Just out @NatureMedicine: Inhibition of HIF-2 alpha in RCC with belzutfian (MK-6482) - phase 1 trial and biomarker analysis- 1st study to report on the 2nd gen. HIF-2 inhibitors in pts with metastatic ccRCC!! @OncoAlert
A THREAD!
nature.com/articles/s4159…

A THREAD!
nature.com/articles/s4159…


1/The HIF2 axis biology is fascinating culminating in a 2019 @nobel prize, including our own @DanaFarber @kaelin_lab 





2/In this study: 95 patients were enrolled (dose-escalation cohort: n=43 and dose-expansion cohort: n=52). Among these, 55 had advanced ccRCC, with a median age of 62 years, a median of 3 previous systemic therapies, and 76% (n=42) with intermediate/poor @IMDConline risk groups.
3/ In the PK and PD analyses, exposure to belzutifan was shown to increase with dose. Importantly, the AUC increased over the dose range of 20-120mg, but remained stable in the 120-240mg range. 

4/ Reductions in plasma EPO were recorded at all doses, with a significant correlation between plasma EPO and belzutifan concentrations, and similar decreases in EPO levels for doses > 120mg 

5/ Maximum tolerated dose was not reached. No dose-limiting toxicities were observed at doses up to 160mg QD, and occurred in 1/7 patients at 240mg QD and 1/6 patients at 120mg BID. Based on safety, PK and PD in the dose-escalation cohort, 120mg QD was selected as the R2PD.
6/ Most common all-grade AEs were anemia (76%), fatigue (71%), dyspnea (49%) and nausea (36%). Most common grade 3/4 AEs were anemia (27%) and hypoxia (16%).
7/ Hypoxia is on-target toxicity. See outstanding paper by another @NobelPrize laureate Sir P. Ratcliffe showing HIF2 inh. rapidly impair ventilatory responses to hypoxia, abrogating ventilatory acclimatization & carotid body cell proliferative responses. bit.ly/3xa3hS6 

8/ In patients with ccRCC, ORR was 25%, and 30 patients (54%) reached SD, providing a disease control rate of 80%. In patients with favorable and int/poor IMDC risk groups, ORR was 31 and 24%, respectively. Median PFS was 14.5 month (still, be careful with single arm PFS!). 





9/In conclusion, HIF-2 inhibitor belzutifan (MK-6482) displayed a favorable safety profile and efficacy in heavily pre-treated ccRCC pts!! This study paves the way for novel therapeutic options in pts with RCC.
10/ Several ongoing randomized trials with Belzutifan:
•Belzu vs. everolimus: clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04… (refractory)
•Belzu+Lenvatinib vs. cabozantinib: clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04… (refractory)
•Pembro+Len +/-CTLA-4 inh or Belzu (3-arm): clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04… (1st line)
•Belzu vs. everolimus: clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04… (refractory)
•Belzu+Lenvatinib vs. cabozantinib: clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04… (refractory)
•Pembro+Len +/-CTLA-4 inh or Belzu (3-arm): clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04… (1st line)
11/ From bench to bedside, the story of HIF-2 inhibitors in #kidneycancer is truly fascinating, with still a lot more to unravel! One of the best laboratory work comes from these 2 simultaneous @nature papers from @brugarolas and @Kaelinlab showing in-vivo activity of HIF2 inh. 

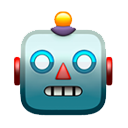
12/ Left: work from @JBrugarolas group @UTSWNews: PET/CT images of mice with subcut. tumorgrafts treated with vehicle or HIF2 in. Kudos to our friend @JBrugarolas also being heavily involved in HIF2 inh! 

13/ Right: @kaelin_lab also showed that mice treated with PT2399 resulted in marked tumor regression. Introducing HIF2a S304M into 2A cells (cells that are 786-metastatic variant) conferred partial resistance to the HIF2 inhibitor. 

14/Shameless plug for the review authored with Bill here in @NatureMedicine few months ago. We probably need an update now...😅: nature.com/articles/s4159… 





15/Thank you to all site PIs, study staff & nurses. Most importantly our patients. They are our daily inspiration and heroes! Team effort w/ many close colleagues/friends @df_hcc & outside: @EJonasch @ERPlimackMD @LenAppleman @Todd_M_Bauer @Twitter-less rest & @Merck team. Fin!
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh