This is a cautionary tale of how anti-Spike antibody may make COVID disease worse. In this study, the authors show that anti-Spike IgG made SARS-CoV disease worse by switching macrophage from wound-healing to proinflammatory phenotype. A thread (1/n)
insight.jci.org/articles/view/…
insight.jci.org/articles/view/…
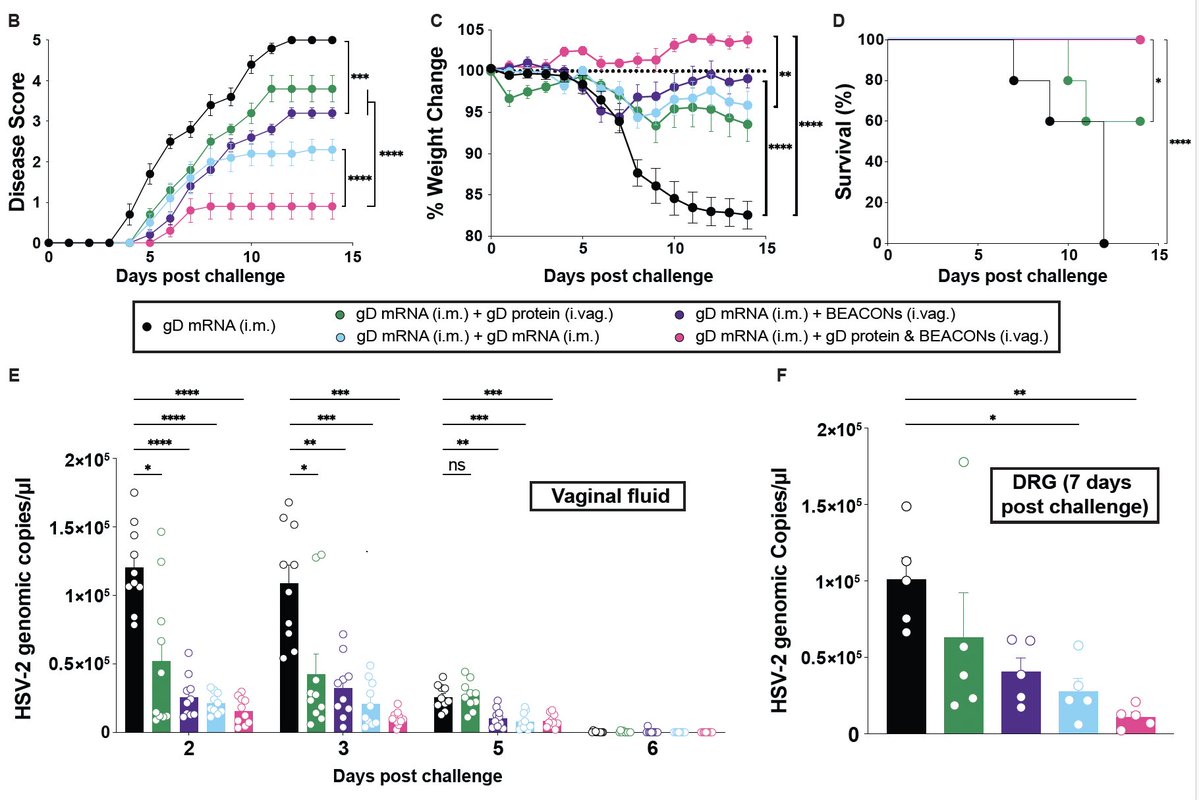
When rhesus macaques were immunized with SARS-Spike MVA vaccine, high titers of neutralizing Ab (NAb) generated correlated with severe diffuse alveolar damage NOT protection upon i.n. challenge with SARS-CoV, despite reducing viral load. Loss of disease tolerance by S-IgG. (2/n) 
