
AWS Lambda recently added container support.
We're going to look into what this offer actually includes and how we could build a containerized Lambda function ourselves. 👨🏻🏫
Start your IDEs and open your AWS consoles because we're going in!
🧵⏬
We're going to look into what this offer actually includes and how we could build a containerized Lambda function ourselves. 👨🏻🏫
Start your IDEs and open your AWS consoles because we're going in!
🧵⏬
1️⃣ AWS Lambda Previous To Container Image Support
Until recently, AWS Lambda only allowed you to write some code and upload a zip-archive containing all files necessary to run your function.
Some frameworks eased up this process, but that's how it went.
Until recently, AWS Lambda only allowed you to write some code and upload a zip-archive containing all files necessary to run your function.
Some frameworks eased up this process, but that's how it went.
Lambda also imposed some pretty strict limits, especially the 50MB default deployment size limit.
You could circumvent this limit, technically, by pulling more deployment dependencies from S3 or by issuing an AWS Service Limits support request. But this wasn't the most...
You could circumvent this limit, technically, by pulling more deployment dependencies from S3 or by issuing an AWS Service Limits support request. But this wasn't the most...
...intuitive or clear thing to do.
This could make it pretty difficult sometimes to create Lambda functions out of a larger deployment. Especially when using data science dependencies like numpy, pandas, or larger JS libraries, you could easily hit that limit.
⏬
This could make it pretty difficult sometimes to create Lambda functions out of a larger deployment. Especially when using data science dependencies like numpy, pandas, or larger JS libraries, you could easily hit that limit.
⏬
2️⃣ What Container Image Support Includes
Container Image Support includes, well...containers.
This means that you can now build an image with your favorite tool (Docker anyone?), using a base image supplied by AWS, and then upload it to the ...
Container Image Support includes, well...containers.
This means that you can now build an image with your favorite tool (Docker anyone?), using a base image supplied by AWS, and then upload it to the ...
... Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR).
And do you know what's even more awesome? Those images can have a size of up to 10GB! You no longer have to worry about the deployment size constraints. It'll be pretty difficult to hit that limit fast.
And do you know what's even more awesome? Those images can have a size of up to 10GB! You no longer have to worry about the deployment size constraints. It'll be pretty difficult to hit that limit fast.
After you push your image to ECR, you can create your Lambda function as you usually would and point Lambda to it. Nothing more to do.
An added bonus:
If you use AWS' base images, which all contain the AWS Lambda Runtime Interface Emulator ...
An added bonus:
If you use AWS' base images, which all contain the AWS Lambda Runtime Interface Emulator ...
... you can even test your containers locally, by using curl or your favorite REST endpoint testing tool of choice (Postman/Postwoman anyone?).
You can find out more about it here:
⛓ github.com/aws/aws-lambda…
You can find out more about it here:
⛓ github.com/aws/aws-lambda…
3️⃣ What Container Image Support Means
Container image support is a pretty huge thing.
Many organizations have invested heavily in containerization, but the paradigm Lambda until recently stood for was a pretty huge shift.
Container image support is a pretty huge thing.
Many organizations have invested heavily in containerization, but the paradigm Lambda until recently stood for was a pretty huge shift.
It was simply a lot of new stuff to learn for all developers involved in creating services and remote endpoints.
And it required a whole other range of tools than those previously used.
Now, developers can use the same tools they are already comfortable with.
And it required a whole other range of tools than those previously used.
Now, developers can use the same tools they are already comfortable with.
The deployment to AWS could be something a little different, but CI pipelines for containers can be reused.
The company-internal container registry? Can be reused.
Locally testing your containers? Stays as it is!
I hope you see where this is going! 😊
⏬
The company-internal container registry? Can be reused.
Locally testing your containers? Stays as it is!
I hope you see where this is going! 😊
⏬
4️⃣ Building A Containerized Lambda Function
We're now going to walk through the process of building your first containerized Lambda function.
I'm pretty sure that you will notice that it's not much different from how you did it before, with only a few additional steps.
We're now going to walk through the process of building your first containerized Lambda function.
I'm pretty sure that you will notice that it's not much different from how you did it before, with only a few additional steps.
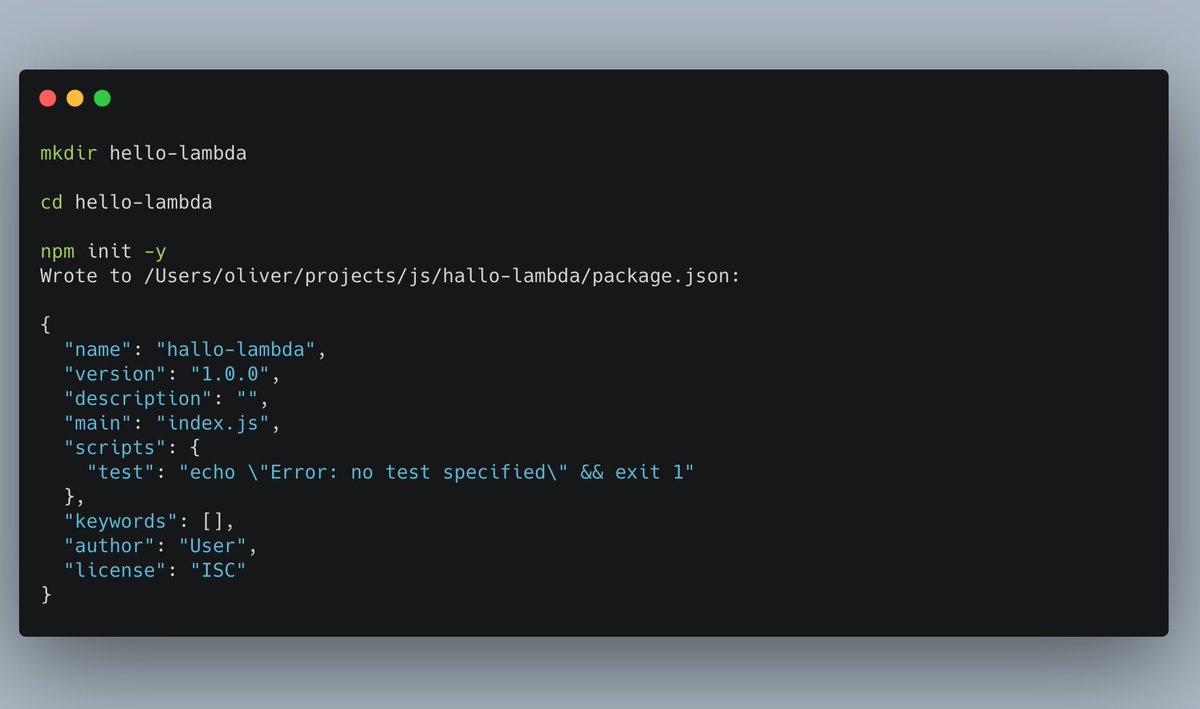
First of all, set up the folder and initialize a new npm project.
You could add a lot more dependencies now, but we're only going to build a pretty basic Lambda, so that's unnecessary at this point.
You could add a lot more dependencies now, but we're only going to build a pretty basic Lambda, so that's unnecessary at this point.
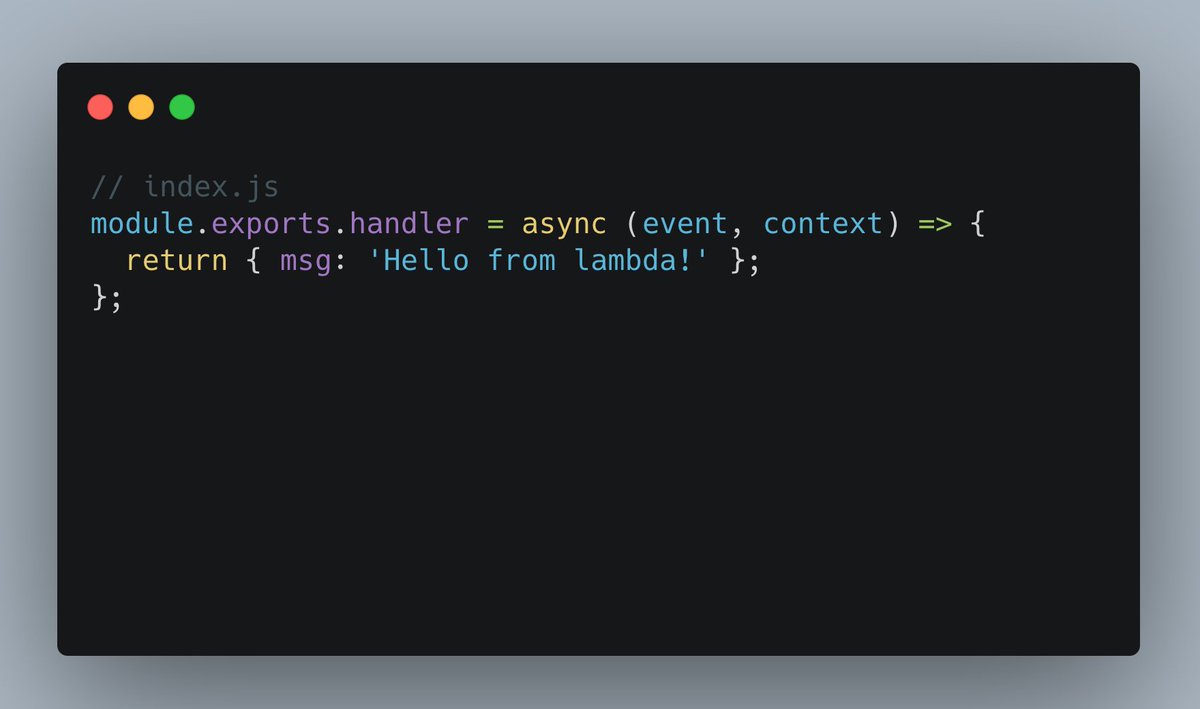
Now you need some code. It's not much, but enough to return a response from your handler.
Create a file "index.js" and put the basic handler code into it, as shown below.
If you worked with Lambda before, you'll notice that the handler has the same signature as it always had.
Create a file "index.js" and put the basic handler code into it, as shown below.
If you worked with Lambda before, you'll notice that the handler has the same signature as it always had.
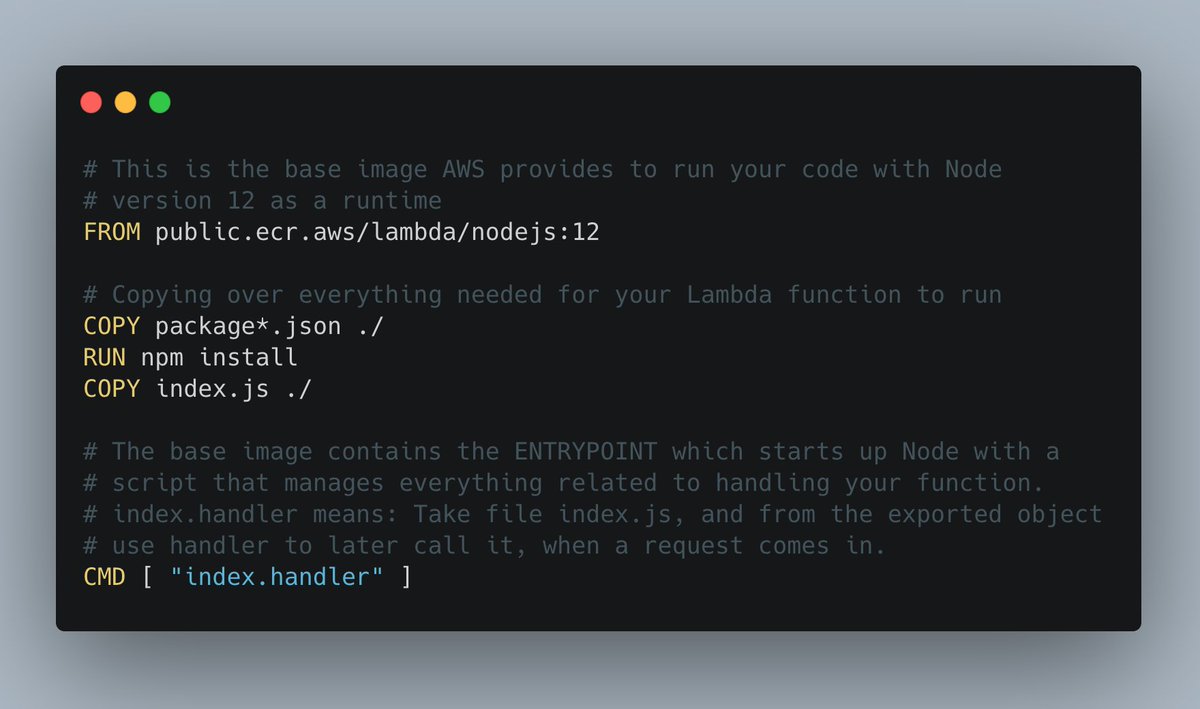
'npm install' once, to create your package-lock.json.
It's not really necessary at this stage as there are no dependencies at all but it helps to prevent further warnings when later building your container image.
It's not really necessary at this stage as there are no dependencies at all but it helps to prevent further warnings when later building your container image.

Then create a Dockerfile and fill it as shown below.
This is the file you will let Docker build your image from.
This is the file you will let Docker build your image from.
Before you go on, here is a gist containing all the contents of the files as they should now be:
⛓ gist.github.com/excelbrium/6db…
⛓ gist.github.com/excelbrium/6db…
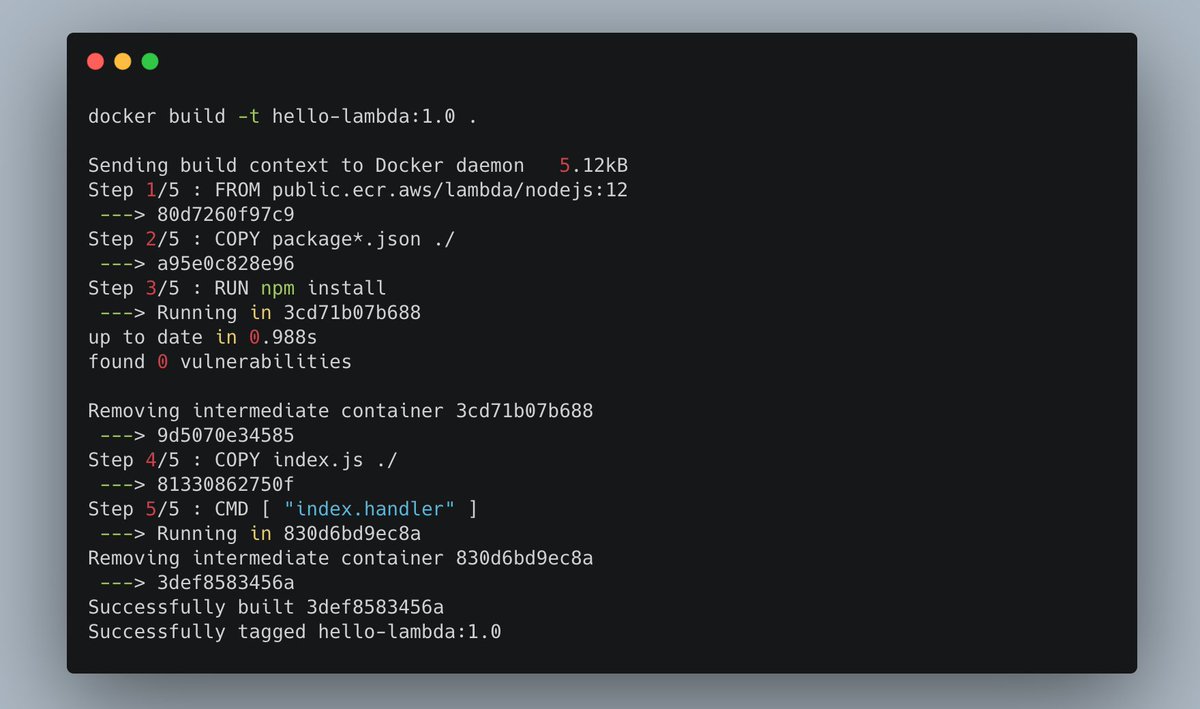
One of the last things to do is to build the container, for example with Docker.
It shouldn't take too much time, as your project is very simple and small at this point.
After building the container, you're nearly done.
It shouldn't take too much time, as your project is very simple and small at this point.
After building the container, you're nearly done.
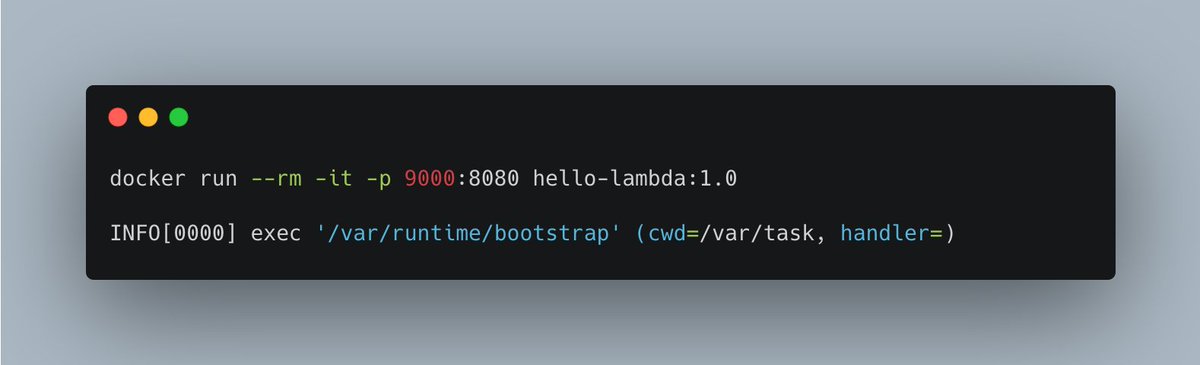
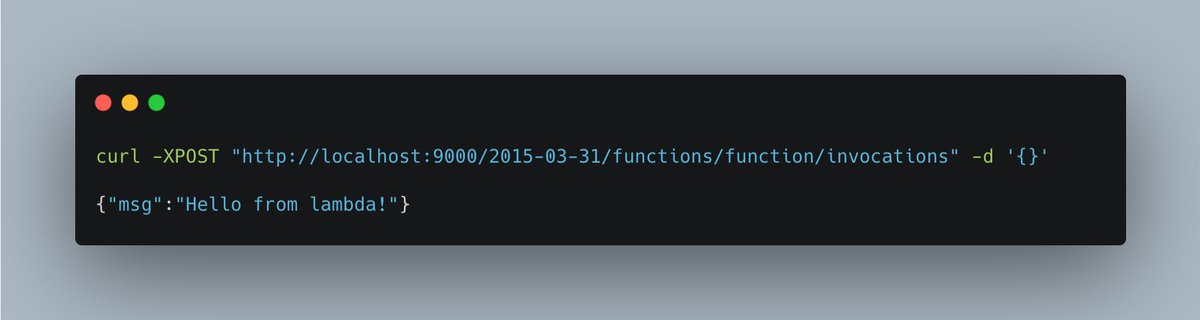
You could now start the container locally, and even issue requests to it, simply to test if everything is working as expected.
You can also use curl to issue a request, and as you hopefully see, it works!
⏬

You can also use curl to issue a request, and as you hopefully see, it works!
⏬
5️⃣ Deploying The Container to AWS Lambda
You now need to upload your container image to ECR to be able to deploy it to Lambda later.
I'd recommend you to have the AWS CLI installed for this task.
⛓ aws.amazon.com/cli/?nc1=h_ls
You now need to upload your container image to ECR to be able to deploy it to Lambda later.
I'd recommend you to have the AWS CLI installed for this task.
⛓ aws.amazon.com/cli/?nc1=h_ls
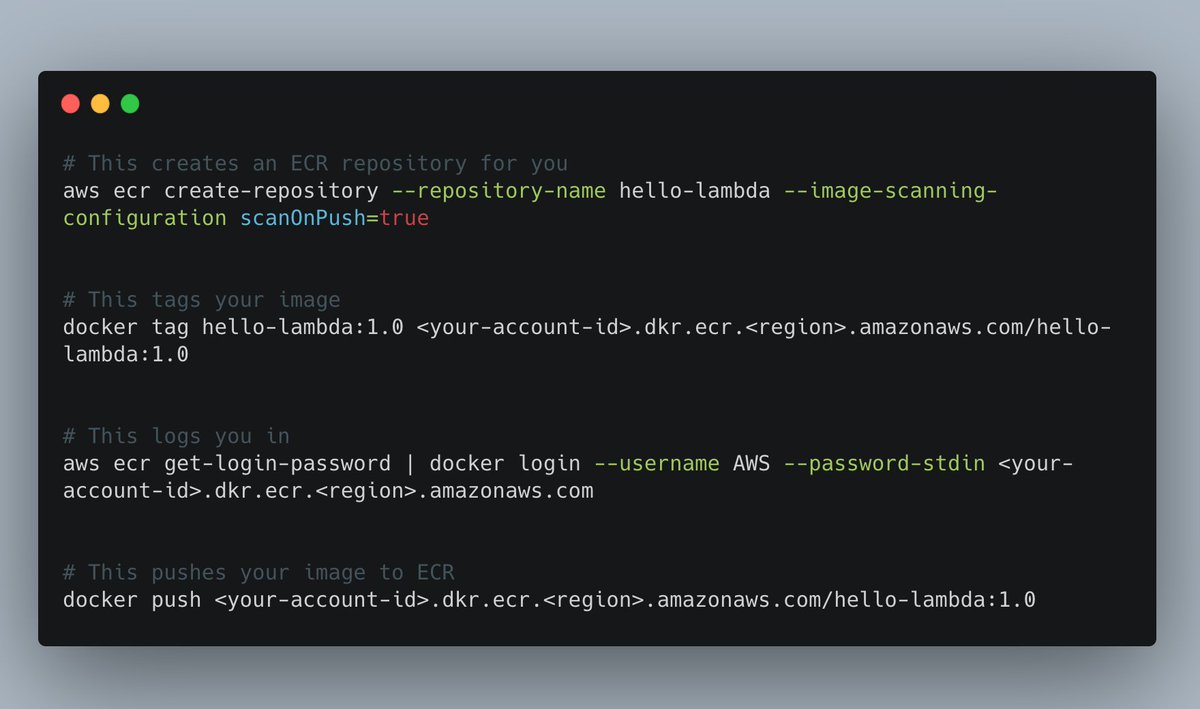
The following steps are then necessary to upload your image to ECR:
1. Create an ECR repository (skip if you already have one)
2. Tag your image
3. Log in to ECR
4. Push the image
1. Create an ECR repository (skip if you already have one)
2. Tag your image
3. Log in to ECR
4. Push the image
Next, go to the Lambda console here:
⛓ console.aws.amazon.com/lambda/home
Click on "Create function", and then choose "Container image".
⛓ console.aws.amazon.com/lambda/home
Click on "Create function", and then choose "Container image".
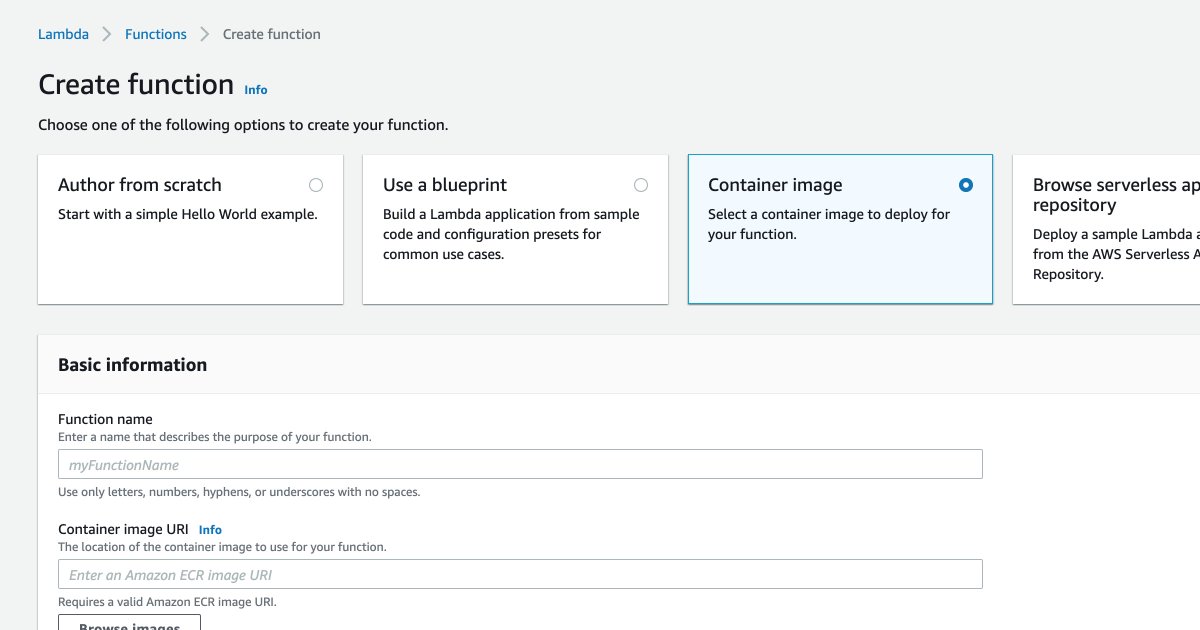
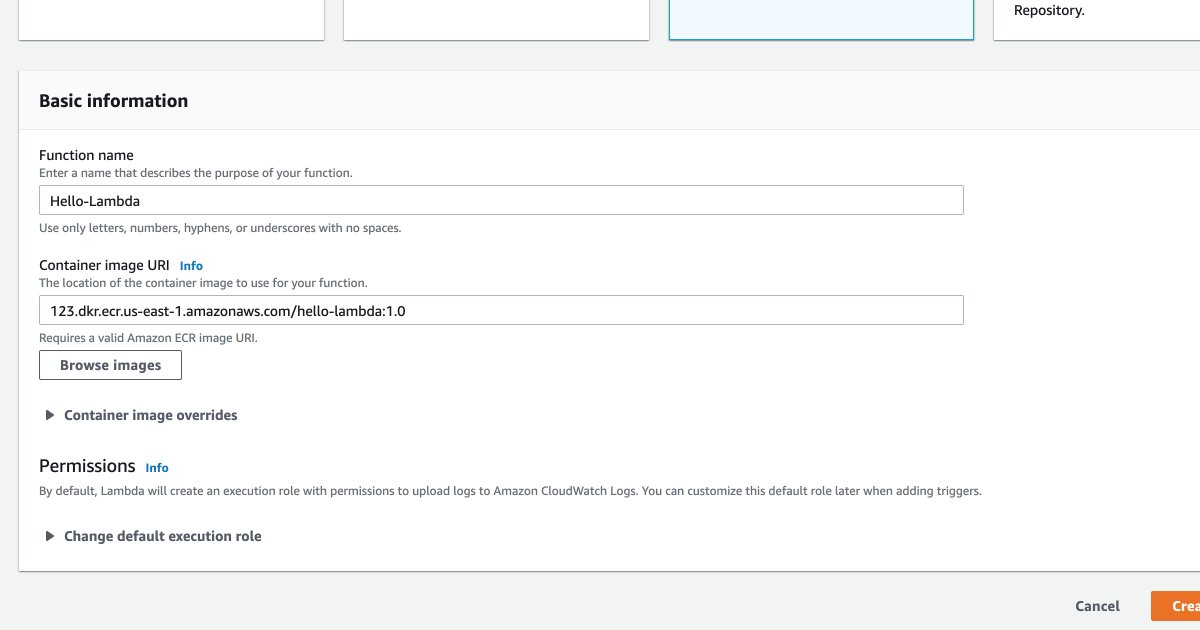
Within the "Basic information" block, give your function a name, and then paste the image URL you used to push your image to ECR.
And that's it. Click on "Create function" in the bottom right corner, and your function will be deployed!
And that's it. Click on "Create function" in the bottom right corner, and your function will be deployed!
You can now do everything you'd do with a "normal" Lambda function. Maybe you want to use API Gateway to redirect incoming traffic to your Lambda function or set up a few events.
That's all up to you now!
⏬
That's all up to you now!
⏬
5️⃣ Some Words Of Advice
Be advised, that AWS tries to make money from all this, of course.
There is a generous free tier for Lambda and ECR, but keep in mind that only a certain amount of traffic and storage is free each month or for a year.
Be advised, that AWS tries to make money from all this, of course.
There is a generous free tier for Lambda and ECR, but keep in mind that only a certain amount of traffic and storage is free each month or for a year.
If you followed this tutorial, try to keep in mind that you used up some of that free tier.
You shouldn't forget your lambda and container, as you might be pleasantly surprised that you have to pay money if you go back to AWS at some point and deploy more stuff!
⏬
You shouldn't forget your lambda and container, as you might be pleasantly surprised that you have to pay money if you go back to AWS at some point and deploy more stuff!
⏬
6️⃣ Conclusion
Container image support has made Lambda even better than it was before.
The paradigm shift has always been a problem for quite a few companies that took some good effort to train their engineers/devs in newer concepts like microservices and containerization.
Container image support has made Lambda even better than it was before.
The paradigm shift has always been a problem for quite a few companies that took some good effort to train their engineers/devs in newer concepts like microservices and containerization.
And especially a lot of the tools that were introduced into organizations to ease up the development process were more and more tailored to containers in recent times.
All that knowledge and all those tools can now also be used with AWS Lambda, which is indeed ...
All that knowledge and all those tools can now also be used with AWS Lambda, which is indeed ...
... a game-changer. Adoption of serverless FaaS is now easier than ever before, even for larger organizations.
Companies can still use their old-school Jenkinses or newer CI tools to build their code and then containerize it afterward.
Maybe those organizations also ...
Companies can still use their old-school Jenkinses or newer CI tools to build their code and then containerize it afterward.
Maybe those organizations also ...
... push their images to ECR already. The change is marginal then: Deploy the container as a Lambda function instead of deploying it to EKS or Fargate.
Deployments that were previously difficult to achieve or impossible, due to the size constraints, are now possible, ...
Deployments that were previously difficult to achieve or impossible, due to the size constraints, are now possible, ...
... which could open up a lot of opportunities for organizations to deploy machine learning models as Lambda functions or generally larger projects.
I personally like those changes. Due to the nature of my job, I've been more focused on containers.
I personally like those changes. Due to the nature of my job, I've been more focused on containers.
All our tools are tailored towards containers. Now I can also use them with Lambda functions.
In the end, I'm pretty happy with the recent development of Lambda.
However, I hope that you enjoyed reading this, and maybe take it as an inspiration to try it out yourself! 😊
In the end, I'm pretty happy with the recent development of Lambda.
However, I hope that you enjoyed reading this, and maybe take it as an inspiration to try it out yourself! 😊
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






