Lodestone - Wikipedia
Pieces of lodestone, suspended so they could turn, were the first magnetic compasses,[3][4][5][6] and their importance to early navigation is indicated by the name lodestone, which in Middle English means "course stone" or "leading en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lodestone
Pieces of lodestone, suspended so they could turn, were the first magnetic compasses,[3][4][5][6] and their importance to early navigation is indicated by the name lodestone, which in Middle English means "course stone" or "leading en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lodestone
stone",[7] from the now-obsolete meaning of lode as "journey, way".
odestones have frequently been displayed as valuable or prestigious objects. The Ashmolean Museum in Oxford contains a lodestone adorned with a gilt coronet that was donated by Mary Cavendish in 1756, possibly to secure her husband's appointment as Chancellor of
Oxford University.[26] Isaac Newton's signet ring reportedly contained a lodestone which was capable of lifting more than 200 times its own weight.[27] And in 17th century London, the Royal Society displayed a six-inch spherical lodestone (a terrella or 'little Earth'), which
was used to illustrate the Earth's magnetic fields and the function of mariners' compasses
The museum opened on 24 May 1683,[5] with naturalist Robert Plot as the first keeper. The building on Broad Street, which became known as the Old Ashmolean, is sometimes attributed to Sir Christopher Wren or Thomas Wood.[6] Elias Ashmole had acquired the collection from the
gardeners, travellers, and collectors John Tradescant the Elder and his son, John Tradescant the Younger. It included antique coins, books, engravings, geological specimens, and zoological specimens—one of which was the stuffed body of the last dodo ever seen in Europe; but by
1755 the stuffed dodo was so moth-eaten that it was destroyed, except for its head and one claw.
The present building dates from 1841 to 1845. It was designed as the University Galleries by Charles Cockerell[8] in a classical style and stands on Beaumont Street. One wing of the building is occupied by the Taylor Institution, the modern languages faculty of the university,
standing on the corner of Beaumont Street and St Giles' Street. This wing of the building was also designed by Charles Cockerell, using the Ionic order of Greek architecture.
The museum became a depository for some of the important archaeological finds from Evans' excavations in Crete.
After the various specimens had been moved into new museums, the "Old Ashmolean" building was used as office space for the Oxford English Dictionary. Since 1924, the
After the various specimens had been moved into new museums, the "Old Ashmolean" building was used as office space for the Oxford English Dictionary. Since 1924, the
building has been established as the Museum of the History of Science, with exhibitions including the scientific instruments given to Oxford University by Lewis Evans (1853–1930), amongst them the world's largest collection of astrolabes.
Charles Buller Heberden (1849–1921) left £1,000 (£45 thousand as of 2021) to the University, which was used for the Coin Room at the museum. 

In 2012, the Ashmolean was awarded a grant of $1.1m by the Andrew W. Mellon Foundation to establish the University Engagement Programme or UEP. The programme employs three Teaching Curators and a Programme Director to develop the use of the museum's collections in the teaching
and research of the University.
The foundation is housed in New York City in the expanded former offices of the Bollingen Foundation, another educational philanthropy supported by Paul Mellon.
The foundation is housed in New York City in the expanded former offices of the Bollingen Foundation, another educational philanthropy supported by Paul Mellon.
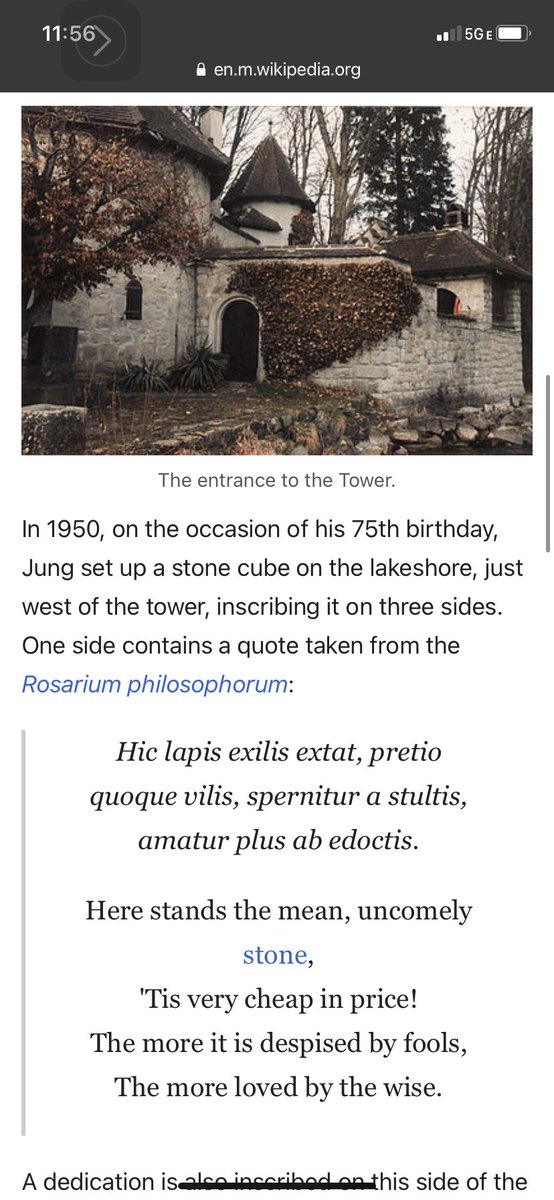
The Bollingen Foundation was an educational foundation set up along the lines of a university press in 1945. It was named after Bollingen Tower, Carl Jung's country home in Bollingen, Switzerland. Funding was provided by Paul Mellon and his wife Mary Conover Mellon. The 

Foundation became inactive in 1968, and its publications were later re-issued by Princeton University Press.
For much of his life Jung spent several months each year living at Bollingen. The Tower is now owned by a family trust and is not open to the public.
For much of his life Jung spent several months each year living at Bollingen. The Tower is now owned by a family trust and is not open to the public.
When Paul Mellon decided in 1963 to dissolve the Bollingen Foundation, he said that the founding generation was reaching the age of retirement, and it would be hard for others to maintain the original mission and standards. What he might have said was that the Bollingen
Foundation was the work of a single generation. For two decades its concerns had been at the center of Western intellectual life, but the 1960s saw a shift in the cultural preoccupations and critical concerns of intellect in the United States and Europe.
In 1948, the foundation donated $10,000 to the Library of Congress to be used toward a $1,000 Bollingen Prize for the best poetry each year. The Library of Congress fellows, who in that year included T. S. Eliot, W. H. Auden and Conrad Aiken, gave the 1949 prize to Ezra Pound
for his 1948 Pisan Cantos.[6] Their choice was highly controversial, in particular because of Pound's fascist and anti-Semitic politics.
Pound was born in a two-story clapboard house in Hailey, Idaho Territory, the only child of Homer Loomis Pound (1858–1942) and Isabel Weston (1860–1948),[4] who married in 1884.[5] Homer had worked in Hailey since 1883 as registrar of the General Land Office.[4] Pound's
grandfather, Thaddeus Coleman Pound, a Republican Congressman and the 10th Lieutenant Governor of Wisconsin, had secured him the appointment. Homer had previously worked for Thaddeus in the lumber business.[6]
Both sides of Pound's family emigrated from England in the 17th
Both sides of Pound's family emigrated from England in the 17th
century. On his father's side, the immigrant ancestor was John Pound, a Quaker who arrived from England around 1650.[5] Ezra's paternal grandmother, Susan Angevine Loomis,[7] married Thaddeus Coleman Pound.
He spent three weeks in Madrid in various libraries, including in the Royal Library. On 31 May 1906 he was standing outside the palace during the attempted assassination of King Alfonso and left the city for fear of being mistaken for an anarchist.
From September 1907 Pound taught French and Spanish at Wabash College,[38] a Presbyterian college with 345 students in Crawfordsville, Indiana,[39] which he called "the sixth circle of hell".[
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh