Here was this week’s #MindteaserMonday poll. Are you ready for all the answers to be revealed? 😸
https://twitter.com/USGS_Quakes/status/1300467576993017856
Magnitude is the physical size of the earthquake!
Multiply the length of the fault segment that slid by the width by how far one side of the fault slid past the other side … and you’ll get a really big number. 😸
Multiply the length of the fault segment that slid by the width by how far one side of the fault slid past the other side … and you’ll get a really big number. 😸

How big is “really big”?
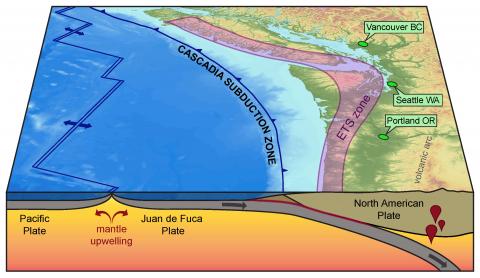
1989 M6.9 Loma Prieta ruptured 25 miles w/ ~6 ft of slip. That’s 30 billion cubic feet of earthquake.
But the 1906 M7.9 San Francisco earthquake ruptured 300 miles of the San Andreas w/ 2-32 ft of slip. 1 trillion cubic feet of earthquake!
*width~7 mi
1989 M6.9 Loma Prieta ruptured 25 miles w/ ~6 ft of slip. That’s 30 billion cubic feet of earthquake.
But the 1906 M7.9 San Francisco earthquake ruptured 300 miles of the San Andreas w/ 2-32 ft of slip. 1 trillion cubic feet of earthquake!
*width~7 mi

Billions and trillions of cubic feet: that’s a lot of zeroes. So we use a log scale to convert those really big numbers into a handy dandy magnitude that can be easily compared across those huge numbers.
FUN FACT 🔥🔥🔥🔥
The scientific paper that coined the phrase moment magnitude scale was written by Hiroo Kanamori and @USGS ‘s Tom Hanks. I bet you didn’t know that besides his other talents Tom Hanks is also a famous seismologist.
The scientific paper that coined the phrase moment magnitude scale was written by Hiroo Kanamori and @USGS ‘s Tom Hanks. I bet you didn’t know that besides his other talents Tom Hanks is also a famous seismologist.

Let’s talk about the other poll options…
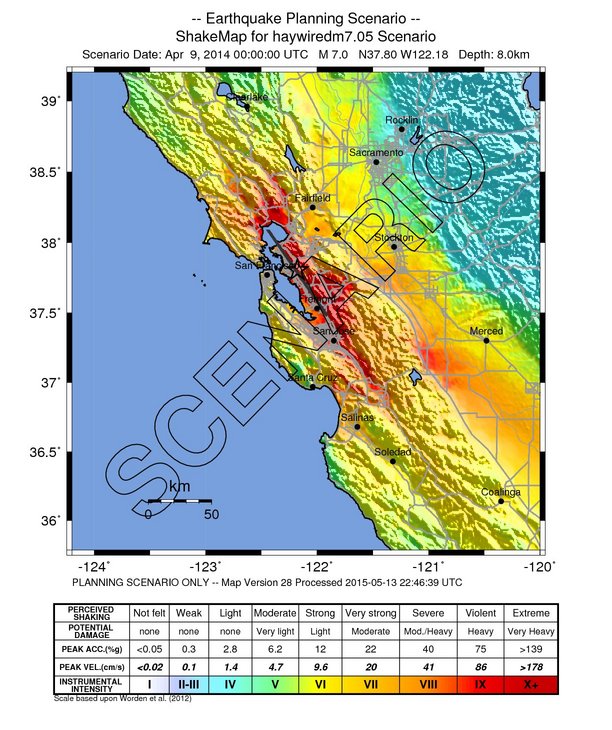
Does magnitude tell you the amount of shaking? Not by itself. Other things matter too, like how close you are. Shaking in Vallejo, CA from the 2014 M6 South Napa earthquake was probably about as strong as in the bigger 1906 M7.9 quake because Vallejo is much closer to Napa. 



Does magnitude tell you how large a region will be shaken? Not by itself. For example, pound-for-pound, earthquakes in the central and eastern U.S. shake a larger area than left coast quakes. Compare how far away people felt the 2011 M5.8 Mineral quake in VA to a M6 in CA. 

This is one of many reasons we need people to fill out Did You Feel It? reports when you feel an earthquake AND when you don’t feel an earthquake. Seriously, let us know when you don’t feel a quake. It really helps us to know where there isn’t shaking.
earthquake.usgs.gov/data/dyfi/
earthquake.usgs.gov/data/dyfi/

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh