#Flutter Animation guide 📑
1️⃣ Implicit - AnimatedFoo & TweenAnimationBuilder
2️⃣ Explicit - FooTransition, AnimatedBuilder & AnimatedWidget
1️⃣.1️⃣ Implicit - Ready-to-use
Add ‘Animated’ to a regular widget (Container, Positioned, .etc) with a duration and you’re good to go!
1/7
1️⃣ Implicit - AnimatedFoo & TweenAnimationBuilder
2️⃣ Explicit - FooTransition, AnimatedBuilder & AnimatedWidget
1️⃣.1️⃣ Implicit - Ready-to-use
Add ‘Animated’ to a regular widget (Container, Positioned, .etc) with a duration and you’re good to go!
1/7
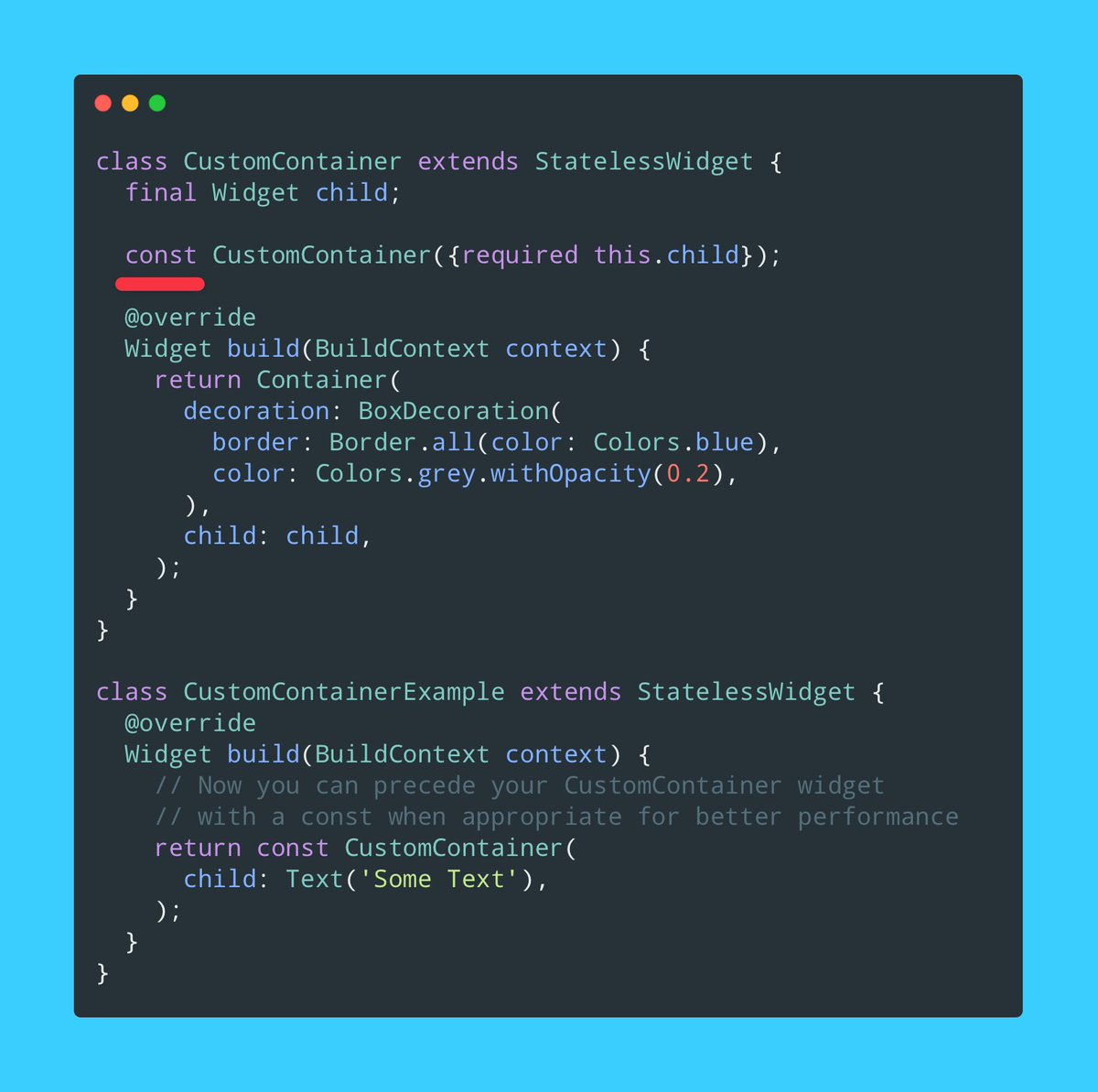
1️⃣.2️⃣ Implicit Animations - Custom
No AnimatedFoo widget fits your requirements and you still want something quick to set up? Use the #TweenAnimationBuilder widget! Simply changing the Tween values triggers an animation.
Use the child param for better performance!
2/7
No AnimatedFoo widget fits your requirements and you still want something quick to set up? Use the #TweenAnimationBuilder widget! Simply changing the Tween values triggers an animation.
Use the child param for better performance!
2/7
2️⃣.1️⃣ Explicit - Ready-to-use
“Control” how your animations are animated with an #AnimationController and a #FooTransition widget (ScaleTransition, RotationTransition, …etc). You can now tell the animation when to start, reverse, repeat, ...etc
3/7
“Control” how your animations are animated with an #AnimationController and a #FooTransition widget (ScaleTransition, RotationTransition, …etc). You can now tell the animation when to start, reverse, repeat, ...etc
3/7
2️⃣.2️⃣ Explicit - Custom
All of the above does not achieve your goal animation? Go wild with the #AnimatedBuilder widget and create controllable animations for any parameter of any widget!
or…
5/7
All of the above does not achieve your goal animation? Go wild with the #AnimatedBuilder widget and create controllable animations for any parameter of any widget!
or…
5/7
Create your own FooTransition widgets using the #AnimatedWidget!
The code below achieves the same previous animation 👆🏼
6/7
The code below achieves the same previous animation 👆🏼
6/7

There are a lot more to cover for Flutter animations! but this should be enough for you to get started and build UI animations for your app with a wide range of complexities!
You can find all the code and animations above in this DartPad:
dartpad.dev/c9bb2627d4f383…
7/7
You can find all the code and animations above in this DartPad:
dartpad.dev/c9bb2627d4f383…
7/7
BONUS 1 🎉 I talked about all of this in detail in the #FlutterFestival Vulsad & Surat session. You can watch it here:
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh