
Aerosol scientist/Aerobiologist, Canadian and #Canucks fan living in the UK. #eurovision enthusiast. I’m also at: https://t.co/Ut3mF6fa5w
5 subscribers
How to get URL link on X (Twitter) App


 Given that this is a research area where our team has made a lot of waves, I thought I should share my thoughts.
Given that this is a research area where our team has made a lot of waves, I thought I should share my thoughts.
 When HVAC systems are installed, certain assumptions are made, largely because they need to be. One is that the air within the space is evenly mixed.
When HVAC systems are installed, certain assumptions are made, largely because they need to be. One is that the air within the space is evenly mixed.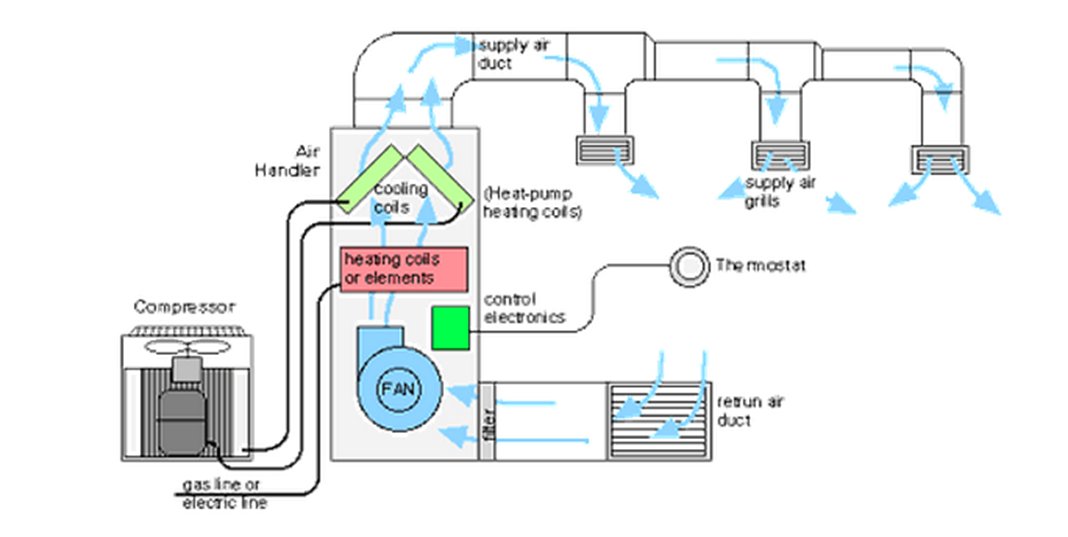

 Here’s a link to the article (the first author is Henry Oswin, a former PhD student from our group who is currently working with Lidia Morawska):
Here’s a link to the article (the first author is Henry Oswin, a former PhD student from our group who is currently working with Lidia Morawska):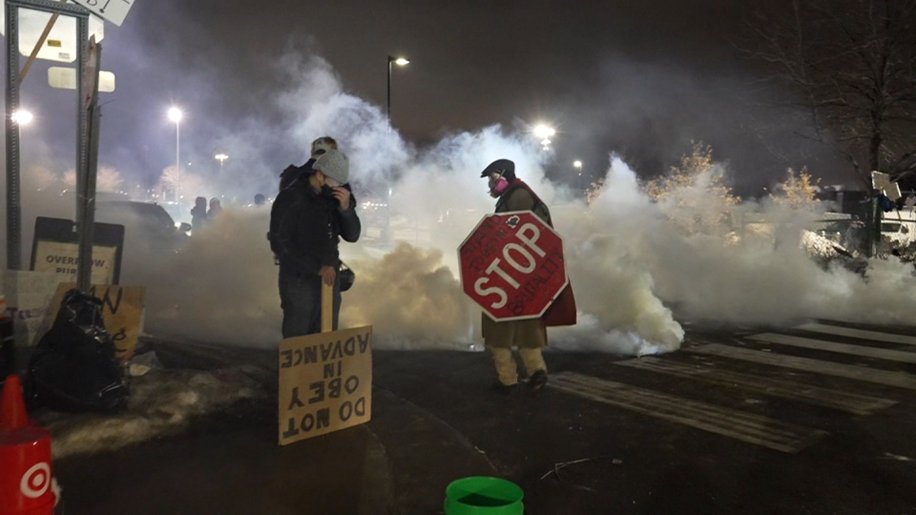
 The burning sensation of tear gas is caused by the compound 2-chlorobenzalmalononitrile.
The burning sensation of tear gas is caused by the compound 2-chlorobenzalmalononitrile.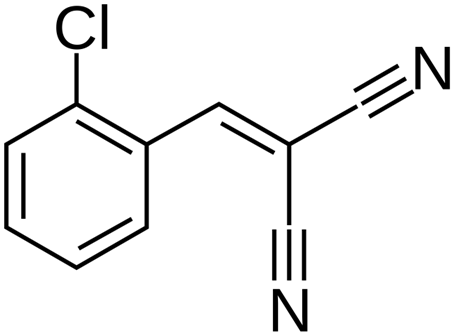

 A few of the threads discussed the fundamental challenges around measuring the effectiveness of mitigation strategies.
A few of the threads discussed the fundamental challenges around measuring the effectiveness of mitigation strategies.https://x.com/ukhadds/status/1982082959097160128
 Here’s a link to the article (free to access on Yahoo).
Here’s a link to the article (free to access on Yahoo).
 An aerosol scientist is simply a scientist that studies aerosol.
An aerosol scientist is simply a scientist that studies aerosol. 

https://twitter.com/clarecraigpath/status/1991541660757684636Shoutout to @CDare10 for flagging up this idiot’s post.

 You can find a link to the article here:
You can find a link to the article here: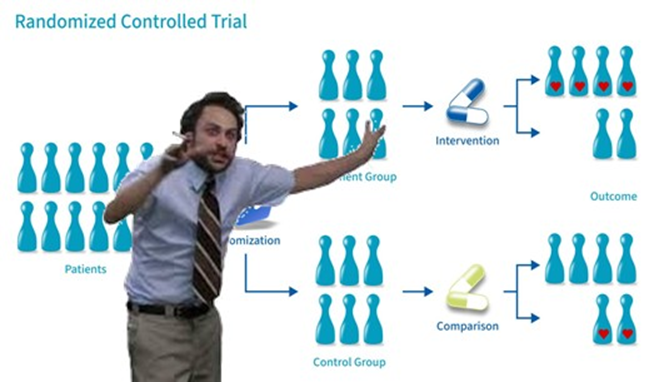
 Airborne disease transmission is extraordinarily complicated, with many steps involved. Consequently, there are many different solutions that have been proposed to limit transmission. They largely involve the removal of exhaled aerosol from the air prior to inhalation.
Airborne disease transmission is extraordinarily complicated, with many steps involved. Consequently, there are many different solutions that have been proposed to limit transmission. They largely involve the removal of exhaled aerosol from the air prior to inhalation. 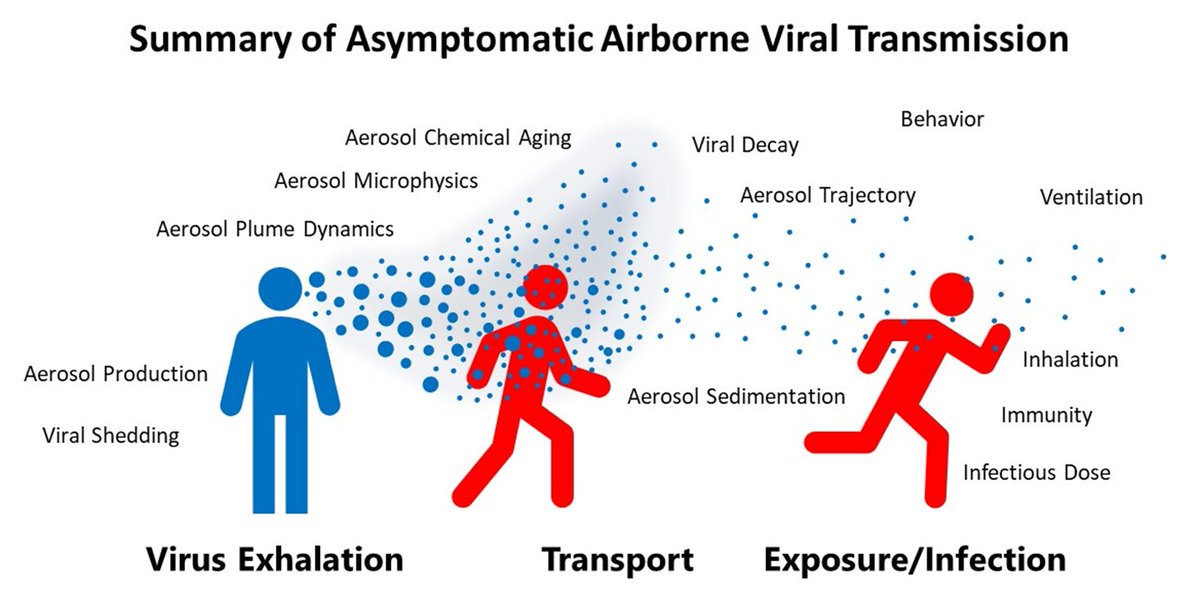

 People spend the majority of their time indoors. As a result, indoor air quality is incredibly important for public health. So then, how do we improve the quality of indoor air?
People spend the majority of their time indoors. As a result, indoor air quality is incredibly important for public health. So then, how do we improve the quality of indoor air?

 Here’s a link to the study:
Here’s a link to the study:
 Augmented Reality (AR): AR is a technology that takes “components of a digital world blend into a person's perception of the real world”. With AR, a person can make “reality” whatever they want it to be.
Augmented Reality (AR): AR is a technology that takes “components of a digital world blend into a person's perception of the real world”. With AR, a person can make “reality” whatever they want it to be.

https://x.com/Claudia_Rizzi/status/1964060928888230344I did my PhD in Simon Fraser University in Vancouver, Canada. As part of the project, I ended up working in St Paul’s hospital, specifically within the James Hogg iCapture Centre.

 First off, here’s a link to the channel.
First off, here’s a link to the channel.
 Here's a link to the video:
Here's a link to the video:

https://x.com/danwalker9999/status/1957605147040739544First off, here’s the article:

 Airborne disease transmission is a complex, and multidisciplinary process. As a result, understanding how various factors affects transmission rates is exceedingly difficult.
Airborne disease transmission is a complex, and multidisciplinary process. As a result, understanding how various factors affects transmission rates is exceedingly difficult.

 Here’s a link to the study. The lead author is Henry Oswin; he did his PhD with us, working with me on Covid. He’s now doing a postdoc with Lidia Morawska.
Here’s a link to the study. The lead author is Henry Oswin; he did his PhD with us, working with me on Covid. He’s now doing a postdoc with Lidia Morawska.
https://x.com/jillneimark/status/1949089765166321959Alright, so the specific quote being highlighted is below. Now, this may seem alarming to many people.
