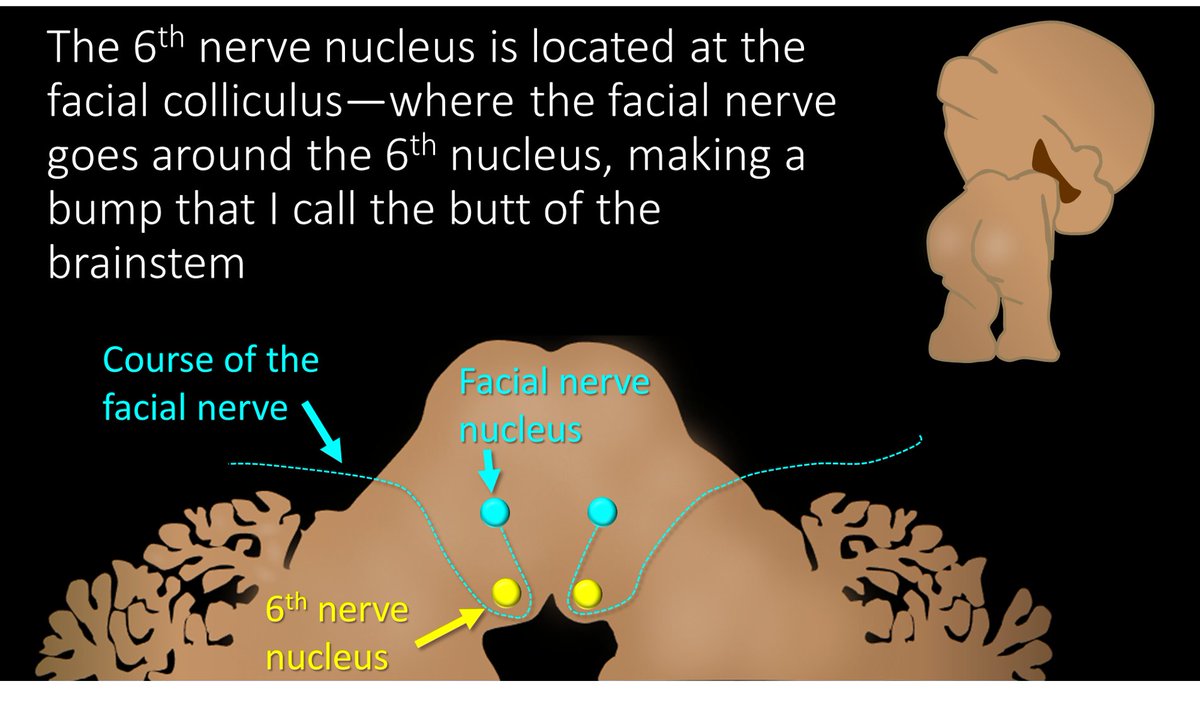
1/
Why is cranial nerve 6 uniquely affected by⬆️ intracranial pressure? Why is it special? A common question after the CN6 tweetorial.
Here is a maybe #tweetorial, but maybe a🧵about why CN6 is alone affected by ⬆️ pressure. #FOAMed #medtwitter #Medstudenttwitter #neurotwitter
Why is cranial nerve 6 uniquely affected by⬆️ intracranial pressure? Why is it special? A common question after the CN6 tweetorial.
Here is a maybe #tweetorial, but maybe a🧵about why CN6 is alone affected by ⬆️ pressure. #FOAMed #medtwitter #Medstudenttwitter #neurotwitter

2/
Think of the intracranial CSF space like a balloon, distended by CSF instead of air. Cranial nerves begin inside the balloon, and then they exit as they begin their extradural portion
Think of the intracranial CSF space like a balloon, distended by CSF instead of air. Cranial nerves begin inside the balloon, and then they exit as they begin their extradural portion

3/
Most cranial nerves move immediately away from the CSF space after they exit—usually going out through their respective foramina. However, CN6 uniquely runs along the outside of the “balloon” in Dorello canal
Most cranial nerves move immediately away from the CSF space after they exit—usually going out through their respective foramina. However, CN6 uniquely runs along the outside of the “balloon” in Dorello canal
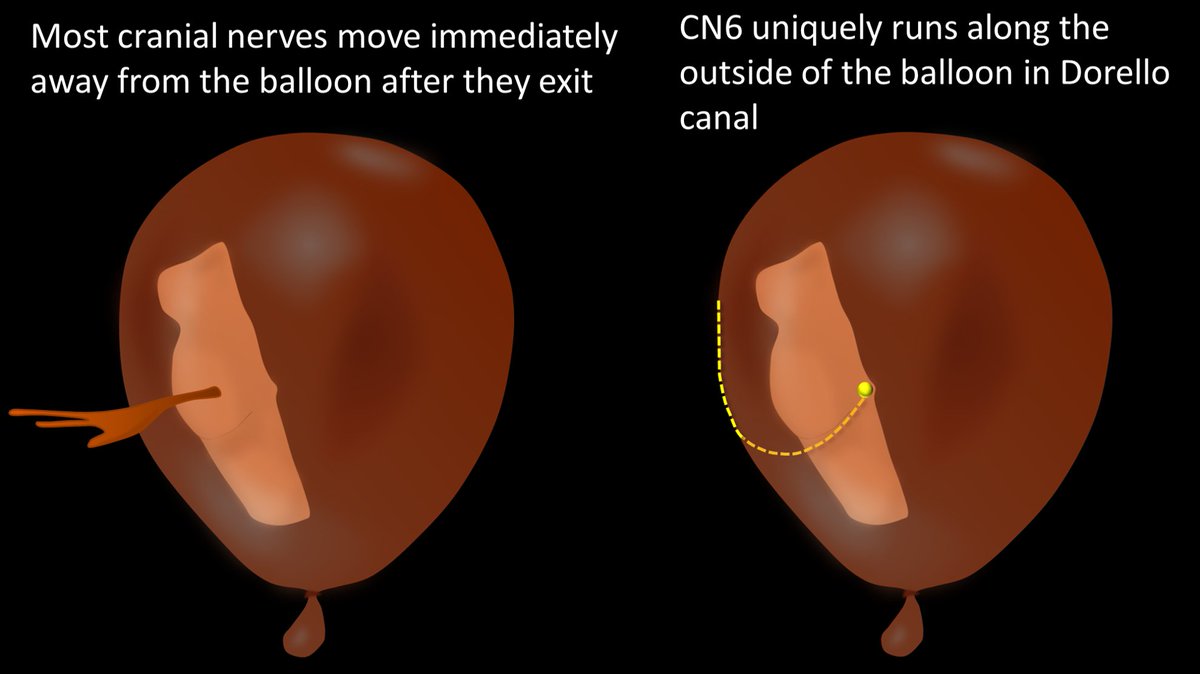
4/
Increased intracranial pressure is like expanding the balloon. Most cranial nerves are not affected by the expanded balloon because they move away from the surface of the balloon right after they exit
Increased intracranial pressure is like expanding the balloon. Most cranial nerves are not affected by the expanded balloon because they move away from the surface of the balloon right after they exit

5/
However, because of the unique course of CN6 along the surface of the “balloon” in Dorello canal, the increased intracranial pressure or expanding “balloon” pushes against the extradural portion of CN6
However, because of the unique course of CN6 along the surface of the “balloon” in Dorello canal, the increased intracranial pressure or expanding “balloon” pushes against the extradural portion of CN6

6/
Unfortunately, CN6 has nowhere to go to escape this increased pressure, as on the other side of it is the clivus. So in the increased pressure pushes it against the clivus in Dorello canal
Unfortunately, CN6 has nowhere to go to escape this increased pressure, as on the other side of it is the clivus. So in the increased pressure pushes it against the clivus in Dorello canal

7/
This makes a “CN6 sandwich”! CN6 gets sandwiched between clivus & dura. It's this compression that uniquely gives you an isolated CN6 palsy w/⬆️pressure!
So when you see an isolated CN6 palsy in intracranial hypertension, think of balloons & sandwiches & you’ll remember why!
This makes a “CN6 sandwich”! CN6 gets sandwiched between clivus & dura. It's this compression that uniquely gives you an isolated CN6 palsy w/⬆️pressure!
So when you see an isolated CN6 palsy in intracranial hypertension, think of balloons & sandwiches & you’ll remember why!

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh