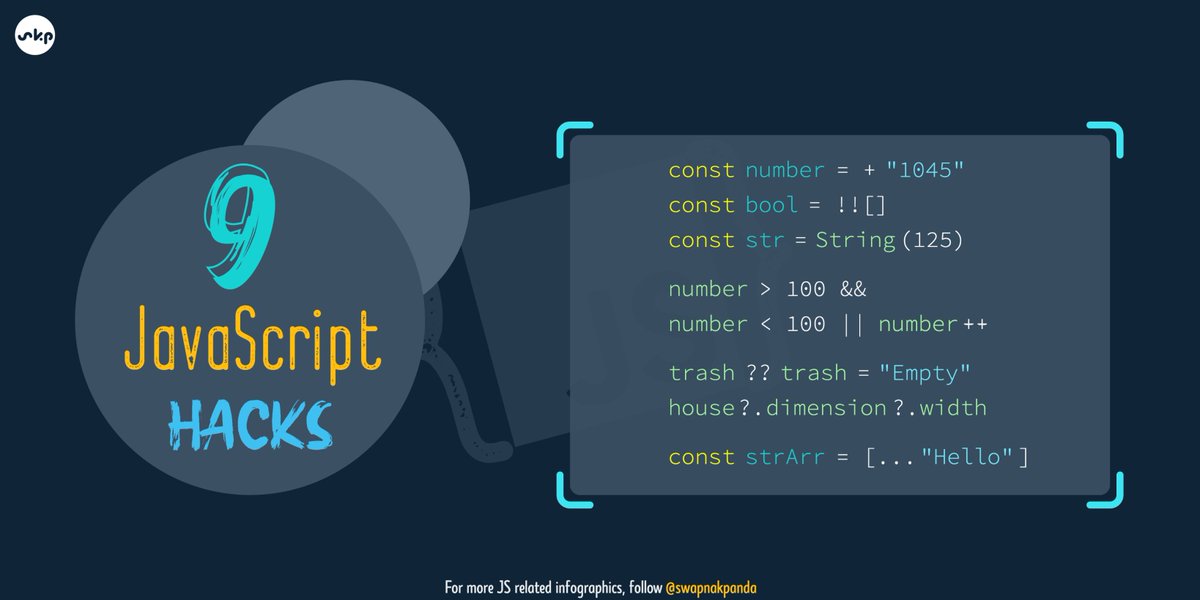
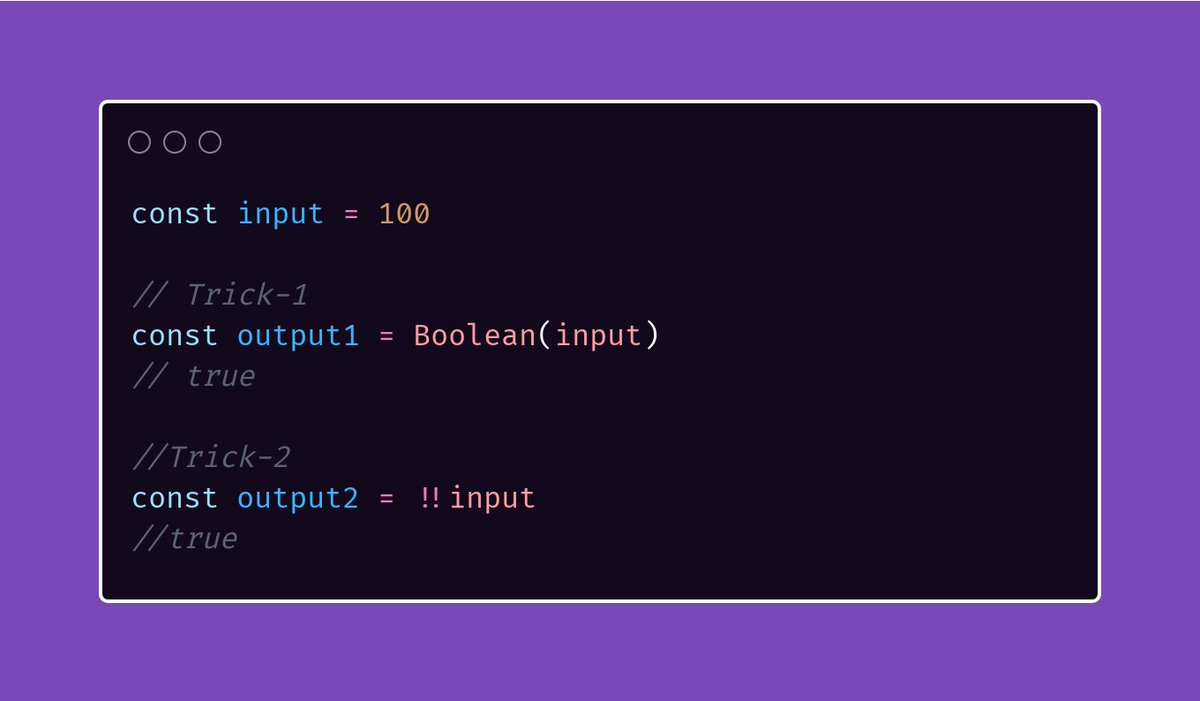
😊 Are you a beginner in programming domain?
😢 Are you getting confused of what approach to take while solving a problem?
🙃 Are you wondering why is DSA so important in Problem Solving?
Let's clear all confusions and master the skill through 1️⃣0️⃣ super simple steps 😎
🧵 👇
😢 Are you getting confused of what approach to take while solving a problem?
🙃 Are you wondering why is DSA so important in Problem Solving?
Let's clear all confusions and master the skill through 1️⃣0️⃣ super simple steps 😎
🧵 👇
1️⃣ Read-Realise-Write-Run-Reshape
Yes. I say it often when someone asks me how to approach during solving a problem.
Let's see what are these.
Yes. I say it often when someone asks me how to approach during solving a problem.
Let's see what are these.
1️⃣.1️⃣ Read & Realise
These 2 actions are so close to each other that we can hardly keep apart.
Do like this.
1. When you try to solve a problem, first "Read" it properly once.
2. Then, "Realise" what it is asking to solve.
++
These 2 actions are so close to each other that we can hardly keep apart.
Do like this.
1. When you try to solve a problem, first "Read" it properly once.
2. Then, "Realise" what it is asking to solve.
++
3. For a bigger or, complex problem, try to divide it into smaller problems. And connect between these smaller problems.
4. Repeat all above steps until you realise and are full confident of what the problem is asking.
4. Repeat all above steps until you realise and are full confident of what the problem is asking.
1️⃣.2️⃣ Write
When we say "Write", it covers both the design and, code.
Design: During design, we take a problem and try to map between real-world things to programming-world things. The output of design could be a "pseudo code".
++
When we say "Write", it covers both the design and, code.
Design: During design, we take a problem and try to map between real-world things to programming-world things. The output of design could be a "pseudo code".
++
Code: Now, it's time to give life to our pseudo code. Go and write a program in your favourite language.
During this step, you should already be familiar with the syntaxes of a programming language. If not, first do that.
During this step, you should already be familiar with the syntaxes of a programming language. If not, first do that.
1️⃣.3️⃣ Run
Before running your program, first list all boundary conditions.
But, what is a boundary condition?
Let's learn it through this example. "Mina decides to sell her old house if someone bids it for 1M"
++
Before running your program, first list all boundary conditions.
But, what is a boundary condition?
Let's learn it through this example. "Mina decides to sell her old house if someone bids it for 1M"
++
Here boundary condition is "bids for 1M". This condition affects the result.
Perform below steps 👇
1. List all boundary conditions.
2. Define the Input and Output for each boundary condition.
++
Perform below steps 👇
1. List all boundary conditions.
2. Define the Input and Output for each boundary condition.
++
3. Combine some or, all boundary conditions and, redefine the Input and Output.
4. Run the program for each input. Verify the actual output with the expected output.
5. Find for which all cases the output is not as expected. We mention it as a "Failed Use case".
4. Run the program for each input. Verify the actual output with the expected output.
5. Find for which all cases the output is not as expected. We mention it as a "Failed Use case".
1️⃣.4️⃣ Reshape
1. Has your program failed for some use cases?
2. Is your program taking longer than expected time for some inputs?
You should come back and, reshape the old program. Inspect the problem. Modify the code and, do an impact analysis (impact on successful use cases)
1. Has your program failed for some use cases?
2. Is your program taking longer than expected time for some inputs?
You should come back and, reshape the old program. Inspect the problem. Modify the code and, do an impact analysis (impact on successful use cases)
In following tweets, we will go through various design steps.
While designing a solution, we have to consider all these and come up with a pseudo code.
While designing a solution, we have to consider all these and come up with a pseudo code.
2️⃣ Value & Variable
Let's learn from example.
The stock price now is $1.45
Here,
"Stock Price" is a variable because it is not constant.
"1.45" is a value.
We write in pseudo code,
StockPrice = 1.45
Let's learn from example.
The stock price now is $1.45
Here,
"Stock Price" is a variable because it is not constant.
"1.45" is a value.
We write in pseudo code,
StockPrice = 1.45
3️⃣ Formula
Formula could be anything. But here I meant it for "Arithmetic Formula".
E.g., For the rate of interest of 5%, find the simple interest for 1 year.
For arithmetic formula, you should be knowing arithmetic operations like +, -, *, /, % and, their precedences.
Formula could be anything. But here I meant it for "Arithmetic Formula".
E.g., For the rate of interest of 5%, find the simple interest for 1 year.
For arithmetic formula, you should be knowing arithmetic operations like +, -, *, /, % and, their precedences.
4️⃣ Comparison
We live in a world where comparison is everywhere 😆
Example: Those whose height is more than 167cm are selected.
And we write it as,
Height > 167
Output of a comparison is typically "Yes" or, "No". Or, more programmatically "True" or, "False".
We live in a world where comparison is everywhere 😆
Example: Those whose height is more than 167cm are selected.
And we write it as,
Height > 167
Output of a comparison is typically "Yes" or, "No". Or, more programmatically "True" or, "False".
5️⃣ Condition
In above example height is compared with a value. And, the whole expression is a condition.
Multiple conditions can be combined.
E.g., Those "who are boys" and have "height more than 167cm" are selected.
2 conditions are "who are boys", "height more than 167cm".
In above example height is compared with a value. And, the whole expression is a condition.
Multiple conditions can be combined.
E.g., Those "who are boys" and have "height more than 167cm" are selected.
2 conditions are "who are boys", "height more than 167cm".
Issue is how should conditions be combined?
Let's see.
AND: Combine conditions using AND (or, && in programming), when "all conditions" should be "True"
OR: Combine conditions using OR (or, || in programming), when "at least one condition" should be "True"
Let's see.
AND: Combine conditions using AND (or, && in programming), when "all conditions" should be "True"
OR: Combine conditions using OR (or, || in programming), when "at least one condition" should be "True"
6️⃣ Assign
When you perform some operation, you assign the output to a "Variable" so that this variable can be used further when the value is needed.
Example:
x = a * b
Here we "multiplied 2 numbers" and "assigned" the result of multiplication to a variable "x"
When you perform some operation, you assign the output to a "Variable" so that this variable can be used further when the value is needed.
Example:
x = a * b
Here we "multiplied 2 numbers" and "assigned" the result of multiplication to a variable "x"
7️⃣ Action
He ran for 2 miles. Here action is "ran for 2 miles".
In programming, we write
RunDistance = 2
Action is real-world is synonymous to "Statements in Programs"
He ran for 2 miles. Here action is "ran for 2 miles".
In programming, we write
RunDistance = 2
Action is real-world is synonymous to "Statements in Programs"
8️⃣ Conditional Action
Conditional Action is an action which is executed on certain conditions.
Example: Those whose height is more than 167cm are selected.
Here "Selection" is the action, but it's conditional.
In Programming, we use
1. If
2. If...Else...
3. If...ElseIf...
Conditional Action is an action which is executed on certain conditions.
Example: Those whose height is more than 167cm are selected.
Here "Selection" is the action, but it's conditional.
In Programming, we use
1. If
2. If...Else...
3. If...ElseIf...
9️⃣ Iteration
Example: They all ran in a 4x400m relay race.
Here, 400m race is "repeated" for 4 times.
When, we need to do a task repeatedly, we need to use iteration.
In Programming, we use
1. for
2. while
3. do...while...
The iteration continues till a condition is met.
Example: They all ran in a 4x400m relay race.
Here, 400m race is "repeated" for 4 times.
When, we need to do a task repeatedly, we need to use iteration.
In Programming, we use
1. for
2. while
3. do...while...
The iteration continues till a condition is met.
1️⃣0️⃣ Data Structures
Values are essential and, important in any program. For effective handling of these values, data structures are important.
Example: Array, Set, Stack, Queue, Tree, Graph etc.
In my upcoming DSA series, I will show how to decide a correct data structure.
Values are essential and, important in any program. For effective handling of these values, data structures are important.
Example: Array, Set, Stack, Queue, Tree, Graph etc.
In my upcoming DSA series, I will show how to decide a correct data structure.
I have written this thread keeping in mind that we should be familiar in "approaching to solve a problem" before starting the DSA series.
I hope this thread helps you to reach a satisfactory point where you can confidently design a solution
Share your feedbacks. See you soon 👋
I hope this thread helps you to reach a satisfactory point where you can confidently design a solution
Share your feedbacks. See you soon 👋
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh