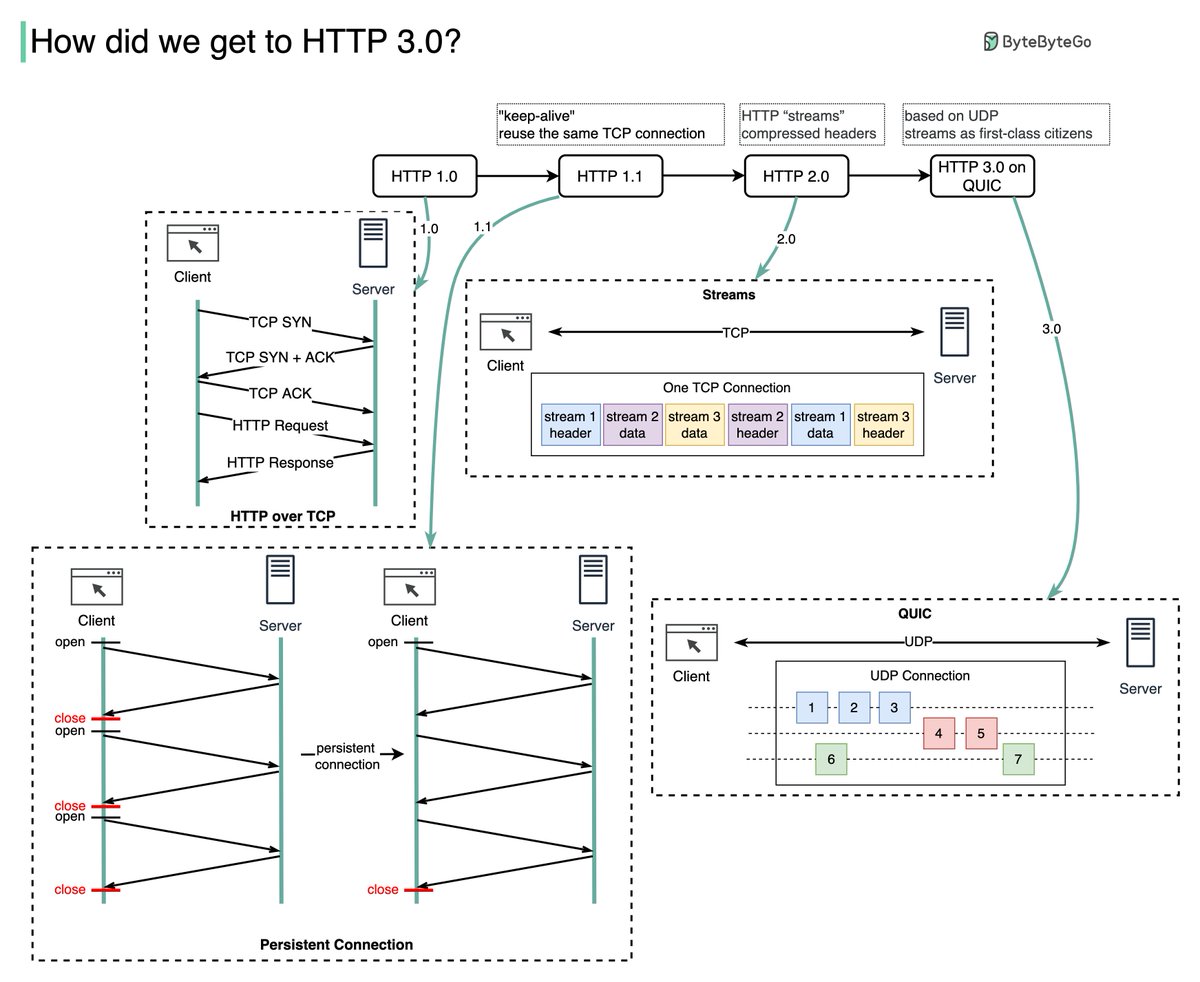
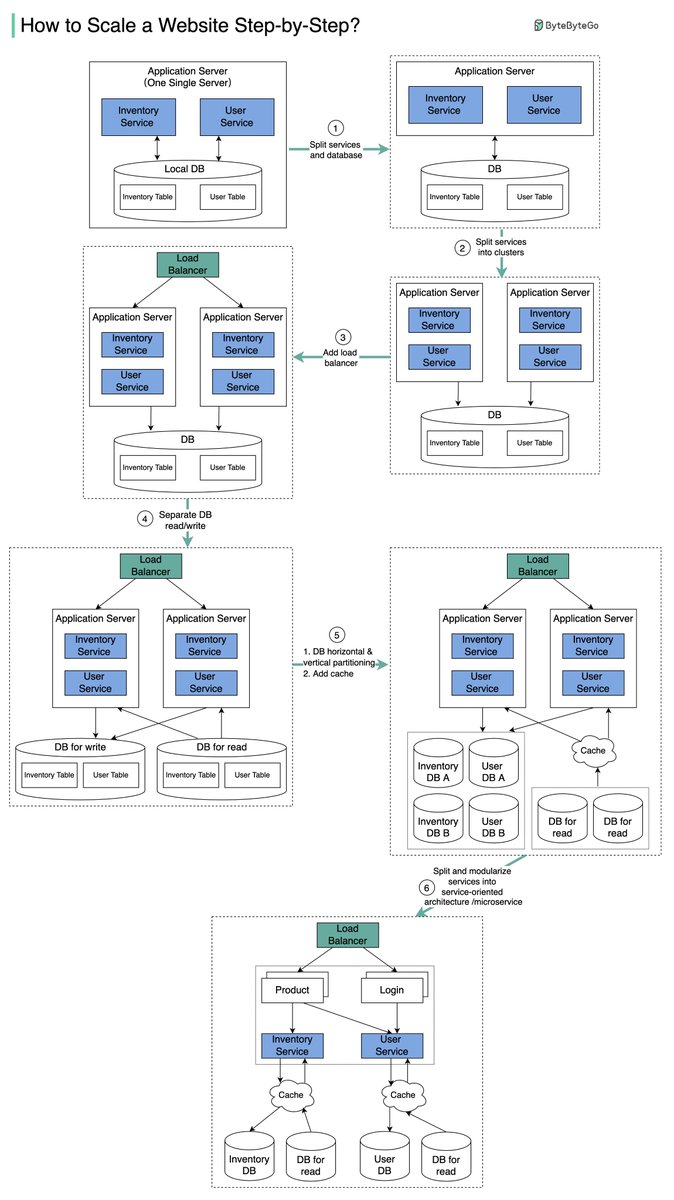
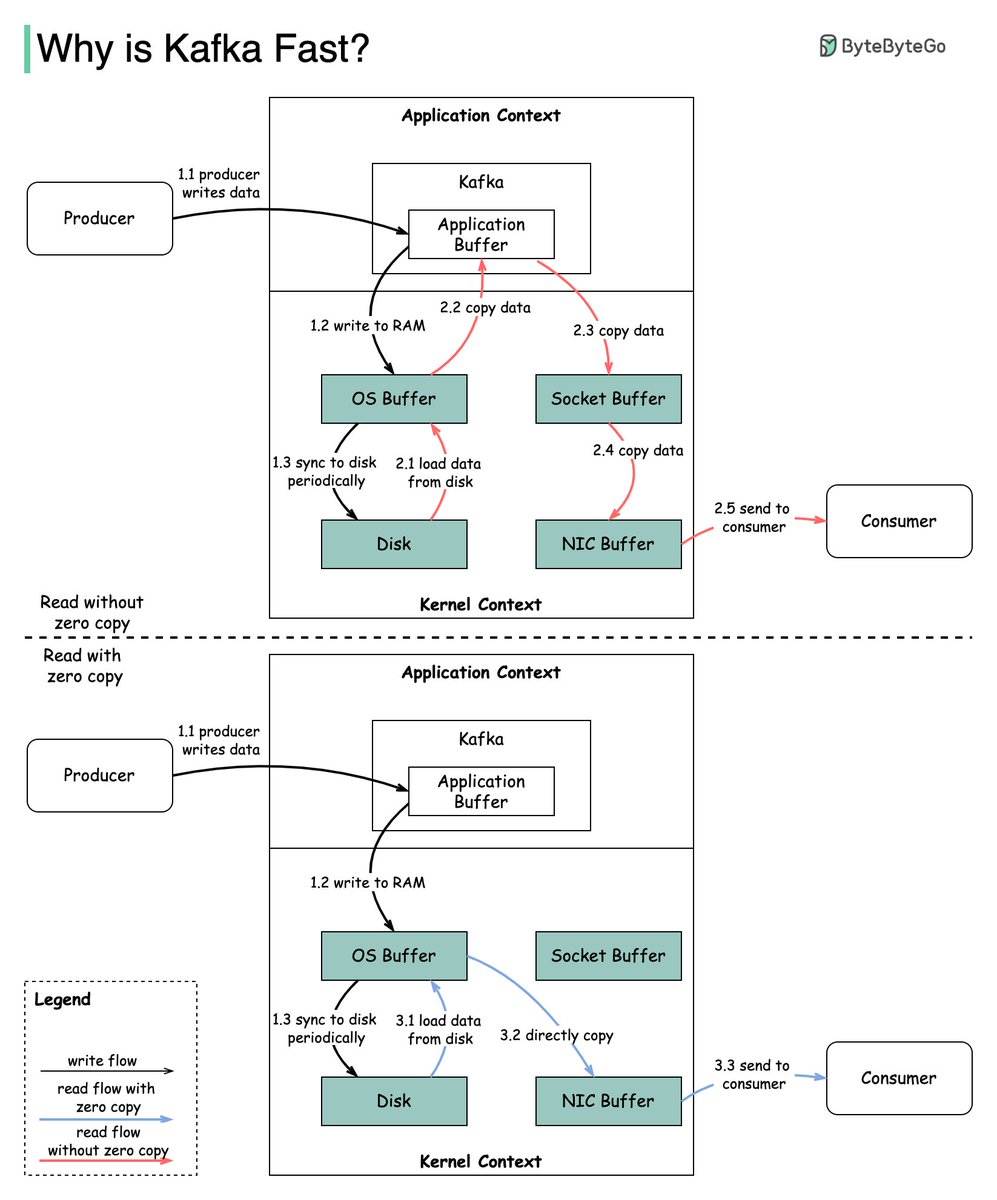
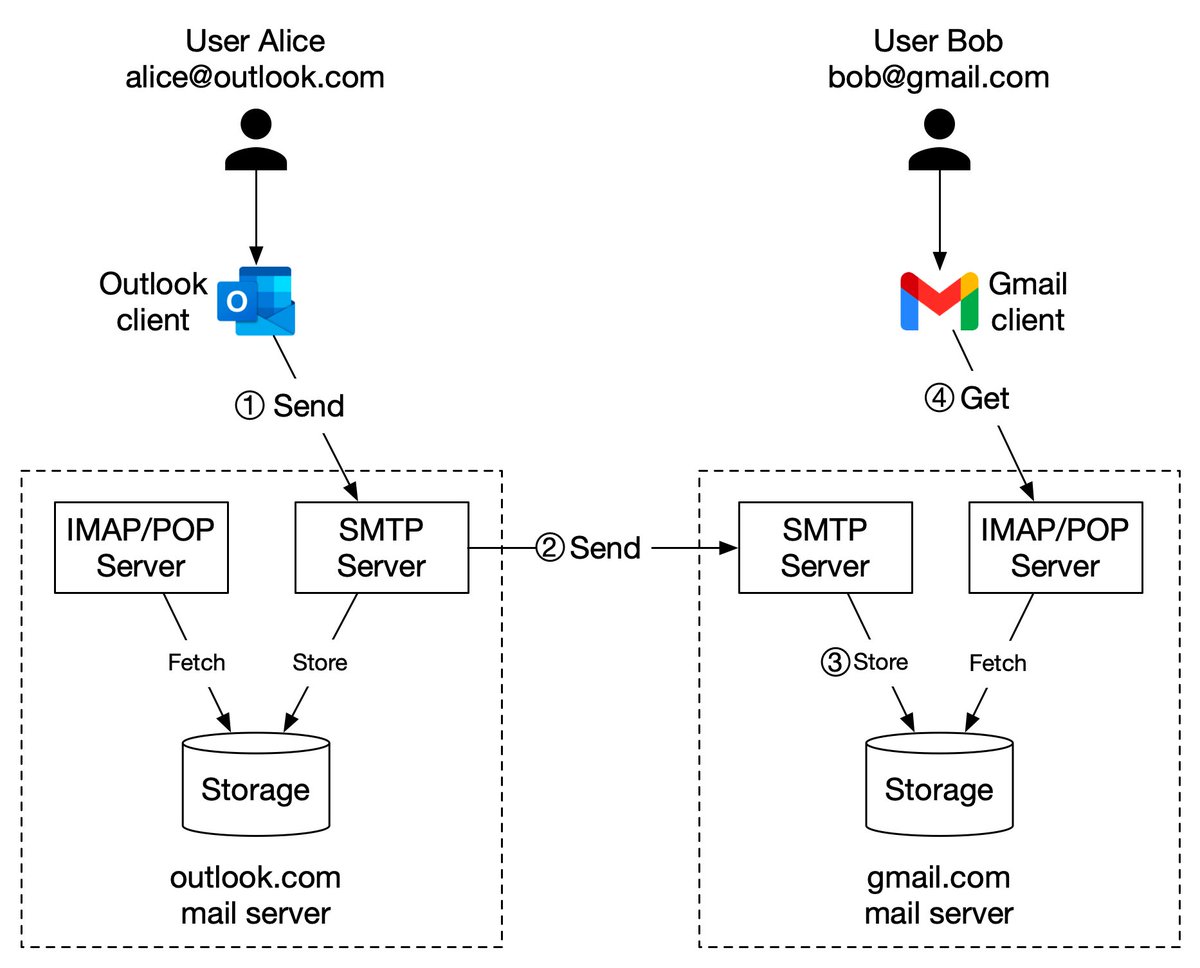
Why is a solid-state drive (SSD) fast?
“A solid state drive reads up to 10 times faster and writes up to 20 times faster than a hard disk drive.” [1].
“A solid state drive reads up to 10 times faster and writes up to 20 times faster than a hard disk drive.” [1].
“An SSD is a flash-memory based data storage device. Bits are stored into cells, which are made of floating-gate transistors. SSDs are made entirely of electronic components, there are no moving or mechanical parts like in hard drives (HDD)” [2].
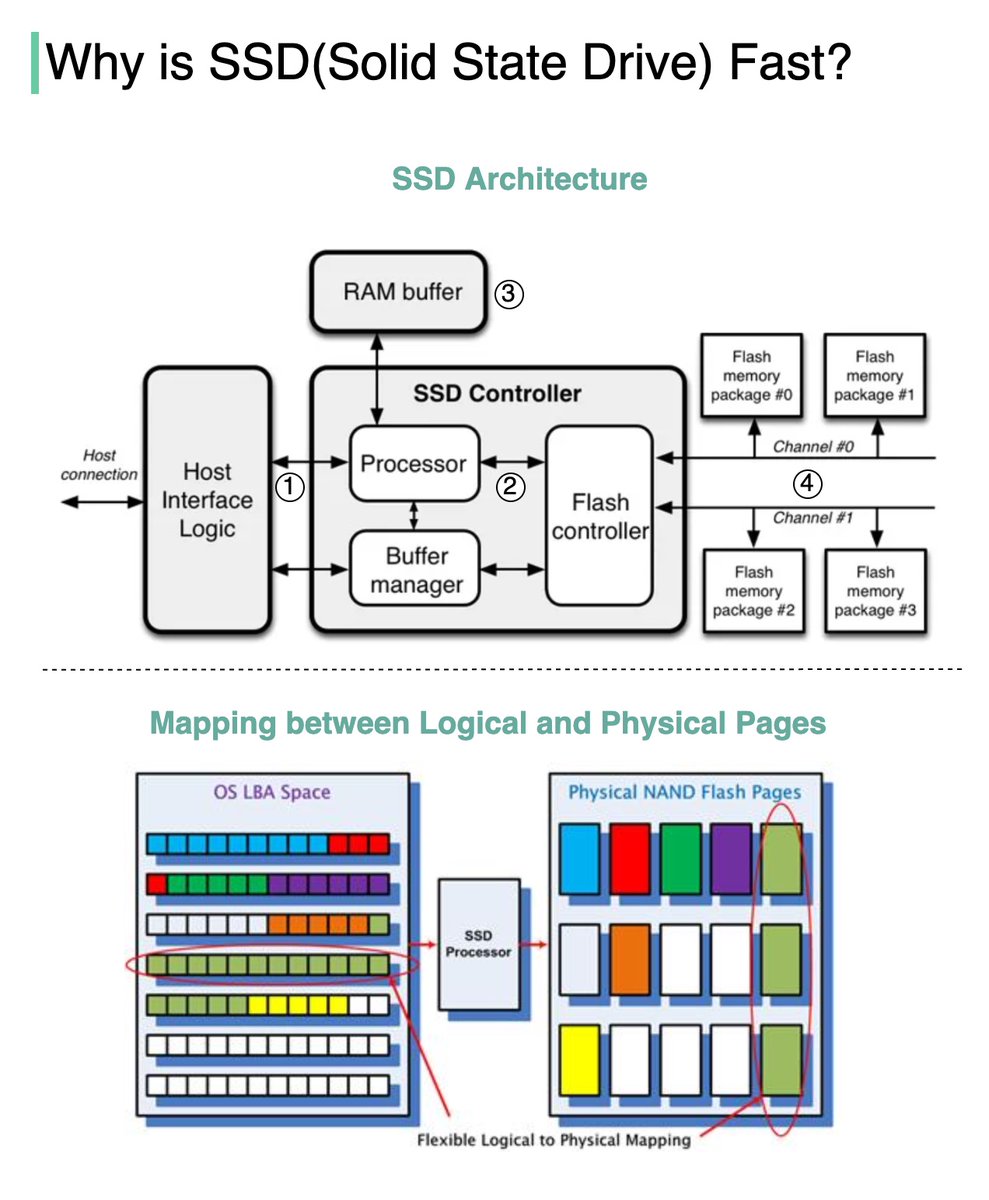
The diagram below illustrates the SSD architecture.
Step 1: “Commands come from the user through the host interface” [2]. The interface can be Serial ATA (SATA) or PCI Express (PCIe).
Step 1: “Commands come from the user through the host interface” [2]. The interface can be Serial ATA (SATA) or PCI Express (PCIe).

Step 2: “The processor in the SSD controller takes the commands and passes them to the flash controller” [2].
Step 3: “SSDs also have embedded RAM memory, generally for caching purposes and to store mapping information” [2].
Step 3: “SSDs also have embedded RAM memory, generally for caching purposes and to store mapping information” [2].

Step 4: “The packages of NAND flash memory are organized in gangs, over multiple channels” [2].
The second diagram illustrates how the logical and physical pages are mapped, and why this architecture is fast.
The second diagram illustrates how the logical and physical pages are mapped, and why this architecture is fast.

SSD controller operates multiple FLASH particles in parallel, greatly improving the underlying bandwidth. When we need to write more than one page, the SSD controller can write them in parallel [3], whereas the HDD has a single head and it can only read from one head at a time.
Every time a HOST Page is written, the SSD controller finds a Physical Page to write the data and this mapping is recorded. With this mapping, the next time HOST reads a HOST Page, the SSD knows where to read the data from FLASH [3].
Question - What are the main differences between SSD and HDD?
Sources:
[1] SSD or HDD: Which Is Right for You?: avg.com/en/signal/ssd-…
[2] Coding for SSDs: codecapsule.com/2014/02/12/cod…
[3] Overview of SSD Structure and Basic Working Principle: elinfor.com/knowledge/over…
[1] SSD or HDD: Which Is Right for You?: avg.com/en/signal/ssd-…
[2] Coding for SSDs: codecapsule.com/2014/02/12/cod…
[3] Overview of SSD Structure and Basic Working Principle: elinfor.com/knowledge/over…
If you like my post, you may want to subscribe to my weekly system design newsletter (10 mins read): bit.ly/3rrcFjh
#systemdesign #coding #interviewtips
#systemdesign #coding #interviewtips
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh