It is 16 days since the Russian invasion of Ukraine began. Today I will examine the the importance of the adaptation battle in war, and how it is playing out in Ukraine. (Image - BBC) 

2/24 As always, a shout out to those reporting on the Russian invasion. This includes @KofmanMichael @maxseddon @IAPonomarenko @RALee85 @shashj @DanLamothe @ikhurshudyan @IanPannell @DefenceHQ @TheStudyofWar @siobhan_ogrady
among others. Please follow them.
among others. Please follow them.
3/24 It is impossible for the military to anticipate every eventuality in war. There are too many scenarios to accurately predict wartime events. As such, a key virtue for military organizations in war must be adaptability to unexpected events.
4/24 In his famous essay, The Use and Abuse of Military History, Sir Michael Howard described the problem thus: “It is not surprising that there has often been a high proportion of failures among senior commanders at the beginning of any war.”
5/24 “These unfortunate men may either take too long to adjust themselves to reality…of they may have had their minds so far shaped by a lifetime of pure administration that they have ceased…to be soldiers.” Read it all here: press.armywarcollege.edu/cgi/viewconten…
6/24 As Williamson Murray writes, because war “is interactive, both sides have the potential to adapt to the conflict at every level…thus the problems posed by the battlespace do not remain constant. More often than not they change with startling rapidity.” 

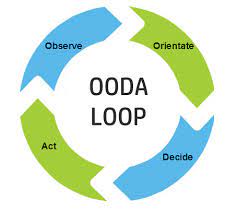
7/24 The exploration of adaptation has resulted in the development of a range of concepts on how adaptation occurs & how it can be applied. In military literature, the best-known adaptive cycle is Boyd’s OODA (observe-orient-decide-act) loop. 
8/24 Frank Hoffman has also proposed a model for military adaptation which he calls Organisational Learning Capacity. It has four parts: leadership; organisational culture; learning mechanisms; and, dissemination mechanisms.
9/24 So, effective military institutions need to adapt in war, at every level, and share lessons broadly to ensure an entire force can learn from both success and failure. Military institutions must win the adaptation battle at the strategic, operational & tactical levels.
10/24 What kind of adaptations have we witnessed in this war so far?
11/24 From the Russians, they had to adapt their campaign within the first 48 hours because their attempt at a lightening conquest of Ukraine failed. This was most obvious in the north and the attempts to capture Kyiv. They had to adapt their campaign to what we are now seeing.
12/24 Further, they have experienced major challenges in the ability to coordinate combined arms warfare on the ground - it has seen them advance much slower, and sustain more casualties, than anticipated. They have therefore adapted to rely more on firepower than maneuver.
13/24 For the Ukrainians, they have clearly recognised that the Russians have poor rear area security. They have adapted their operations to fight the Russians in the rear areas. It is hard for the Russians to advance when they have to constantly look over their shoulders.
14/24 The Ukrainians also appear to have adapted based on the big inflow of western crew served anti-tank and anti-aircraft weapons. This isn’t to say they did not have them previously. But it appears these now have greater emphasis in Ukrainian operations.
15/24 Finally, the Ukrainians have adapted in the info environment. Not only did they seize the initiative at the start of the war, they have learned and evolved in a tactical, operational and strategic influence fight against Russian misinformation. (Image - @IAPonomarenko) 

16/24 There will be many other adaptations on the ground we are not seeing. In due course, we will need to study other military adaptations – from both sides – that will emerge.
17/24 Finally, what military adaptations might we see in the near future in Ukraine?
18/24 The Russians are clearly still attempting to improve their ability to plan and coordinate large scale ground maneuver. We may see them adapt their communications to be more secure, improve logistics, and replace incompetent commanders to improve tactical performance.
19/24 We may see increased Russian operations in the west as they adapt their overall campaign. They will need to halt, or severely restrict the flow of western arms and other aid, into Ukraine. This will force Ukraine to adapt is defensive campaign.
20/24 From the Ukrainians, we may see an #adaptation to their overall scheme of defence where they start focussing more on support to insurgent forces in areas already captured by the Russians. At the same time they will need to sustain conventional operations.
21/24 The Ukrainians are also adapting their tactical force structure to absorb foreign combatants and support personnel. Given training, language and cultural differences, this will be a significant adaptation for them to manage.
22/24 As I note in #WarTransformed, military organizations are never at a steady state. The rapid pace of change means that they will be adapting at each level concurrently and doing so constantly. This adaptation battle is what we are seeing play out now in Ukraine.
23/24 There are other good references on this topic. Here are just three of my favourites – among many – on the topic of military adaptation. 

24/24 Adaptation is a central component of war, and a 'learning culture' is key to institutional adaptation. There will be more adaptations to observe in Ukraine in the days & weeks ahead. I will take a break tomorrow, and return with my daily thread on Monday. End.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh