
Dementia
Acute cognition change with altered consciousness & impaired attention that fluctuates over time. Often unrecognized & unRx. May be preventable & early detec/ facilitates urgent assessment &Rx 1/16
#MedTwitter #MedEd #USMLE #FOAMed #hospitalist #mbbs #medicine #doctor
Acute cognition change with altered consciousness & impaired attention that fluctuates over time. Often unrecognized & unRx. May be preventable & early detec/ facilitates urgent assessment &Rx 1/16
#MedTwitter #MedEd #USMLE #FOAMed #hospitalist #mbbs #medicine #doctor
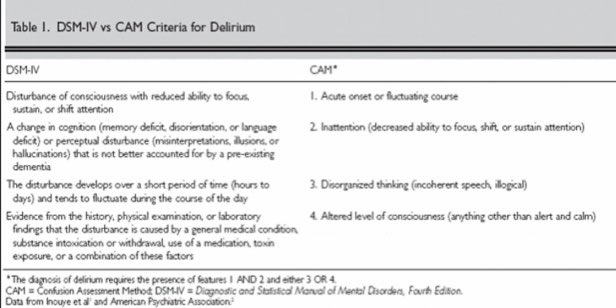
The criteria for delirium listed in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders vs Confusion Assessment Method (CAM) 👇👇. CAM has a sensitivity of 94% to 100% and a specificity of 90% to 95%.
2/16
2/16
Features:
disturbances of sleep, altered psychomotor activity, and changes in emotion (eg, anxiety, apathy, lability, irritability, or anger). Subtypes of delirium are hyperactive, hypoactive & mixed. Hypoactive form >> hyperactive form. Inattention is hallmark. 3/16
disturbances of sleep, altered psychomotor activity, and changes in emotion (eg, anxiety, apathy, lability, irritability, or anger). Subtypes of delirium are hyperactive, hypoactive & mixed. Hypoactive form >> hyperactive form. Inattention is hallmark. 3/16
In contrast to delirium, dementia has a gradual onset with a progressive, irreversible decline in cognitive function over years (Table 2). 4/16 

Delirium is associated with ⬆️ M&M in hospitalized patients, & are at ⬆️risk for falls, pressure ulcers, and pneumonia. Delirium is a predictor of 12-month mortality, independent of dementia status & ⬆️ hospital stays with ⬆️ health care costs (Table 3).
5/16
5/16

Prevalence 10-30% in the hospitalized medically ill & from 10-40% in the hospitalized elderly. Incidence during hospitalization 6-56% among general hospital populations. 15-53% of older patients postoperatively, 70-87% on ventilator patients, & 83% at the end of life.
6/16
6/16
25% of cancer of patients develop delirium. Delirium goes undetected in 33-66%, explained by failure of providers to recognize its s/s & to detect the hypoactive form, fluctuating nature, lack of tools & under-appreciation of the seriousness of diagnosis & its consequences.
7/16
7/16
RF associated with the development of are age >70 y, dementia or other underlying brain disease (eg, cognitive impairment, CVA, or PD), medical illness, OH abuse, & depression. Other RF include hearing & visual impairment, dehydration, immobility, & a history of delirium.
8/16
8/16
Etiology, modifiable or iatrogenic. Meds & drug toxicity account for 20-40%. Other include physical restraints, malnutrition, a bladder catheter, >3 new inpatient meds, & any iatrogenic event (hosp acquired infec, falls, procedural complication, or drug toxicity-Table 4).
9/16
9/16

Table 5 summarizes the independent delirium correlates and the risk of the development of delirium based on the total number of points accrued.
10/16
10/16

Once a high-risk patient has been identified using the clinical prediction rule or based on clinical experience, the MDS team should implement prevention strategies focusing on modifiable RF. Multicomponent intervention strategies prevent delirium in inpatients.
11/16
11/16
Evaluation includes a focused H&P and a search for reversible causes. Hypoglycemia, hypoxia, hyperthermia, hypertensive encephalopathy, thiamine deficiency, withdrawal states, & substance-induced delirium (Table 6) are readily identifiable and treatable disorders.
12/16
12/16

It is critical to review the home and in-hospital medication lists with dosages, especially as-needed and over-the-counter drugs (Table 7). All potentially offending and unnecessary medications should be discontinued if possible.
13/16
13/16

Pharmacologic therapy is indicated to treat the agitated symptoms if the pt is a danger to himself, staff, or others; the s/ would interrupt essential therapy or the s/ do not respond to nonpharmacologic interventions. Antipsychotic meds are the agents of choice.
14/16
14/16

Atypical, 2 gen antipsychotics are commonly used. They have ⬇️ incidence of extrapyramidal side effects vs conventional antipsychotics. All antipsychotic medications should be used with caution & for the shortest duration possible.
15/16
15/16
Benzo’s should not be used to treat, may precipitate confusion, especially in the elderly, & are associated with ⬆️ & worsening of delirium s/. Reserved for use in pts undergoing sedative & OH withdrawal, CI to antipsychotics, or with the neuroleptic malignant synd.
16/16
16/16
@threadreaderapp please “unroll”
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh









