I think it's easy to assume more of this is riding on "access and cooperation" between China and the WHO / other countries than history would suggest is actually true (thread)
https://twitter.com/NYTHealth/status/1325503777999368197
Take SARS-CoV as a counterfactual, where tracing back to wildlife trade was efficient and transparent. Civets are linked to SARS-CoV before the outbreak ends, and horseshoe bats are implicated as the reservoirs of SARS-like viruses by 2005. Access and cooperation at work! But...
The actual reservoir species isn't fully tracked down and published until 2017. That has less to do with early outbreak transparency, and more to do with the arduous nature of tracing viral origins in the wild:
nature.com/articles/d4158…
nature.com/articles/d4158…
This kind of work is a huge pain, ESPECIALLY because coronaviruses seem to like using "bridge hosts" - a stepping stone between bats and humans, like civets for SARS-CoV or camels for MERS-CoV. That decouples "early outbreak" from "where it came from"
nature.com/articles/s4157…
nature.com/articles/s4157…
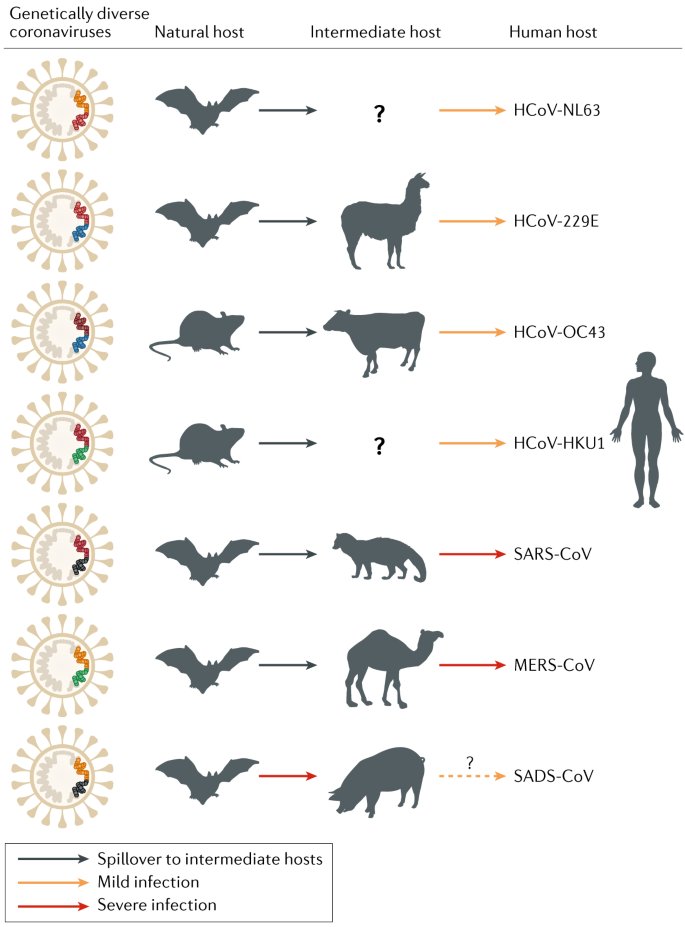
Or, to put it another way: let's say it *was* pangolins in the wildlife trade - knowing that doesn't actually, necessarily, help us find SARS-CoV-2's ancestor in bats. It took 2002 to 2017 for SARS-Cov, and could take just as long this time - regardless of this investigation.
That's why our team at @viralemergence uses machine learning to help narrow the search, with a candidate list of species that should be sampled for SARS-CoV-2's closest relatives, plus 200 other bats that might host betacoronaviruses like SARS and MERS:
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…
But the bottom line is, if it takes a long time to figure out where SARS-CoV-2 came from, don't chalk it up to "China's fault" - it's just as much, if not more, about luck, optimization of basic science, and scientists' ability to resume normal fieldwork & research
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh