Tenkamenin (African king ruled over a democratic nation centuries before Abraham Lincoln)
______
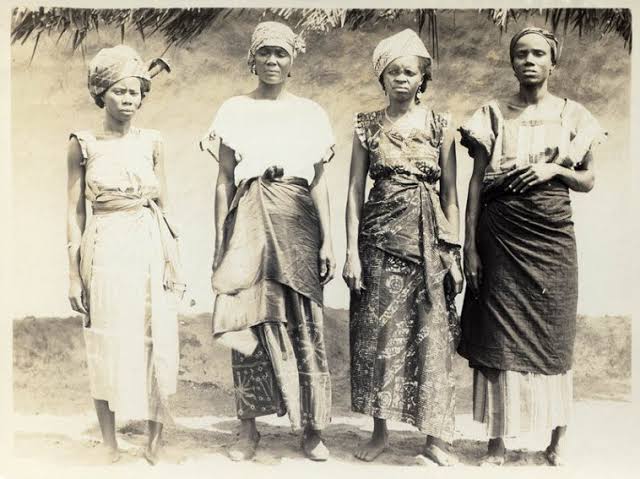
Tenkamenin, (A.k.a. People's king). Tenkamenin ruled from 1062 until 1075 in the Ancient Ghana Empire Throughout Tenkamenin’s brief reign Ghana reached great heights.
______
Tenkamenin, (A.k.a. People's king). Tenkamenin ruled from 1062 until 1075 in the Ancient Ghana Empire Throughout Tenkamenin’s brief reign Ghana reached great heights.

Tenkamenin’s empire prospered economically through his tactful management of the gold trade across the Sahara desert in West Africa.
https://twitter.com/Joe__Bassey/status/1297941957898121218?s=19
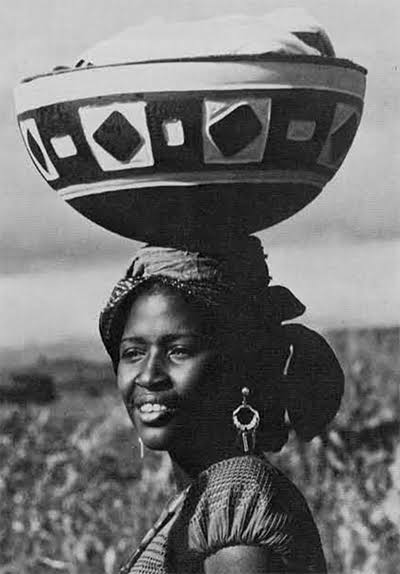
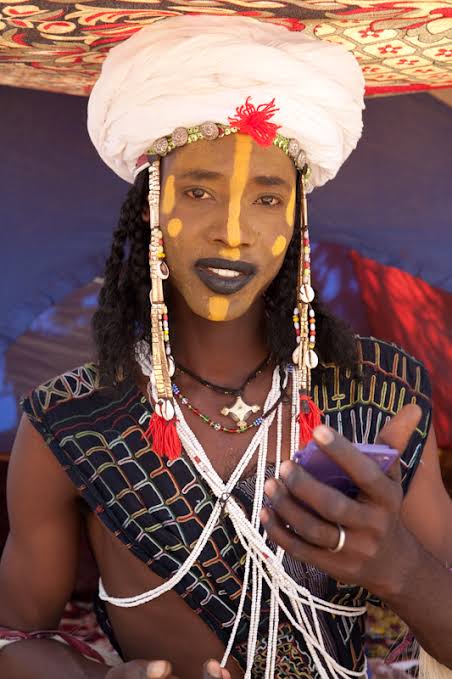
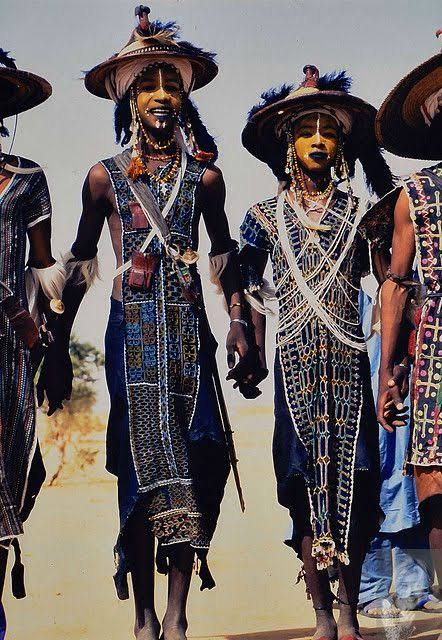
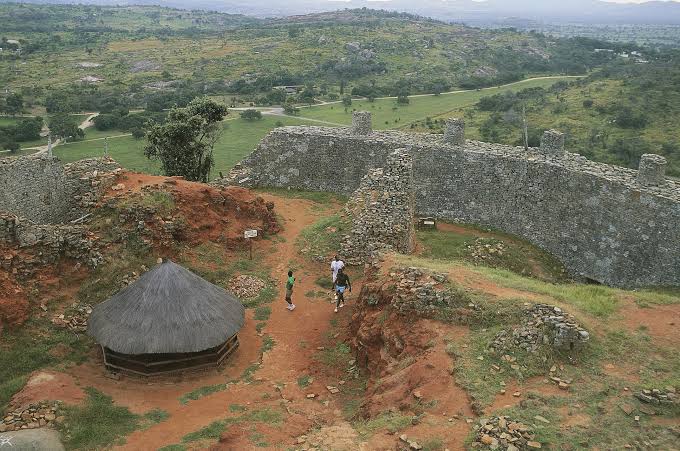
The Ghana Kingdom that existed between 830-1235AD remains one of the strongest ever and richest African kingdoms with a rich culture. It is often mistaken for modern-day Ghana, formerly known as the Gold Coast.
https://twitter.com/Joe__Bassey/status/1312075064003776513?s=19
Tenkamenin is known as the king of the people, because of his people’s empathy. He would ride out on horseback each day, listening to his people’s problems and concerns. As a consequence, it became clear that the most significant quality of Tenkamenin was in government. 
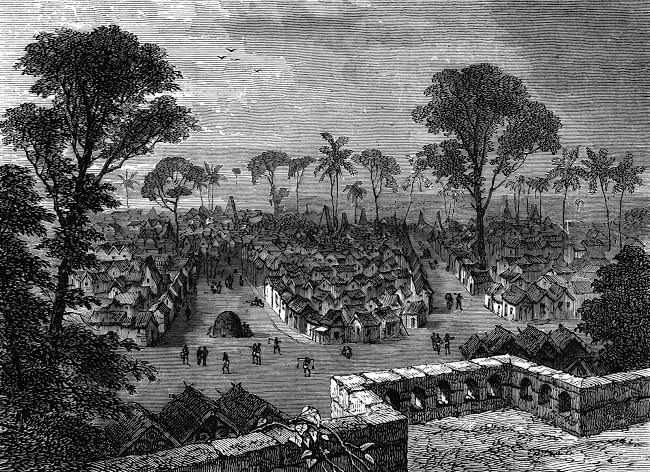

His principle of democracy and responsiveness make him one of the greatest monarchs ever to be in Africa. Known as “the king of the people” or “the king of the people,” King Tenkamenin who ruled the kingdom around the 9th century is regarded as one of the greatest kings of Africa 

The kingdom prospered during his reign, and became very wealthy to reach its peak in economic wealth and power. Tenkamenin is recognized and celebrated as his reign was a reign of peace and prosperity.
https://twitter.com/Joe__Bassey/status/1295767625197334528?s=19
He worked with his messengers to break the rules of divinity and a ruler’s higher worship. Tenkamenin made it a point every day to sit on a horse and talk to the town people. He ‘d spend long hours tackling their problems.
https://twitter.com/Joe__Bassey/status/1307726595260592139?s=19
Before making decisions, he sent his servants to seek his people’s opinion on issues that had affected the kingdom. He also allowed the people to remain in his presence, when they came to him with their problems and made it a point that they stayed until the solution is found. 

Tenkamenin is also well respected for the way he organized his governance, he was very specific about taxes, and he made a point of collecting taxes that would benefit his kingdom’s people. Tenkamenin was extremely concerned about his people’s social wellbeing. 

Though His reign was short, it was influential and is regarded as one of the best-structured monarchies of all time. The Ghana Empire fall sfter his death due to the Almoravid movement in 1076–77, although Ghanaians resisted attack for a decade. 

To know more about ancient African civilization and history check my likes and follow me to see my future post. 

@threadreaderapp unroll
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh