Management of iron overload for #phodocs to pay attention to. Talk by Dr. Lalefar from @UCSFBenioffOAK. Follow this thread 1/n 

Who should be monitored for iron overload? Those that have a transfused volume >100 ml/kg (~10 transfusions) #ASPHO2021 2/n
Dr. Lalefar suggests checking ferritin, but remember to check with other iron studies. She says a serum ferritin >1000 ug/L is the common threshold used. (But this was based on correlation studies with liver iron from mostly Caucasian hemochromatosis patients) 3/n
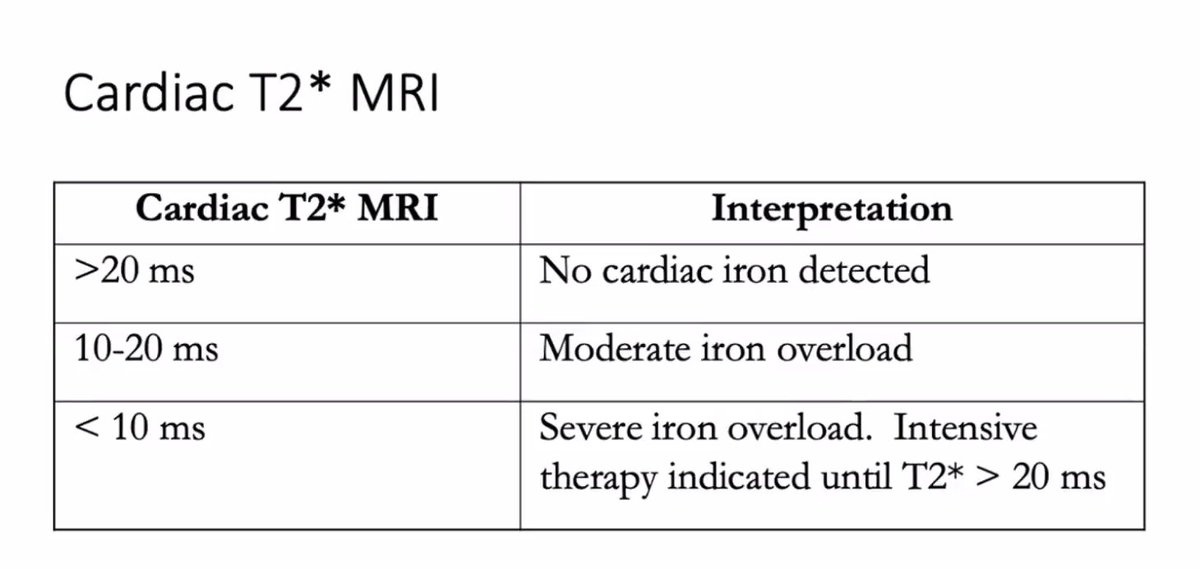
You can also use T2* MRI -- normal values are 0.48-2.8 mg/gm dry liver weight and values of >7 mg/gm are associated with severe iron overload. Of note, has been validated for testing of iron in the heart. (See next) 4/n
Value less than 10 ms on cardiac T2* really require intensive therapy to prevent life threatening arrhythmias and more. 5/n 
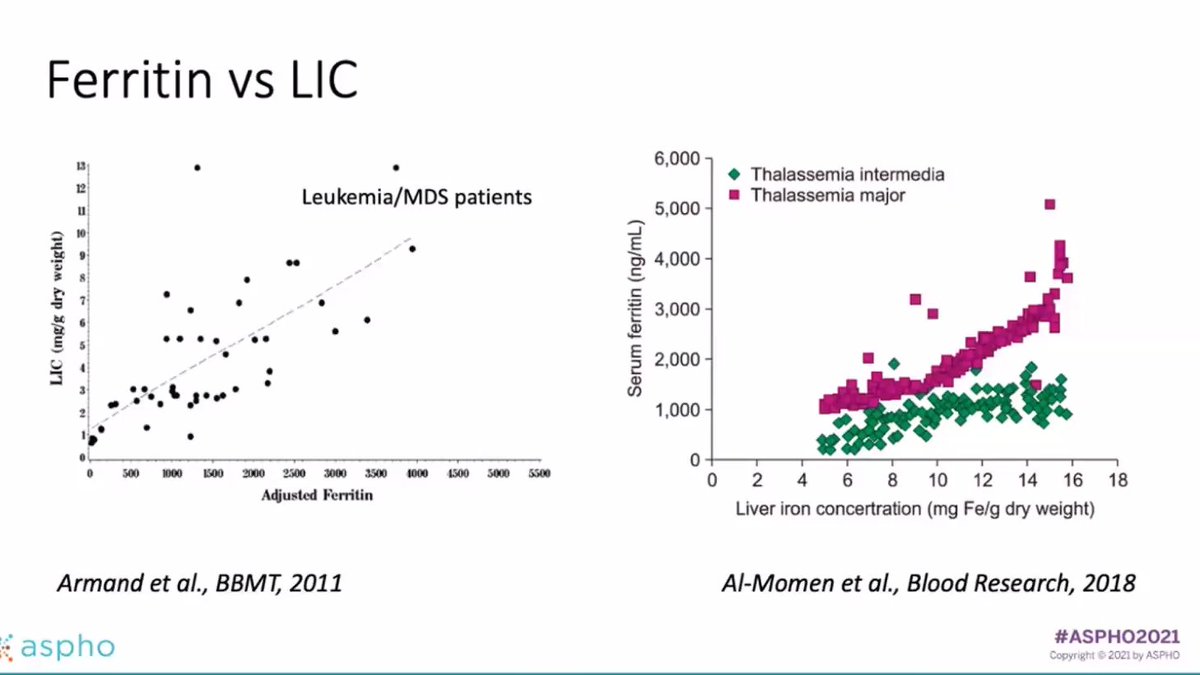
But some of these options are difficult to use (SQUID, T2*, liver biopsy) so people would want to see if a ferritin and LIC have a correlation. This study by Armand et al for leukemia/MDS was hard to draw conclusions based on lower numbers. 6/n 
What modalities do people use for treatments? Based on a survey study from 2017 - ppl said they used oral chelation +/- phlebotomy for iron overload in BMT/peds onc patients. Phlebotomy is done if Hgb >11 where you take 5 ml/kg with replacement of fluids. 7/n
Dr. Lalefar says when you do phlebotomy, check LIC every 6-12 months (CBC with each session). Oral iron chelation options include deferasirox (once daily dosing - start 3.5 mg/kg/day and can increase to 7 mg/kg/day - monitor for GI AE, transaminitis, renal tox). 8/n
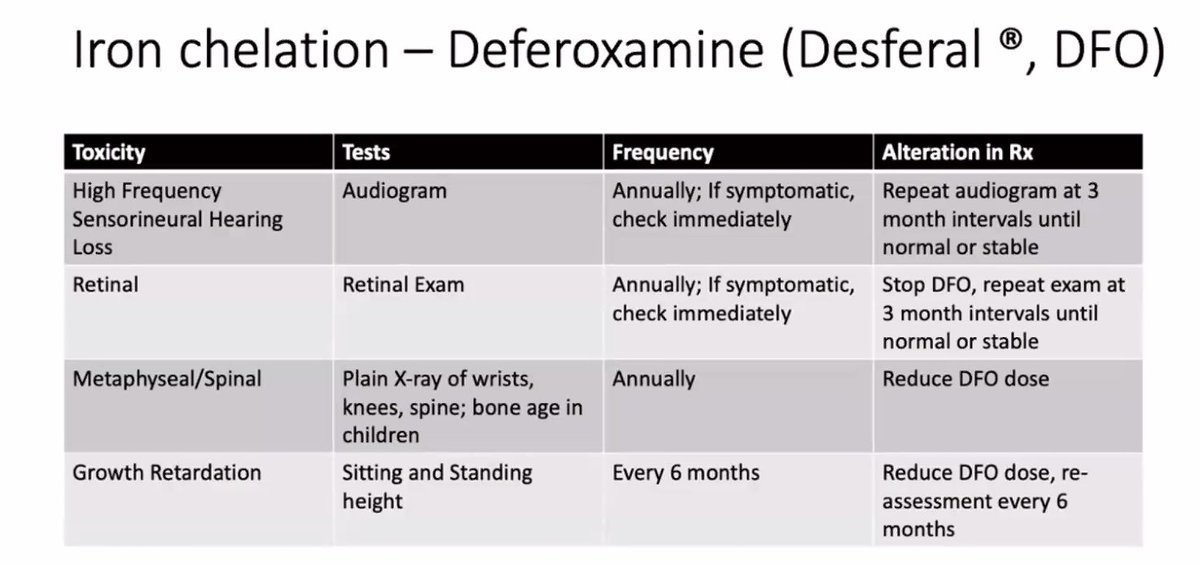
Another option is deferoxamine (subcut or IV infusion - start at 20 mg/kg over 8 hours 3 nights/week) - Toxicities attached here and how to monitor for these things. 9/n 
Is one better than the other? (phlebotomy vs oral chelation for those that are transfusional iron overloaded but no longer are getting transfusions) -- Inati (PBC 2016) said deferasirox had increased benefit in decreasing liver iron -- although you have to consider safety. 10/n
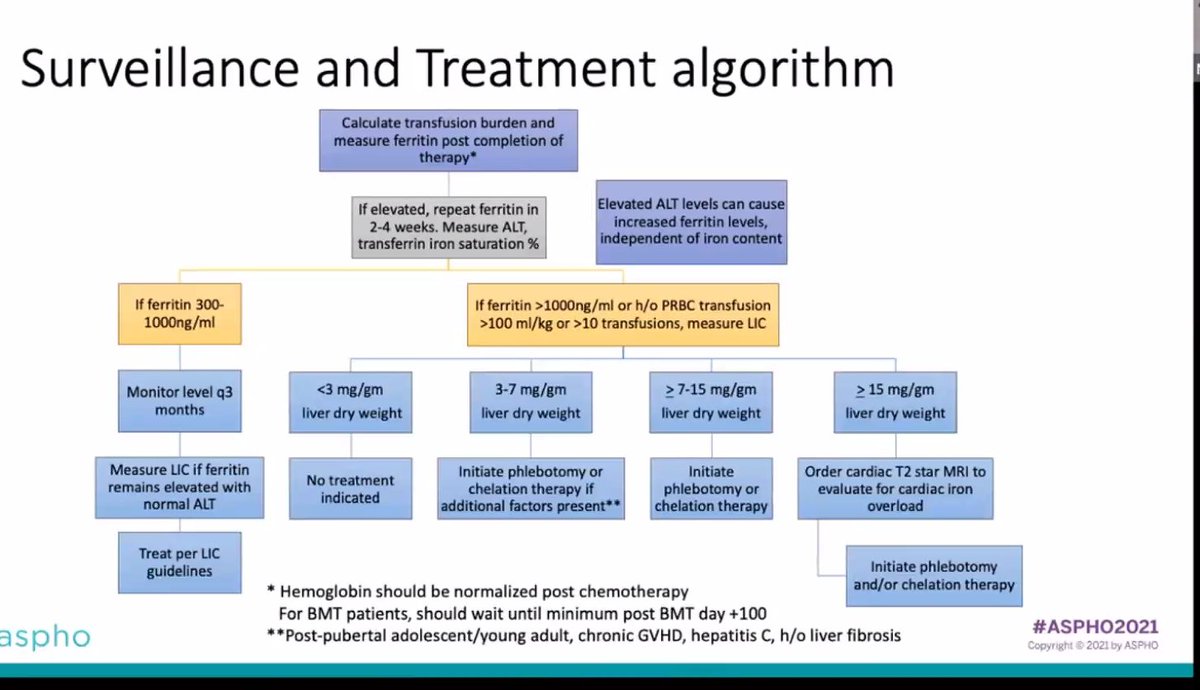
Dr. Lalefar uses this surveillance and treatment algorithm - depending on LIC (liver iron concentration), decides on chelation strategies. #ASPHO2021 11/11 (end!) 
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh