
1/ Let’s review pediatric sedation with Dr. Amy Alayari (PGY3)!
Classify the following level of sedation: someone is in a controlled state of depressed consciousness during which airway is maintained. Patient can respond to questions and light touch (e.g. “open your eyes”)
Classify the following level of sedation: someone is in a controlled state of depressed consciousness during which airway is maintained. Patient can respond to questions and light touch (e.g. “open your eyes”)
2/ Think of sedation as a continuum, understand that a patient can go from mild to general anesthesia within seconds! Review the slide here for the answer to the question above 

3/ Always be prepared before giving sedation! That includes giving informed consent and making sure you have all materials in the SOAP-ME mnemonic ready 

4/ Let’s review some pharmacologic agents. What agent you choose depends on the patient, procedure, comfort/experience of the clinician, and qualities of the agent 

5/ Here are the opiates. Of these, fentanyl has the least sedating quality of all of the opioids, but it is short-acting following single doses. Fentanyl can also be long-acting following infusions due to its “context-sensitive half-life” 

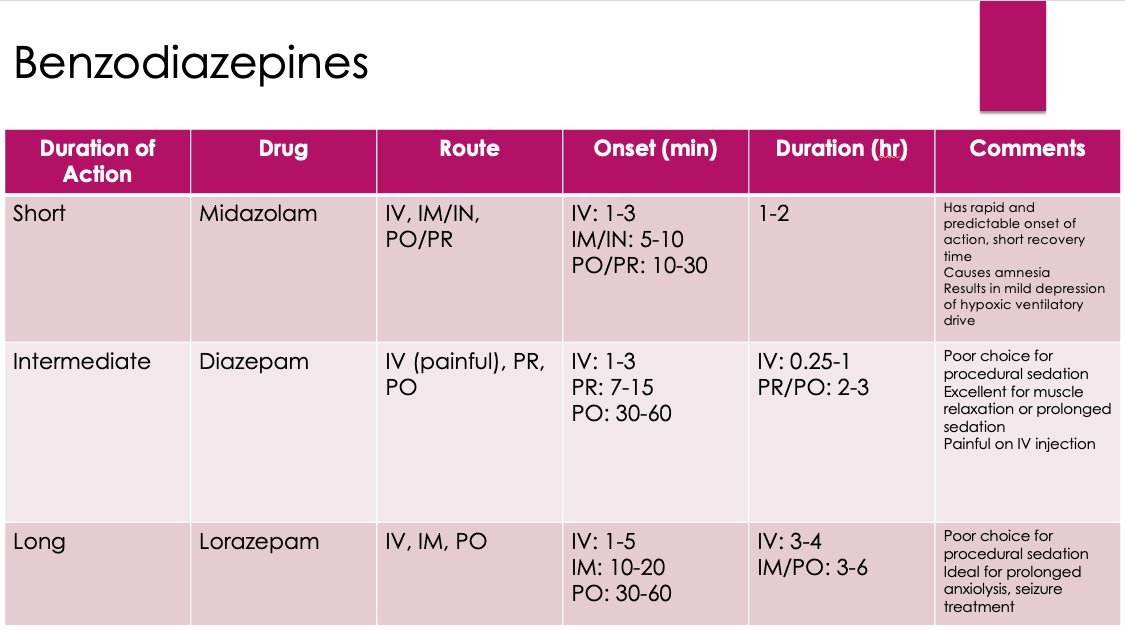
6/ Let's review some benzodiazepines which are the most widely used class of drugs for anxiolysis and sedation 
7/ Here’s a visual for classes of pharmacologic agents. Some protocols will combine sedatives with analgesics to provide adequate sedation. Note that ketamine can uniquely result in a deep level of depressed consciousness while generally maintaining airway reflexes & patency! 

8/ Let’s practice! An otherwise healthy 3yo F presents with prolonged sudden onset torticollis & neck pain. She is extremely anxious and upon exam is crying, pulls away, and actively avoids any physical exam. Which sedation agent would be most appropriate for her MRI study?
9/ An otherwise healthy 2yo M presents after an accidental fall with ice skating. He has a 1 inch-long simple laceration on his inferior chin. You decide to perform a suture repair in the ED. Which is the most appropriate sedation agent for this child’s suture repair?
10/ 9 yo healthy M presents with an arm fracture requiring a closed reduction in the ED. What pharmacologic agent is most appropriate for this patient?
11/ Answers
-
-
-
-
8/ C) IV propofol. MRIs can be a long study. No analgesia needed
9/ A) Simple analgesia and anxiolysis is enough for a quick procedure
10) B) IV ketamine provides needed sedation & analgesia for a painful procedure. Less resp depression than propofol alone
-
-
-
-
8/ C) IV propofol. MRIs can be a long study. No analgesia needed
9/ A) Simple analgesia and anxiolysis is enough for a quick procedure
10) B) IV ketamine provides needed sedation & analgesia for a painful procedure. Less resp depression than propofol alone
#MorningReport #TeachingSenior #sedation #analgesia #GenPeds #benzodiazepine #opiates #opioids #PEM #PICU #anesthesia
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh



