1/
My fellows complained they hate memorizing classifications, like LeFort. I thought, “There must be a better way—maybe understanding instead of memorizing.”
A #tweetorial about understanding the LeFort classification. #FOAMed #medtwitter #Medstudenttwitter @medtweetorials
My fellows complained they hate memorizing classifications, like LeFort. I thought, “There must be a better way—maybe understanding instead of memorizing.”
A #tweetorial about understanding the LeFort classification. #FOAMed #medtwitter #Medstudenttwitter @medtweetorials
2/
To understand LeFort, you need to understand facial buttresses.
These are not true anatomic structures but a way of understanding facial structure.
Facial bones support facial structures like a table supports food, with legs (vertical buttresses) and table top (horizontal)
To understand LeFort, you need to understand facial buttresses.
These are not true anatomic structures but a way of understanding facial structure.
Facial bones support facial structures like a table supports food, with legs (vertical buttresses) and table top (horizontal)

3/
In the face, the two main structures the buttresses are supporting are the orbits and the alveolar ridges of the maxilla and mandible supporting the teeth
In the face, the two main structures the buttresses are supporting are the orbits and the alveolar ridges of the maxilla and mandible supporting the teeth

4/
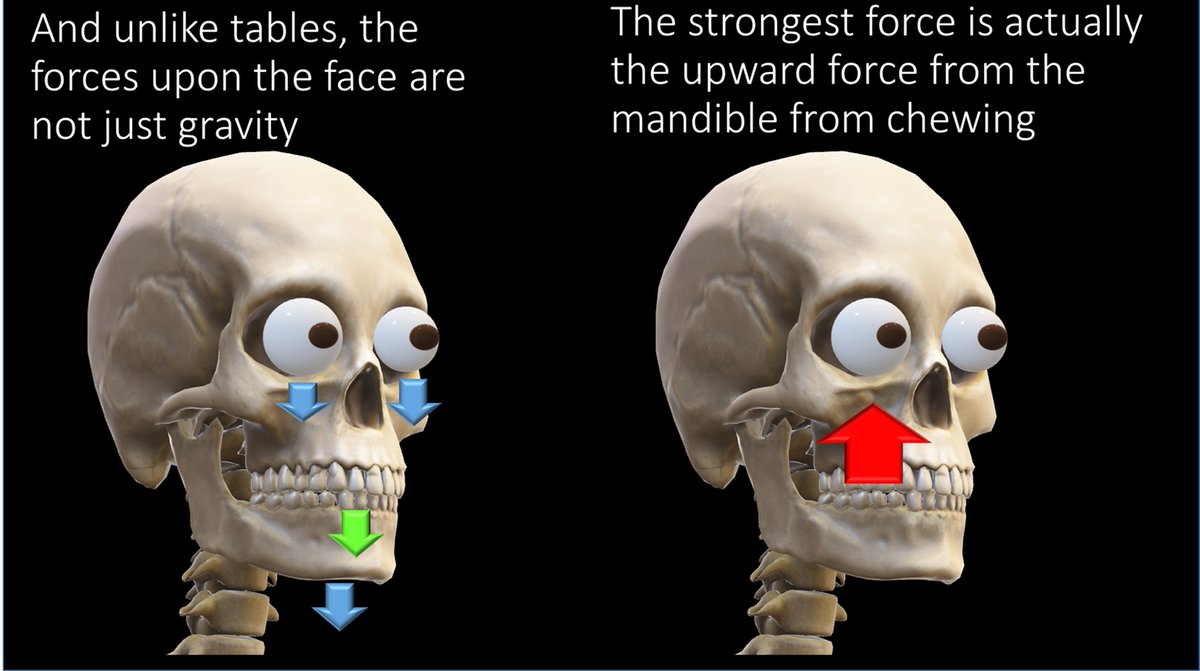
The buttresses not only support against gravity, but also against the force of mastication, which sends force from the mandible all the way through the maxilla to the skullbase
The buttresses not only support against gravity, but also against the force of mastication, which sends force from the mandible all the way through the maxilla to the skullbase
6/
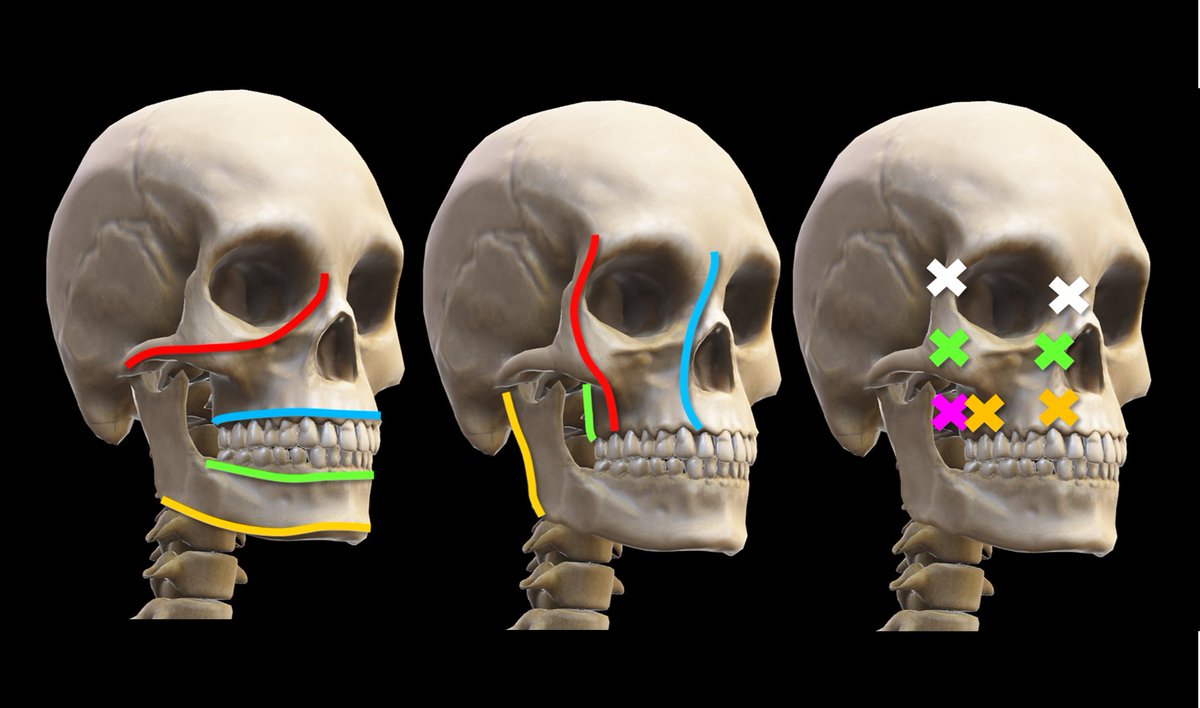
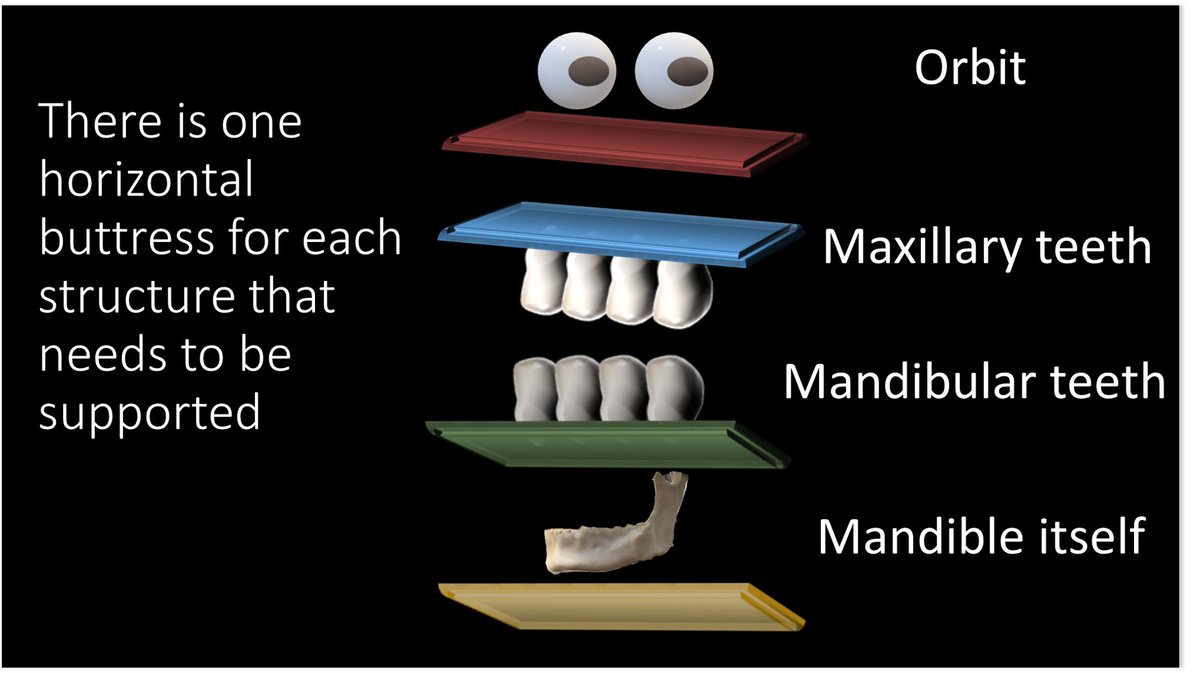
Horizontal buttresses—there is a tabletop underlying each of the structures that need support in the face: the orbit, maxillary teeth, mandibular teeth, and mandible
Horizontal buttresses—there is a tabletop underlying each of the structures that need support in the face: the orbit, maxillary teeth, mandibular teeth, and mandible
7/
Here is the illustration of the horizontal buttresses and their official anatomic names. However, the names aren’t as important as remembering where they are—and you can do that by remembering that each important structure has a tabletop right below it.
Here is the illustration of the horizontal buttresses and their official anatomic names. However, the names aren’t as important as remembering where they are—and you can do that by remembering that each important structure has a tabletop right below it.

8/
Vertical buttresses—these are the support posts. And they are arranged just how you would arrange them if you were building a house. Two in front, two in back.
Vertical buttresses—these are the support posts. And they are arranged just how you would arrange them if you were building a house. Two in front, two in back.

9/
Here is the illustration of the vertical buttresses and their official anatomic names. But again, names aren’t important—function is!
Here is the illustration of the vertical buttresses and their official anatomic names. But again, names aren’t important—function is!

10/
Vertical buttresses act as suspension wires for the maxilla, suspending it from the skullbase. They are what keep your face on!
Vertical buttresses act as suspension wires for the maxilla, suspending it from the skullbase. They are what keep your face on!

11/
LeFort fx is when your face (maxilla) gets take off! To take it off, we have to cut the suspension wires--all three (posterior, medial, and lateral). The posterior buttress (pterygoid plate) is always cut. That is why pterygoid fx's are the signature of LeFort injuries
LeFort fx is when your face (maxilla) gets take off! To take it off, we have to cut the suspension wires--all three (posterior, medial, and lateral). The posterior buttress (pterygoid plate) is always cut. That is why pterygoid fx's are the signature of LeFort injuries

12/
Where we cut the other two buttresses determines which LeFort fx we get.
And now, you can just think of cutting the suspension wire to the maxilla, and never have to memorize the LeFort classification again!
Where we cut the other two buttresses determines which LeFort fx we get.
And now, you can just think of cutting the suspension wire to the maxilla, and never have to memorize the LeFort classification again!

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh























