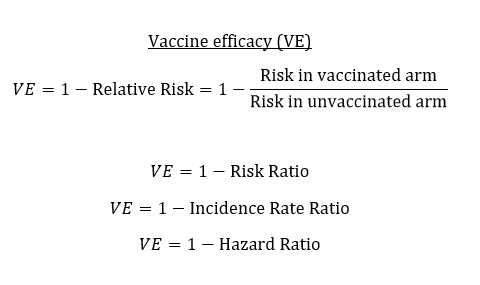
With @mlipsitch, our new piece in @ScienceMagazine on the open questions that may remain even after vaccine efficacy trials are completed. How well does the vaccine work in high-risk subgroups? And how well does the vaccine reduce onward transmission? 1/5
science.sciencemag.org/content/early/…
science.sciencemag.org/content/early/…
Vaccine efficacy trials are designed to measure individual-level protection, which serves as the basis for regulatory decision-making. But when we think about vaccination strategy at a population-level, other features like indirect protection come into play. 2/5
As a motivating example, to best protect high-risk groups like the elderly, we either need a vaccine that directly protects the elderly or we need a vaccine that can prevent younger people from transmitting to the elderly (ideally both!). 3/5
To generate evidence about whether the vaccine reduces infectiousness, viral shedding is one proxy, but we can also study the household contacts of breakthrough infections to measure secondary attack rate, like has been done for pertussis. 4/5
amstat.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.119…
amstat.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.119…
Understanding these features will be useful for comparing vaccines, as vaccines may have different strengths and weaknesses. Thanks again to @mlipsitch. We hope this stimulates some useful discussion on how to generate broader evidence to inform strategic decisions. 5/5
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh