from February 2013 to December 2015.
- This prospective study used data from the UK Biobank cohort, which provided accelerometer-based physical activity data for a full week from February 2013 to December 2015.

 More about the physical activity paradox can be found in my previous posts:
More about the physical activity paradox can be found in my previous posts: 
 - This was a systematic review and meta-analysis that aimed to investigate the effects of combining omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-3 PUFAs) supplementation with exercise training...
- This was a systematic review and meta-analysis that aimed to investigate the effects of combining omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-3 PUFAs) supplementation with exercise training...

 - This study aimed to evaluate associations of muscle-strengthening activity with all-cause, cardiovascular disease, and cancer mortality in adults with diabetes, independent of and jointly with moderate-to-vigorous aerobic physical activity.
- This study aimed to evaluate associations of muscle-strengthening activity with all-cause, cardiovascular disease, and cancer mortality in adults with diabetes, independent of and jointly with moderate-to-vigorous aerobic physical activity.

 - The primary aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to compare the acute and chronic effects of superset and traditional set prescriptions on mechanical, metabolic, and perceptual variables.
- The primary aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to compare the acute and chronic effects of superset and traditional set prescriptions on mechanical, metabolic, and perceptual variables.

 - The aim of this study was to examine the influence of time-restricted feeding on fat oxidation during exercise, whereby participants performed an 8-week individualized intensity intervention targeting maximal fat oxidation...
- The aim of this study was to examine the influence of time-restricted feeding on fat oxidation during exercise, whereby participants performed an 8-week individualized intensity intervention targeting maximal fat oxidation...

 - This study conducted parallel human and rodent trials to characterize the effect of exogenous ketone supplementation on indices of brain health.
- This study conducted parallel human and rodent trials to characterize the effect of exogenous ketone supplementation on indices of brain health.
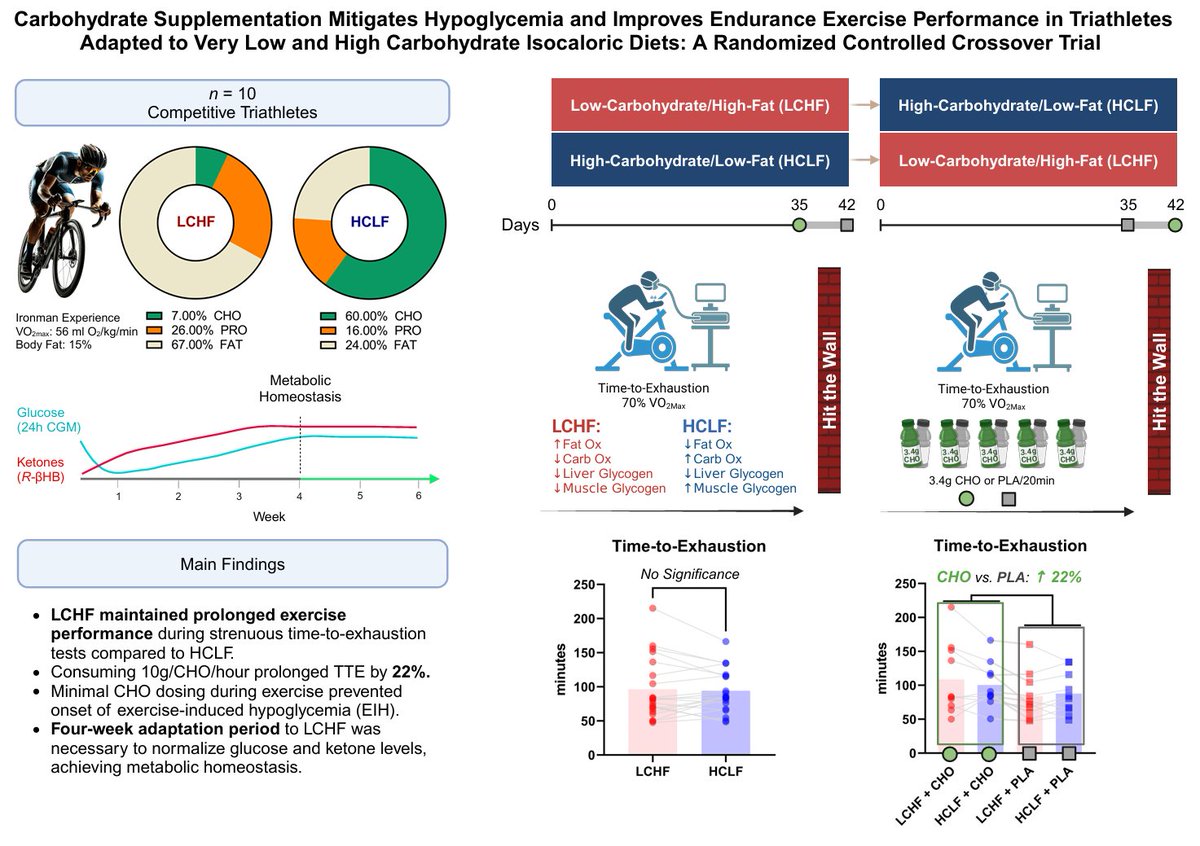
 - Leveraging a randomized crossover design, this study evaluated performance during strenuous time-to-exhaustion (70%⩒O2max) tests in trained triathletes following 6-week high- (380g CHO/day) or low-carbohydrate diets (40g CHO/day) to determine:
- Leveraging a randomized crossover design, this study evaluated performance during strenuous time-to-exhaustion (70%⩒O2max) tests in trained triathletes following 6-week high- (380g CHO/day) or low-carbohydrate diets (40g CHO/day) to determine:

 - This study explored the dose-response relationship of exercise prescriptions for improving frailty in older adults, based on the 2024 Older Adult Compendium.
- This study explored the dose-response relationship of exercise prescriptions for improving frailty in older adults, based on the 2024 Older Adult Compendium.

 - This study investigated the effects of increasing previous resistance training weekly set volume by 30% and 60% on muscle hypertrophy and strength.
- This study investigated the effects of increasing previous resistance training weekly set volume by 30% and 60% on muscle hypertrophy and strength.