
Thread on Drug Development process 🧵
Hit like & Retweet for more learnings ! 💊🧪🩺💉
@unseenvalue
Topics Covered :
1.Introduction to CRO,CDMO,CMO & CRAMS
2.Discovery
3.Clinical Trials
4.Commercialization and Surveillance
5.Success Rates
6.CRO
7.CMO
8.CDMO
9.CRAMS
Hit like & Retweet for more learnings ! 💊🧪🩺💉
@unseenvalue
Topics Covered :
1.Introduction to CRO,CDMO,CMO & CRAMS
2.Discovery
3.Clinical Trials
4.Commercialization and Surveillance
5.Success Rates
6.CRO
7.CMO
8.CDMO
9.CRAMS
1. Introduction :
What are CROs, CDMOs, CMOs and CRAMS? How are they different from each other and what value do they add to the Pharma Value Chain? To understand these concepts, we took a look at the drug discovery process.
What are CROs, CDMOs, CMOs and CRAMS? How are they different from each other and what value do they add to the Pharma Value Chain? To understand these concepts, we took a look at the drug discovery process.
The APIs manufactured by our Indian players lie at the end of this value chain. There is a whole process that comes before it that takes a lot more time and costs a lot of money.
On average, it takes about 10 to 15 years for a drug to make it to market. It costs hundreds of millions, if not billions of dollars to bring one drug to market.
A drug goes through 3 big phases on it’s way to make it to market - the discovery phase, clinical testing phase and the commercialization phase. Once we understand these phases, it makes it easy to understand the role of CROs and CDMOs 
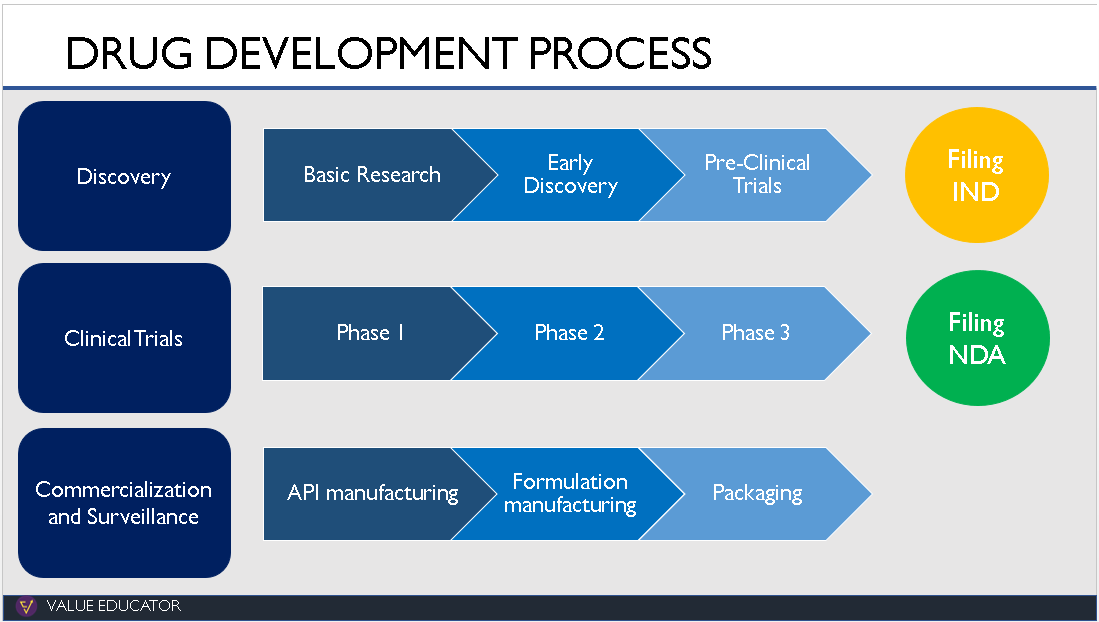
2.Discovery:
The discovery of a new drug starts in the research lab where researchers study hundreds of diseases. They analyse what part of the body a disease affects and what reaction the body has to these diseases.
The discovery of a new drug starts in the research lab where researchers study hundreds of diseases. They analyse what part of the body a disease affects and what reaction the body has to these diseases.
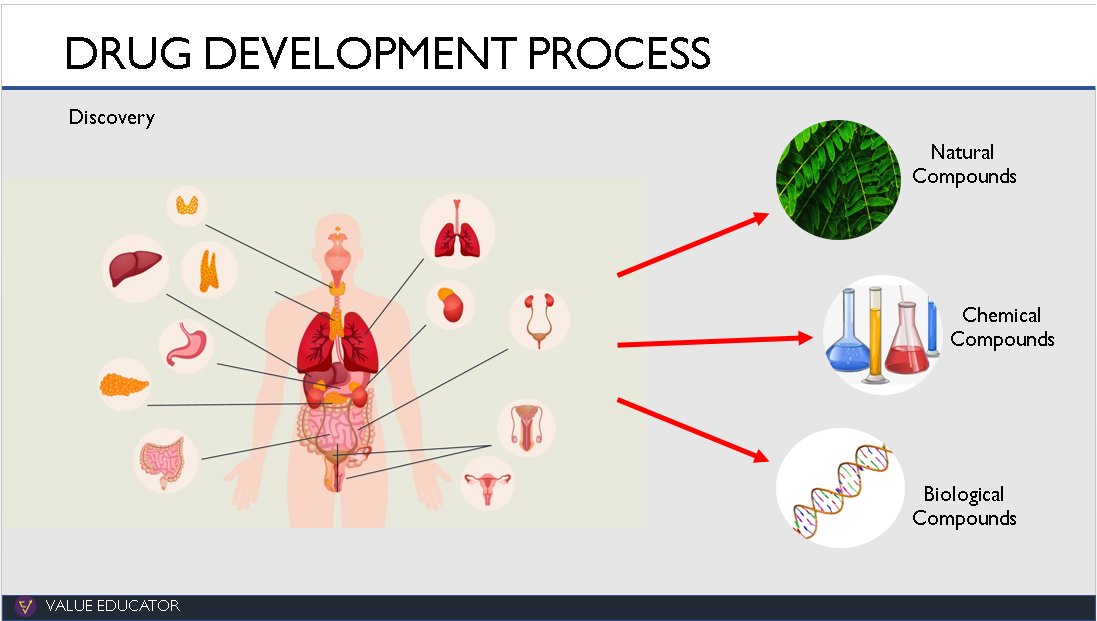
Once all the causes for the disease have been identified, they investigate what could stop the spread of the disease, what could reduce its effects and what could reverse its effects.
They examine thousands of compounds like natural compounds, synthetic compounds and even bio-engineered compounds that could help with curing or preventing a disease.
The process of narrowing down these compounds is very long. They test these compounds on cell cultures and animals and collect vast amounts of data on how these compounds react. They then narrow these options down to one compound which has the best chance of success to
make the drug out of. This process can take upto 6 years.
Once all this data has been collected, they file an Investigational New Drug (IND) Application with the US FDA. The US FDA reviews the IND within 6 months of filing. Once the IND is approved,
Once all this data has been collected, they file an Investigational New Drug (IND) Application with the US FDA. The US FDA reviews the IND within 6 months of filing. Once the IND is approved,
they have permission to test this drug on human volunteers.
3. Clinical Trials:
The drug now moves to the Clinical Trials phase. It will be the first time a novel drug will be given to human beings. The clinical trials itself take place in 3 phases.
3. Clinical Trials:
The drug now moves to the Clinical Trials phase. It will be the first time a novel drug will be given to human beings. The clinical trials itself take place in 3 phases.
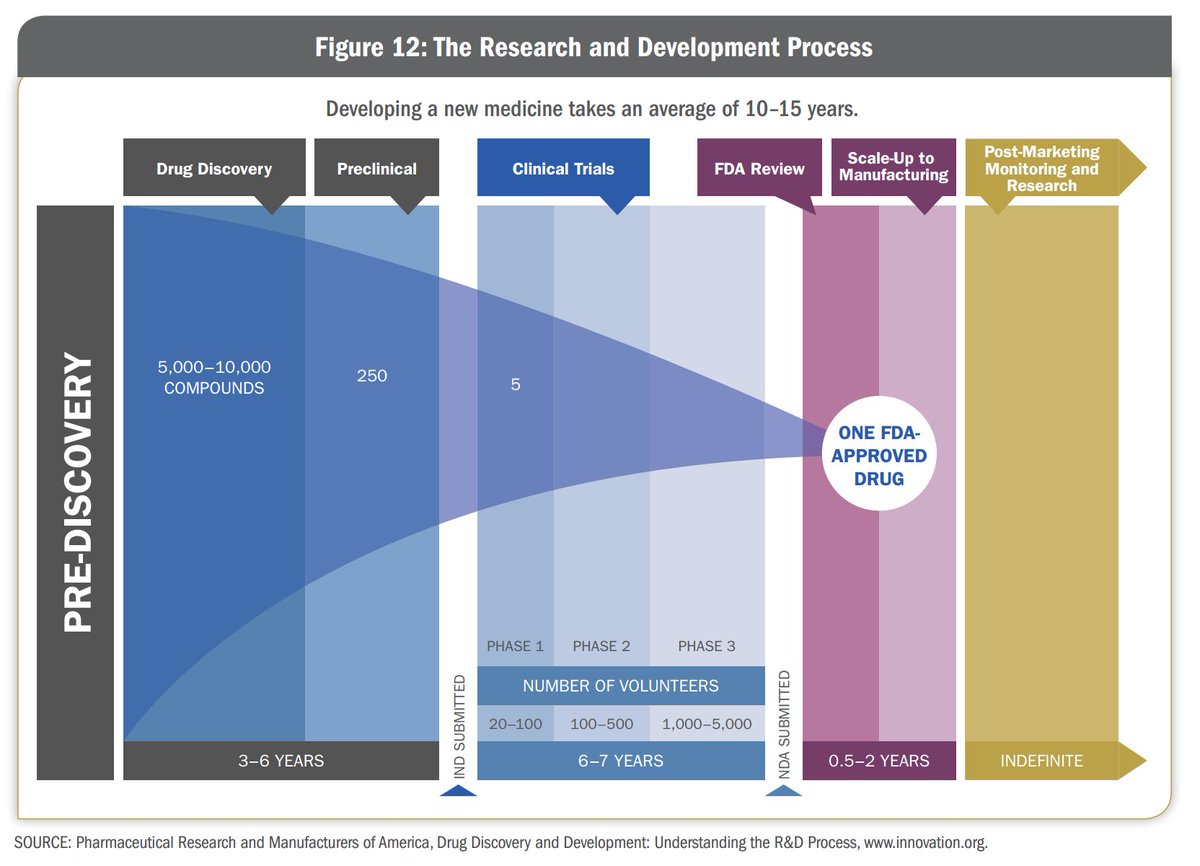
In Phase 1, the focus is on safety. In Phase 2, they focus on the effectiveness of the drug and dosing. Phase 3 testing is the largest and is done to make sure that the drug is safe and effective for a wide variety of people. The clinical trial phase can last for 6-7 years.
In Phase 1 -the drug is given to 20-100 HEALTHY(not suffering from the disease) volunteers. This is done to test if the drug is safe for human beings to consume and does not cause any adverse reaction in the body.
In Phase 2, the drug is given to a larger group of patients (several 100) suffering from the disease and is undertaken to test if the drug is actually effective on the disease. The safety tests are also continued from Phase 1 to see if the drug has any adverse side effects.
In Phase 3, the drug is tested on 300-3000 volunteers who are suffering from the disease. The drug is given to people of different genders, age groups, ethnicities to determine if it is effective for a major portion of the population.
Once the Phase 3 trials are completed, the company files an NDA - New Drug Application. The NDA contains the data from all the clinical trials for the FDA to review.
4. Commercialization and Surveillance:
If the FDA approves the NDA, the company can manufacture and market the drugs to the public. But the testing does not end here. The drug now moves into Phase 4 testing.
If the FDA approves the NDA, the company can manufacture and market the drugs to the public. But the testing does not end here. The drug now moves into Phase 4 testing.
In Phase 4, the drug which is being sold to the public is continuously monitored to see if it is having the intended effect on the public and not causing any adverse side effects. If it does have any adverse effects, the drug is recalled.
5. Success Rates:
Approximately 70% of the drugs move from Phase 1 to Phase 2, 33% move from Phase 2 to Phase 3, 25-30% move from Phase 3 to Phase 4. About 70-90% of drugs in Phase 4 are successful in staying in the market.
Approximately 70% of the drugs move from Phase 1 to Phase 2, 33% move from Phase 2 to Phase 3, 25-30% move from Phase 3 to Phase 4. About 70-90% of drugs in Phase 4 are successful in staying in the market.
CRO & CDMO :
So where do the CROs and CDMOs come in? Contract research organizations help with the first 2 phases whereas Contract development and manufacturing organizations help with the last 2 phases
So where do the CROs and CDMOs come in? Contract research organizations help with the first 2 phases whereas Contract development and manufacturing organizations help with the last 2 phases
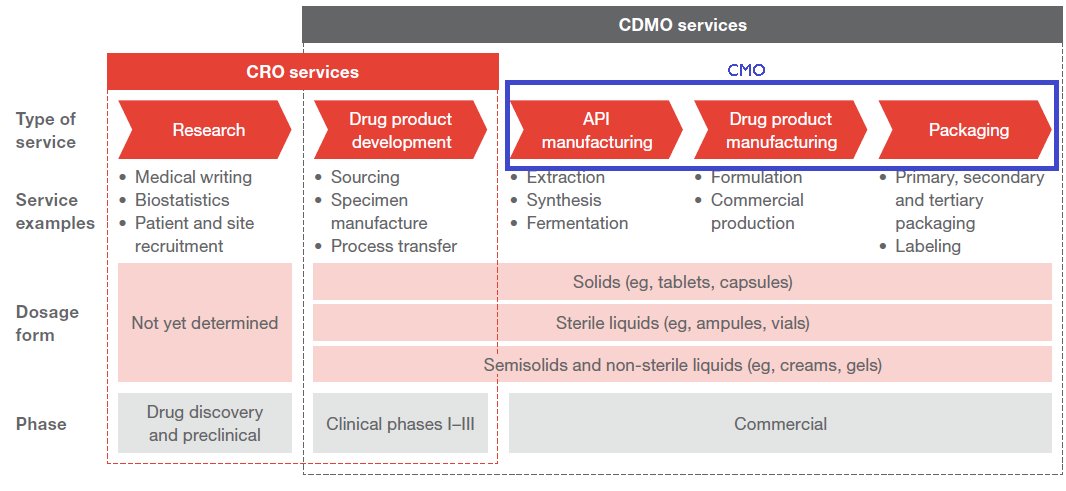
6. CROs
CROs support the innovators by providing services from drug discovery right up to commercialization. They provide services like target discovery, pre clinical trials, management of clinical trials, help with regulatory filings and pharmacovigilance(Phase 4).
CROs support the innovators by providing services from drug discovery right up to commercialization. They provide services like target discovery, pre clinical trials, management of clinical trials, help with regulatory filings and pharmacovigilance(Phase 4).

7. CMOs
Contract manufacturing organizations (CMO) on the other hand provide outsourced manufacturing solutions to the innovator. They are involved with the manufacturing of APIs and Formulations and oftentimes even involved with the final packaging of the product.
Contract manufacturing organizations (CMO) on the other hand provide outsourced manufacturing solutions to the innovator. They are involved with the manufacturing of APIs and Formulations and oftentimes even involved with the final packaging of the product.
8.CDMO
CDMOs are a hybrid between these two. They come in at the clinical trials stage to help with development of the drug, small batch manufacturing for the trials, scaling up the manufacturing process for commercial production, large scale manufacturing and packaging of drugs
CDMOs are a hybrid between these two. They come in at the clinical trials stage to help with development of the drug, small batch manufacturing for the trials, scaling up the manufacturing process for commercial production, large scale manufacturing and packaging of drugs
9. CRAMS
Finally there are players who provide all the above services right from drug discovery to manufacture and packaging. This is known as CRAMS - Contract Research and Manufacturing.
Finally there are players who provide all the above services right from drug discovery to manufacture and packaging. This is known as CRAMS - Contract Research and Manufacturing.

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh










