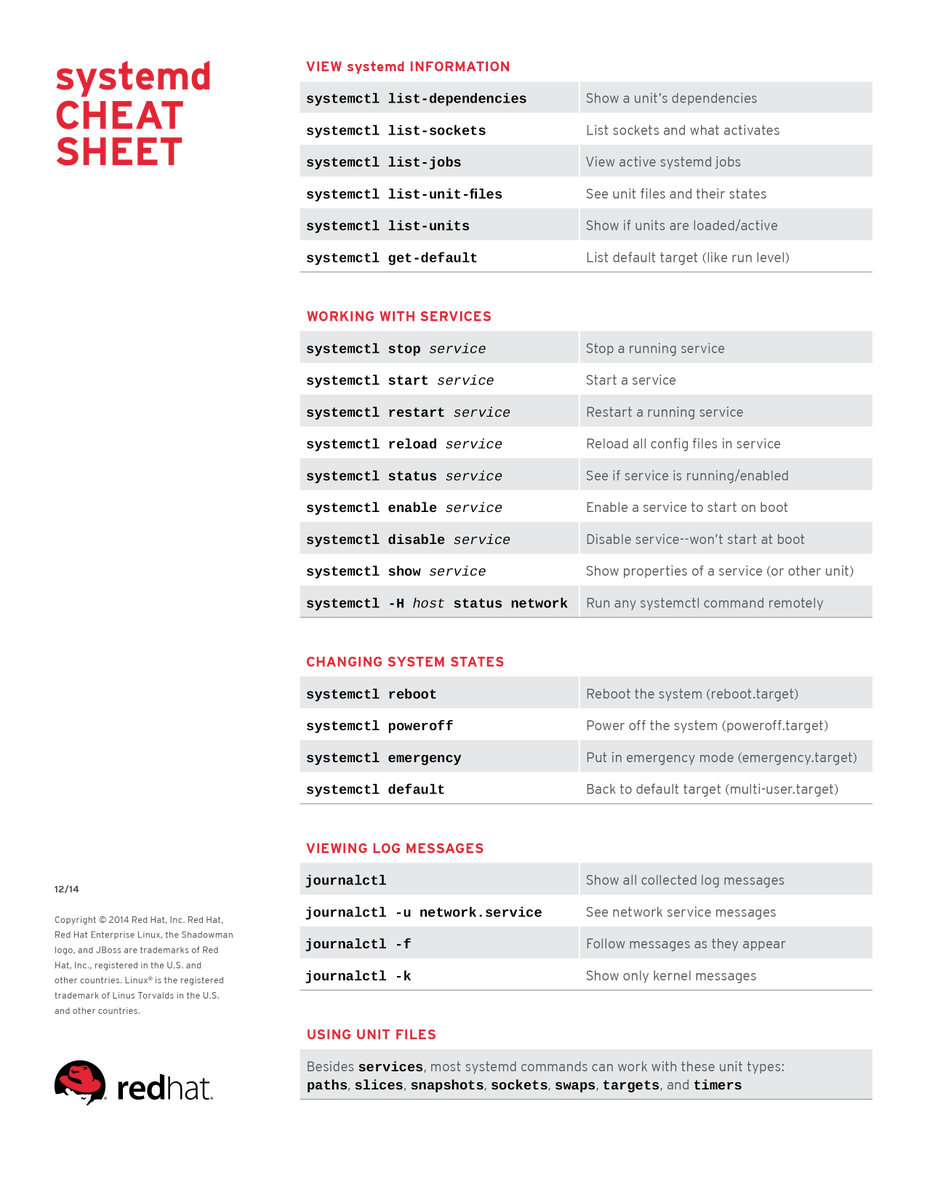
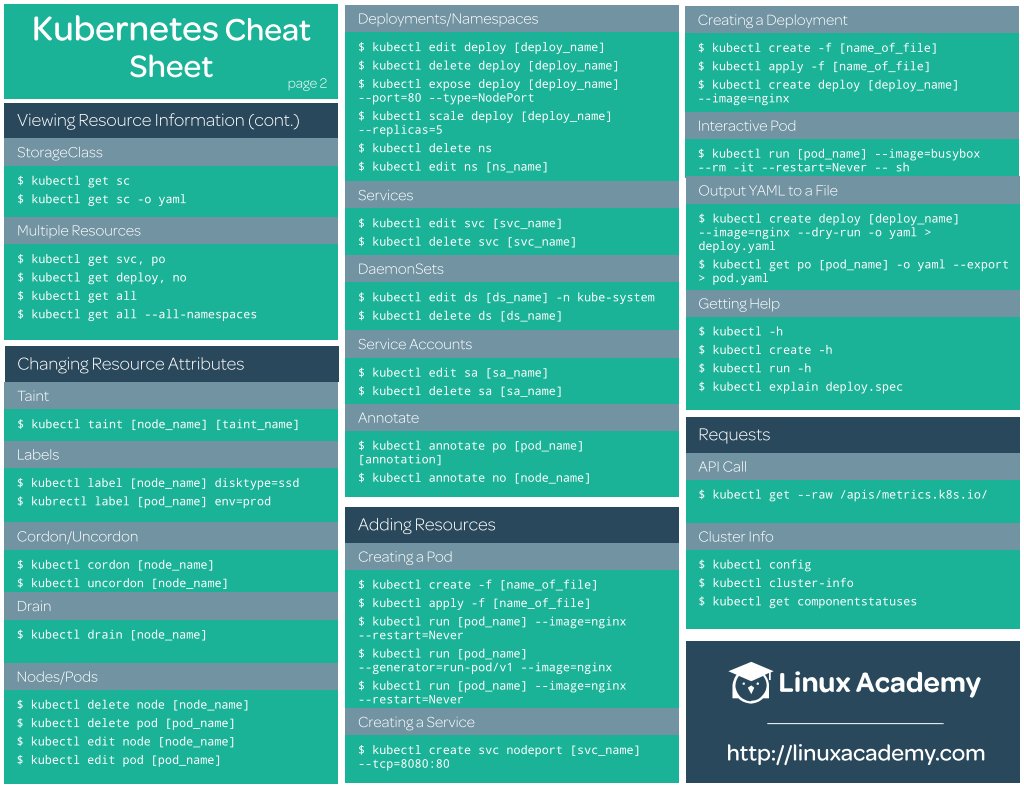
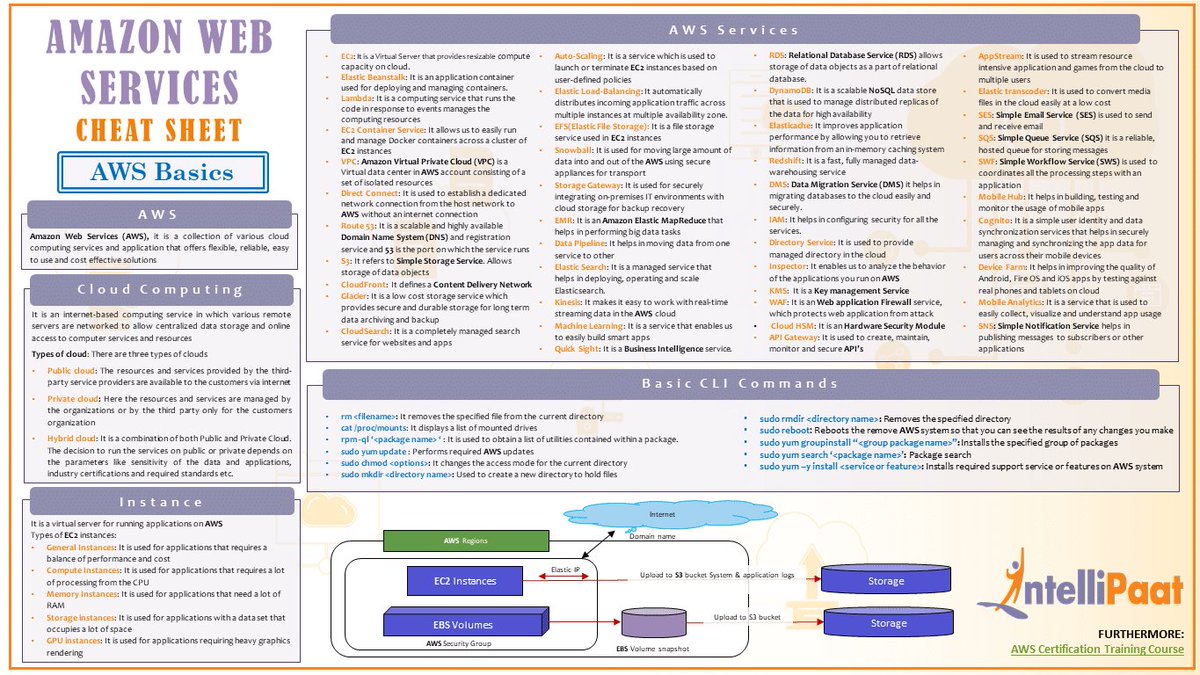
Collection of Cheat Sheets:
Linux Commands, Networking Tools, Hacking Tools, Docker, Kubernetes, AWS etc.
#Linux #infosec #DevOps #cheatsheet
A Thread. (Will continue to add more)
Linux Commands, Networking Tools, Hacking Tools, Docker, Kubernetes, AWS etc.
#Linux #infosec #DevOps #cheatsheet
A Thread. (Will continue to add more)
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh