- Gurukul System- Guru-Shishya Parampara
- focuses more on the musical structure
- Scope of improvisation
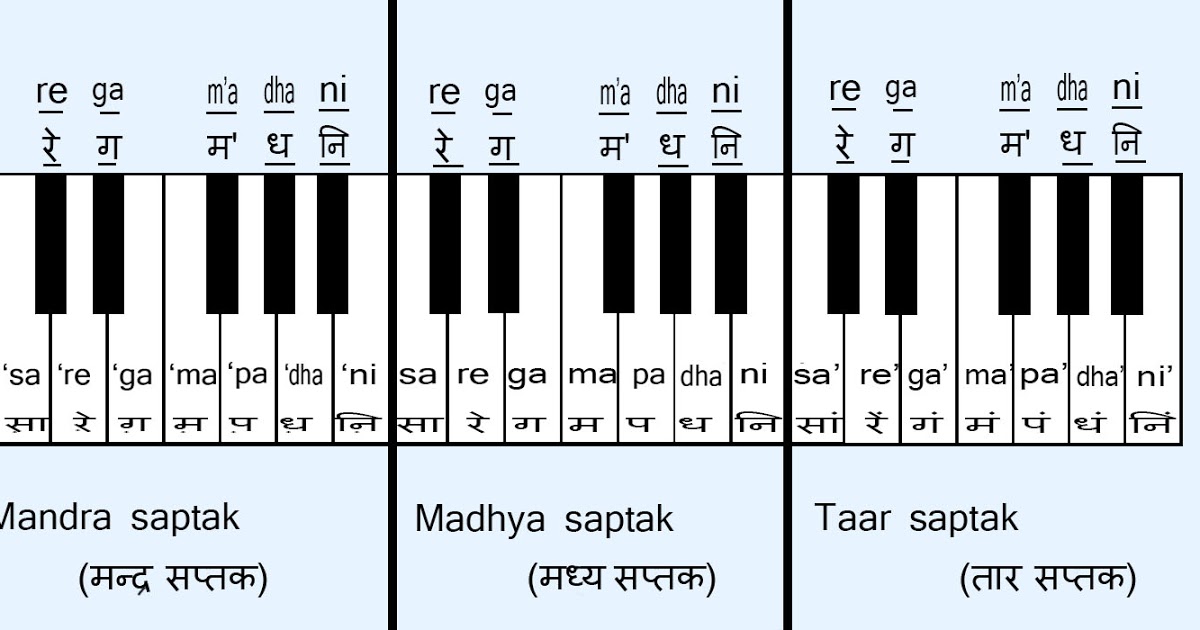
- Scale of Shudha Swara Saptaka
- 3 Main Pillars - Raga, Tala, Swara
- Form the basis of melodies
- According to no of notes in ragas
- Odava Raga – 5notes
- Shadava Raga – 6 notes
- Sampurna Raga – 7 notes
- 3Speeds – Drut(fast); Madhya(medium); Vilambit(slow)
- 6 main ragas – Bhairav, Deepak, Hindol, Megh, Shree, Malkauns
- Shuddha Raga – Nature and form doesn’t change if any note that is absent from composition is played
- Chhayalag Raga - Nature and form changes if any note that is absent from composition is played
- Sankeerna Raga – the combination of 2+ ragas
- 4th/ 5th note in relation to principal raga – Samvaadi
- All other notes – Anuvaadi
- Notes which are not present –Vivadi
-Aaaroha – Avaroha
- Form the basis of rhythm
- Grouping of beats
- The tempo of tala – uniformity of time span – Laya
- 30 talas currently known and 12-15 in use
- Carnatic music – more rigid structure
- Sanskrit syllables – temple origin
- 4-5 stanzas, Tanpura, Pankhwaj
- Dhrupad singing can be further divided into four forms on the basis of vanis or banks:
A) Dagari Gharana: sings in the Dagar Van, great emphasis on alap.
- Khyal- idea or imagination
- Origin- Amir Khusrau.
- popular amongst the artists as this provides greater scope for improvisation.
- short songs - two to eight lines- Bandish
- composed in a particular raga
- Bada Khyal –slow tempo; Chhota Khyal – fast tempo
- Inspired by Bhakti Movement
- romantic & devotional singing
- Compositions are mostly on love, separation and devotion.
- Distinct feature: Erotic subject matter portrayed picturesquely from the various episodes of the lives of Lord Krishna & Radha.
-ccrtindia.gov.in
-iccr.gov.in
-Indian Art and Culture by Nitin Singhania
-Indian Art and Culture by Gaurav Agarwal