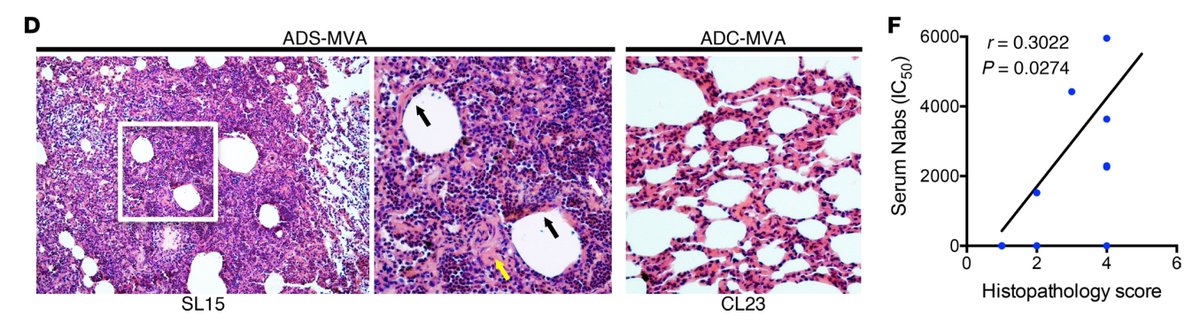
Next, rhesus macaques injected with low or high dose of anti-Spike-IgG (passive transfer) and challenged with SARS developed worse disease. Thus, S-IgG alone can lead to SARS disease exacerbation. (3/n) 
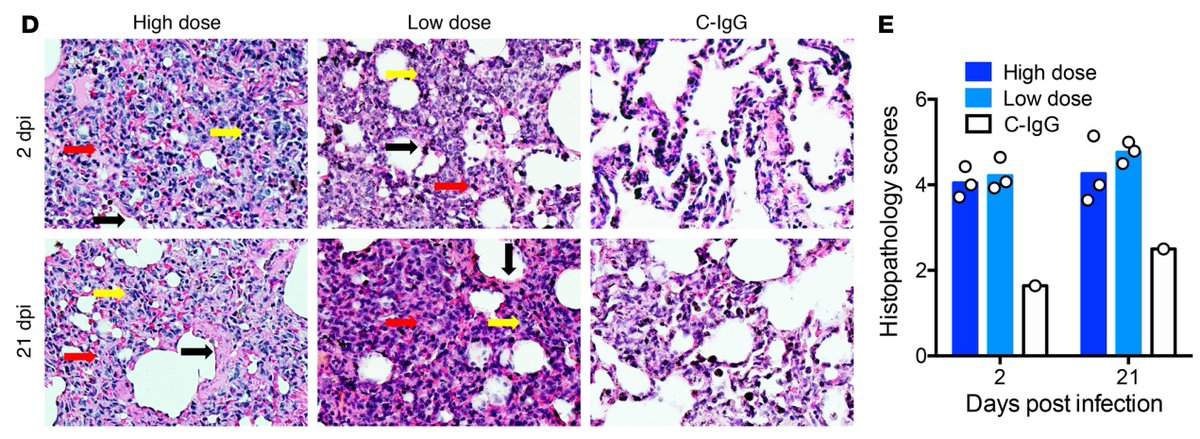
Anti-Spike IgG fails to prevent viral entry. Instead, it binds to virus, facilitating uptake by macrophages expressing FcR. This leads to macrophage stimulation and their production of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-8, MCP1) and loss of tissue-repair cytokine (TGFb). (4/n) 
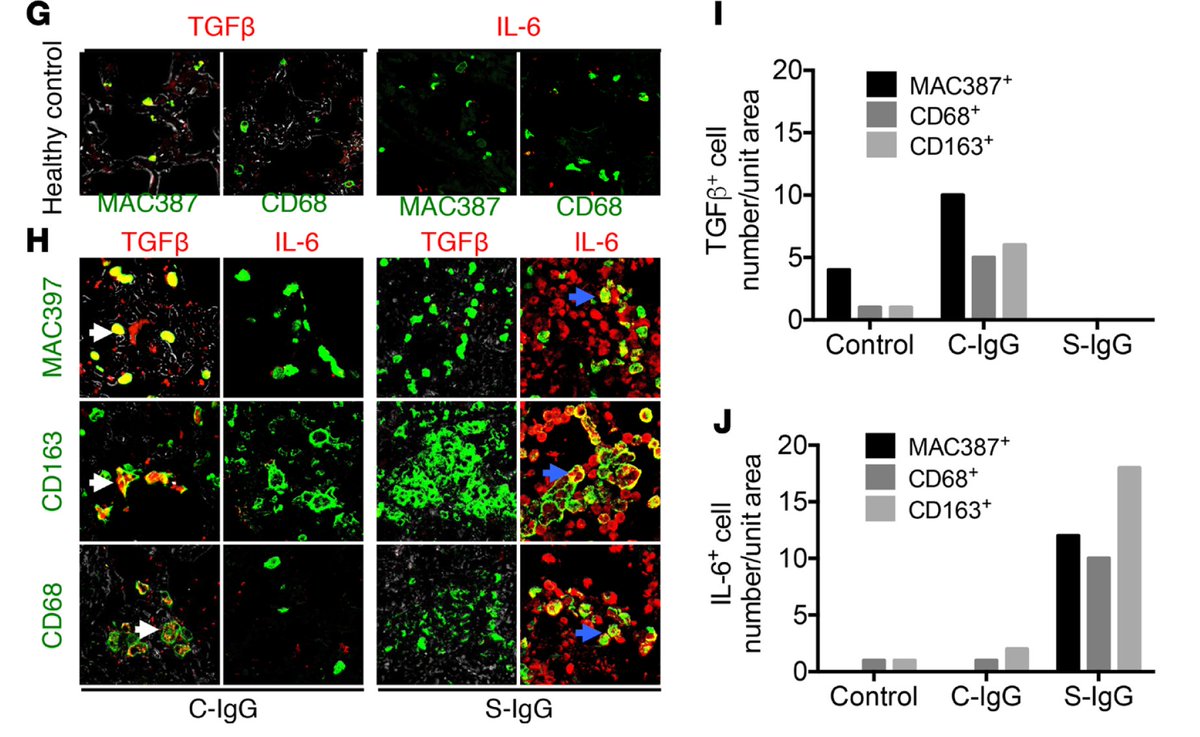
Finally, sera from early stage SARS-infected patients reveal that elevated anti-Spike IgG was observed in those that ended up dying from infection. (5/n) 
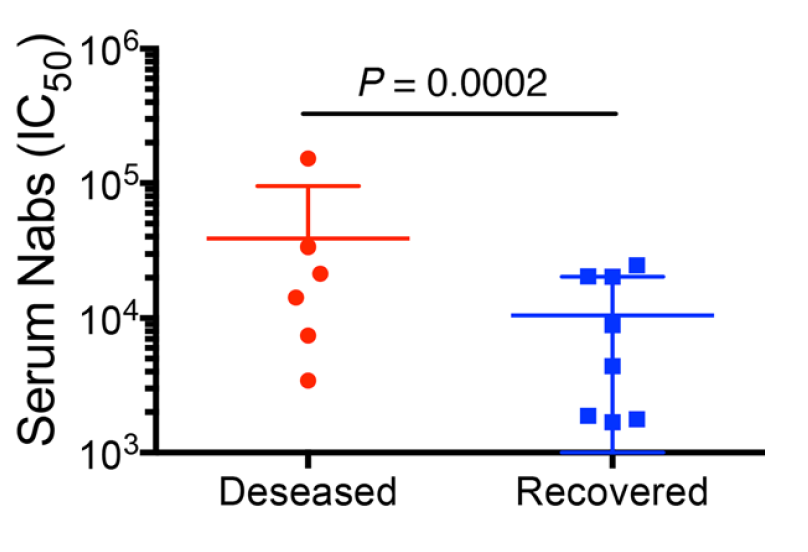
If these results also apply to #COVID19, targeting Spike as vaccine antigen may have detrimental effects. Passive transfer of anti-Spike mAb alone also may have detrimental effects. A protective vaccine approach may need to include other viral antigens (nucleocapsid?). (6/n)
Relevant to this thread is that in #COVID19 patients, the level of serum IgG against Spike protein correlates with older age, disease severity and lymphopenia. (7/n)
medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
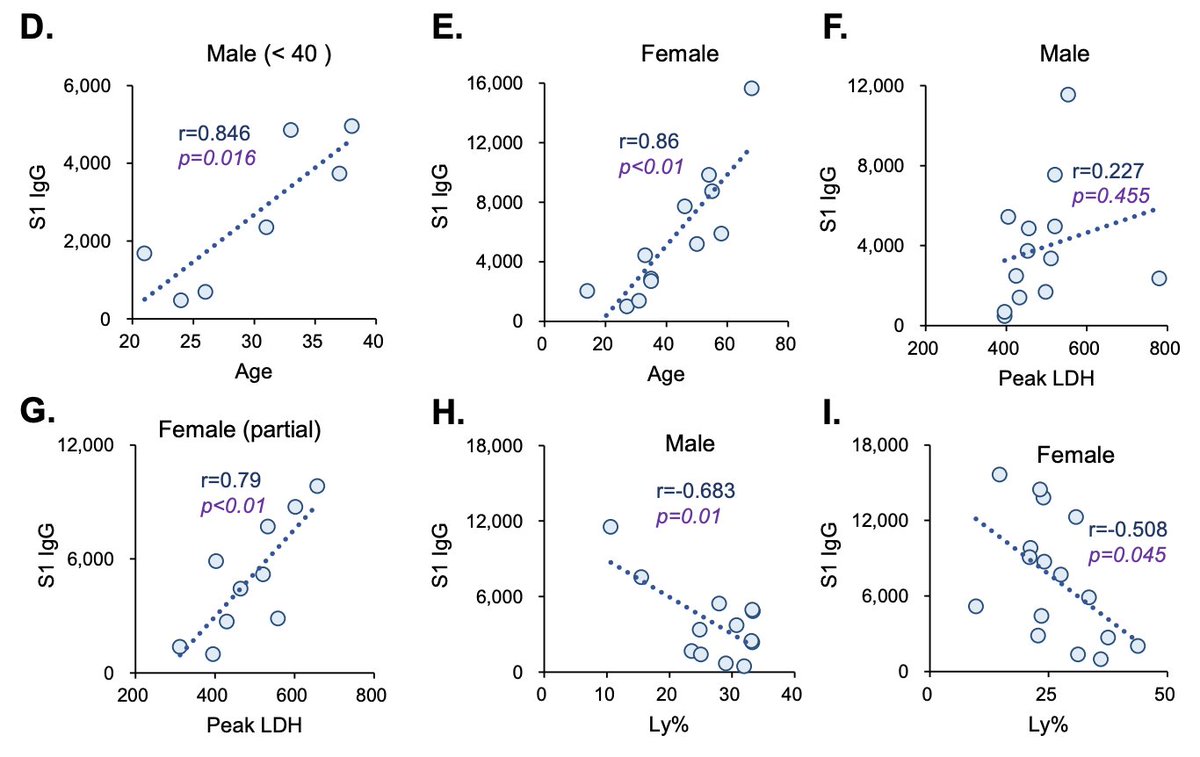
I hope this thread will spur productive discussion by others. Please feel free to chime in. Thanks @aaronmring for your insights that inspired me to post this thread.
Bottomline: we need to carefully consider vaccine approach to #COVID19.
(end)
Bottomline: we need to carefully consider vaccine approach to #COVID19.
(end)
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh