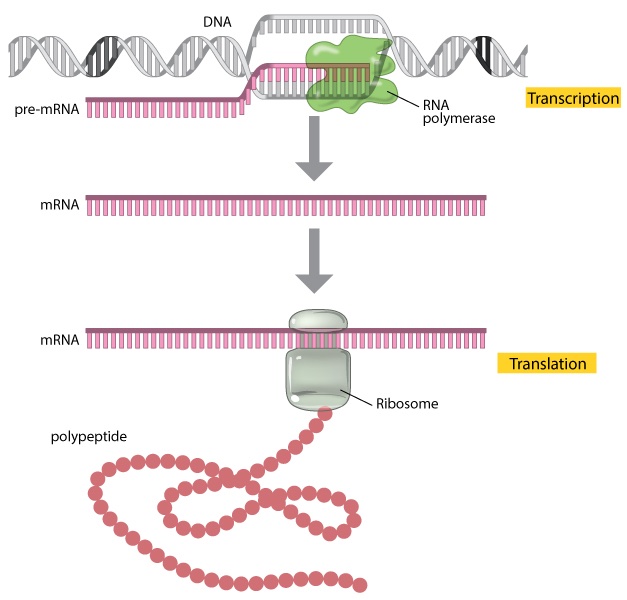
1/ The Vax$ contains the RNA (encapsulated in liposome) to make one of the spikes found on the outside of the coronavirus. When injected, it is absorbed into a cell and makes one of those spikes on the outside of whatever cell it went in to.
#VaccineMandate #VaccinePassport
#VaccineMandate #VaccinePassport
2/
The RNA shot was supposed to stay in the arm muscle, making those spikes on the outside of muscle fibres, but instead most of it got flushed into the blood and spread around the body.
#VaccineMandate #VaccinePassport
The RNA shot was supposed to stay in the arm muscle, making those spikes on the outside of muscle fibres, but instead most of it got flushed into the blood and spread around the body.
#VaccineMandate #VaccinePassport

3/
The place where blood slows down the most is in the capillaries & this is where the RNA has mostly been absorbed & those are the cells that started growing those little spikes.
Problem is those capillaries are supposed to be nice and smooth.
#VaccineMandate #VaccinePassport
The place where blood slows down the most is in the capillaries & this is where the RNA has mostly been absorbed & those are the cells that started growing those little spikes.
Problem is those capillaries are supposed to be nice and smooth.
#VaccineMandate #VaccinePassport

4/ But those capillaries are now rough with all the spikes. The body sees this and thinks its damaged, so tries to fix the damage by making blood clots. These tiny, microscopic bloodclots are now travelling around in your bloodstream.
#VaccineMandate #VaccinePassport
#VaccineMandate #VaccinePassport

5/
Travelling around the blood, these clots start blocking other capillaries, mainly in the brain, lungs, heart, kidneys and reproductive organs. Its looking increasingly like the blood clotting doesn't stop even months after taking the #vaccine.
#VaccineMandate #VaccinePassport
Travelling around the blood, these clots start blocking other capillaries, mainly in the brain, lungs, heart, kidneys and reproductive organs. Its looking increasingly like the blood clotting doesn't stop even months after taking the #vaccine.
#VaccineMandate #VaccinePassport

Although our bodies keeps making these clots, thankfully this can detected with a standard blood test called D-Dimer. If you took the shot, you are 65% likely to be producing clots continuously. Some of them are what doctors call “micro-clots” and are benign. Measure IL-6 & CRP. 



Now this thrombotic processes are complex, and deep in biochemistry. What makes it even more complex is there are around 1206 genetic SNPs associated with DVT
jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/…
This coupled with any co-existing lipid disorders makes the statistical variance high.
jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/…
This coupled with any co-existing lipid disorders makes the statistical variance high.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh