Stuart H. Ingersoll - Wikipedia
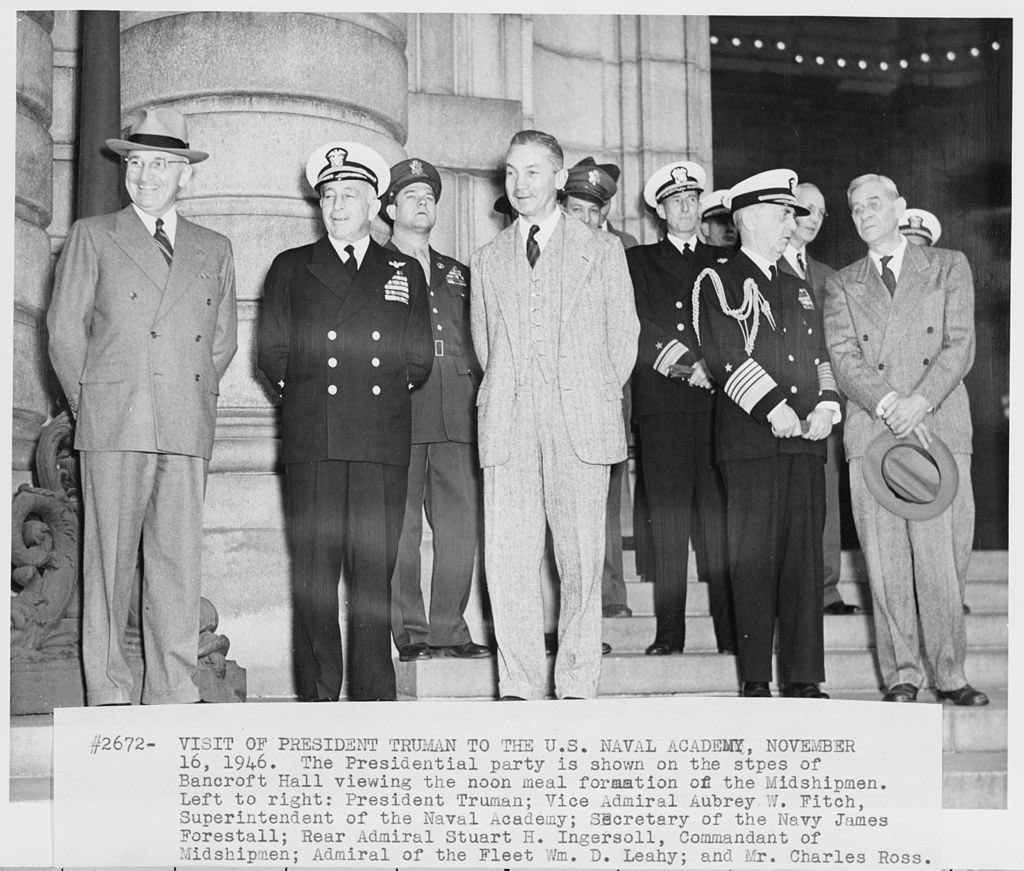
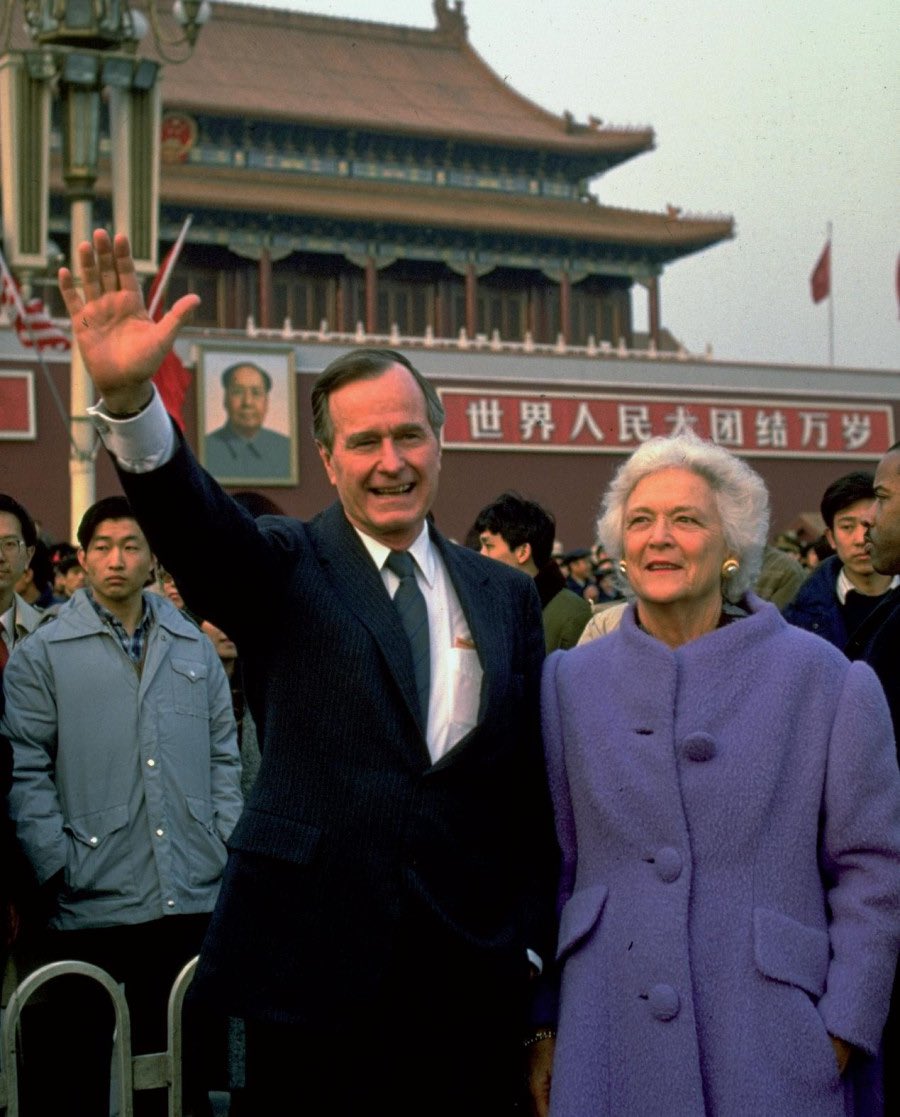
Ingersoll as a rear admiral and United States Naval Academy Commandant of Midshipmen during a visit by President Harry S Truman on 16 November 1946. Left to right are Truman, Academy Superintendent Vice Admiral Aubrey en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stuart_H.…
Ingersoll as a rear admiral and United States Naval Academy Commandant of Midshipmen during a visit by President Harry S Truman on 16 November 1946. Left to right are Truman, Academy Superintendent Vice Admiral Aubrey en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stuart_H.…
W. Fitch, presidential physician General Wallace Graham, Secretary of the Navy James Forrestal, Ingersoll, Admiral of the Fleet William D. Leahy, and Presidential press secretary Charlie Ross. 

The US Department of Navy officially founded the Newport Training Station in 1883, but the legwork between the state of Rhode Island and the Navy dated back to the late 1870's. The Training Station was intended to provide education for young men and boys for a ten month period. 
During the Civil War, the US Naval Academy was temporarily moved from Annapolis, Maryland to Newport to avoid any potential conflicts relating to the insurgency. Naval training ships, including the USS Constitution, USS Santee and USS John Adams were also moved to Newport Harbor
during the conflict to train midshipmen for the Union. In February 1919, sailor Thomas Brunelle and chief machinist's mate Ervin Arnold were patients at the naval hospital at Naval Station Newport in Newport, Rhode Island. Brunelle disclosed to Arnold that both naval and
civilian men who have sex with men regularly met at the Army and Navy YMCA and the Newport Art Club for companionship and sex. Arnold independently investigated Brunelle's claims, discovering parties involving cross-dressing, same-sex sexual activity, and liquor and cocaine use 





Arnold presented his Navy superiors with a detailed report of his findings. Admiral Spencer S. Wood, commander of the 2nd Naval District, ordered an investigation and created a court of inquiry to review Arnold’s claims. On March 19, 1919, the court concluded that a thorough 







investigation was warranted. Then-Assistant Secretary of the Navy Franklin D. Roosevelt approved the court's recommendation, and asked Attorney General A. Mitchell Palmer to undertake the investigation. The Providence Journal published the letter, which put the Navy on the 







defensive and named Secretary of the Navy Josephus Daniels and Roosevelt. Assistant Secretary Roosevelt angrily charged that press coverage like Rathom's would damage the Navy's reputation to the point that parents would not allow their sons to enlist. Also at issue, however, 







were the methods employed in the investigation. Rathom and Roosevelt had a "tart exchange of telegrams" disputing whether anyone in the naval hierarchy in Washington had supervised the investigation closely or authorized the actual participation of investigators in illicit acts. 







While investigations dragged, Roosevelt resigned from his position as Assistant Secretary of the Navy in July 1920 when he accepted the Democratic Party's nomination for vice president. He and presidential candidate James M. Cox were on the losing end of Warren G. Harding's
landslide victory that year.
On July 19, 1921, a subcommittee of the Senate Committee on Naval Affairs denounced both Daniels and Roosevelt for the methods used in the Newport investigations. The New York Times reported that most of the details of the affair were "of an
On July 19, 1921, a subcommittee of the Senate Committee on Naval Affairs denounced both Daniels and Roosevelt for the methods used in the Newport investigations. The New York Times reported that most of the details of the affair were "of an

unprintable nature" but explained that the committee believed that Daniels and Roosevelt knew that "enlisted men of the navy were used as participants in immoral practices for the purpose of obtaining evidence." 

Roosevelt rejected the report, noting that the subcommittee's two Republican members had condemned him while the one Democrat issued a minority report. He contested many details and interpretations in the committee's report, and then went on the attack: "This business of using 







the navy as a football of politics has got to stop." He had nothing to say about the court-martial's assessment. 







• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh