
#Week_2: #DeFi Day 4: Decentralized Finance: On Blockchain- and Smart Contract-Based Financial Markets by @chainomics, will break it into 2 parts
A very good read coming from an academic professor!
This article highlights opportunities and potential risks of the DeFi ecosystem.
A very good read coming from an academic professor!
This article highlights opportunities and potential risks of the DeFi ecosystem.
2- DeFi uses smart contracts on top of blockchains to create open protocols that replicate existing financial services in a permissionless, interoperable, and transparent way,
Agreements are enforced by code (no middleman) transactions are executed in a secure and verifiable way.
Agreements are enforced by code (no middleman) transactions are executed in a secure and verifiable way.
3- So the adv here: unprecedented transparency, equal access rights, and little need for custodians, central clearing houses, or escrow services, as most of these roles can be assumed by "smart contracts."
So The backbone of all DeFi protocols and applications is smart contracts
So The backbone of all DeFi protocols and applications is smart contracts
4- They are executed by a large set of validators, so the network is designed so that each participant can be involved in and verify the correct execution of any operation.
Which makes them highly transparent and minimize the risk of manipulation and arbitrary intervention.
Which makes them highly transparent and minimize the risk of manipulation and arbitrary intervention.
5- Look in the real world: the user is not in control of the execution environment. Either one or both could be manipulated. As a result, the user has to trust the application service provider. Smart contracts mitigate both problems and ensure that an application runs as expected
6- Additionally, they can store crypto assets and assume the role of a custodian, with entirely customizable criteria for how, when, and to whom these assets can be released. This allows for a large variety of novel applications and flourishing ecosystems.
plus composability!
plus composability!
7- DeFi numbers grew rapidly in the last 2 years regards: market cap, available applications, and development activity. Look at the figure for ETH DeFi until 2021, there is much potential to growth and sparked interest among policymakers, researchers, and financial institutions. 

8- *DeFi BUILDING BLOCKS*
DeFi uses a multi-layered architecture, Every layer has a purpose. The layers build on each other and create an open and highly composable infrastructure.
as shown in the figure
1:Settlement layer consists of the blockchain and its native protocol asset
DeFi uses a multi-layered architecture, Every layer has a purpose. The layers build on each other and create an open and highly composable infrastructure.
as shown in the figure
1:Settlement layer consists of the blockchain and its native protocol asset

9- The blockchain can be seen as the foundation for trustless execution.
2: The asset layer consists of all assets that are issued on top of the settlement layer(native+ any issued one on this blockchain)
3:The protocol layer provides standards for specific use cases -
2: The asset layer consists of all assets that are issued on top of the settlement layer(native+ any issued one on this blockchain)
3:The protocol layer provides standards for specific use cases -
10- Such as decentralized exchanges, debt markets, derivatives, and more (DeFi application)
4: The application layer creates user-oriented applications that connect to individual protocols
5: Aggregation layer is an extension of the application layer comparing to get best rates
4: The application layer creates user-oriented applications that connect to individual protocols
5: Aggregation layer is an extension of the application layer comparing to get best rates
11- Let us take a closer look at tokenization and the protocol layer, investigating different Defi Services after, so we can have the foundation needed for analysis of the potential and risks of DeFi
*Asset Tokenization
The process of adding new assets to a blockchain-
*Asset Tokenization
The process of adding new assets to a blockchain-
12- is called tokenization, referred to as Tokens.
The idea is to make assets more accessible and transactions more efficient (transferred easily and within seconds from and to anyone in the world).
As of Jan 2021, there are over 350,000 ERC-20 token contracts deployed on Eth
The idea is to make assets more accessible and transactions more efficient (transferred easily and within seconds from and to anyone in the world).
As of Jan 2021, there are over 350,000 ERC-20 token contracts deployed on Eth

13- One of the main concerns with tokenized assets is issuer risk,
when someone introduces tokens with a promise, for example, interest payments, dividends, or the delivery of a service, the corresponding token's value will depend on this claim's credibility.
when someone introduces tokens with a promise, for example, interest payments, dividends, or the delivery of a service, the corresponding token's value will depend on this claim's credibility.
14- If an issuer is unwilling or unable to deliver, the token may become worthless or trade at a significant discount. This logic also applies to stablecoins (e.g what happened with UST lately)
Generally, there are three backing models for promise-based tokens: --
Generally, there are three backing models for promise-based tokens: --
15- off-chain collateral, on-chain collateral, and no collateral.
1*Off-chain collateral means that the underlying assets are stored with an escrow service, for example a commercial bank (eg: usdc)
Adv: minimizing the exchange risk
Disadv: external dependencies, regular audits=
1*Off-chain collateral means that the underlying assets are stored with an escrow service, for example a commercial bank (eg: usdc)
Adv: minimizing the exchange risk
Disadv: external dependencies, regular audits=
16- This process is costly and, in many cases, not entirely transparent for the token holders.
2*On-chain collateral means that the assets are locked on the blockchain= meaning several advantages: Being highly transparent, and claims can be secured by smart contracts =
2*On-chain collateral means that the assets are locked on the blockchain= meaning several advantages: Being highly transparent, and claims can be secured by smart contracts =
17- allowing executions in a semi-automatic way,
the disadvantage here is that this collateral is usually held in a native protocol asset (Like DAI and ETH) = price fluctuations
3*No-collateral: The risk is at its highest. In this case, the promise is entirely trust-based.
the disadvantage here is that this collateral is usually held in a native protocol asset (Like DAI and ETH) = price fluctuations
3*No-collateral: The risk is at its highest. In this case, the promise is entirely trust-based.
18- *Decentralized Exchange Protocols
in most cases, crypto asset trades are conducted through centralized exchanges. Centralized exchanges are relatively efficient, but they have one severe problem,
You have to trust the exchange, they will hold your assets= potential hacks-
in most cases, crypto asset trades are conducted through centralized exchanges. Centralized exchanges are relatively efficient, but they have one severe problem,
You have to trust the exchange, they will hold your assets= potential hacks-
19- Dishonest or unprofessional exchange operators may confiscate or lose assets.
Decentralized exchange protocols try to mitigate these issues by removing the trust need. Users no longer must deposit their funds with a centralized exchange, it happens through smart contracts-
Decentralized exchange protocols try to mitigate these issues by removing the trust need. Users no longer must deposit their funds with a centralized exchange, it happens through smart contracts-
20- So the code runs it again.
There is various types of decentralized exchange protocols as bellow in the image,
*Decentralized Order Book Exchanges
here, order book can be implemented in a variety of ways, They all use smart contracts for transaction settlement-
There is various types of decentralized exchange protocols as bellow in the image,
*Decentralized Order Book Exchanges
here, order book can be implemented in a variety of ways, They all use smart contracts for transaction settlement-

21- But they differ significantly in how the order books are hosted, on-chain and off-chain order books.
On-chain order books have the advantage of being entirely decentralized. Every order is stored within the smart contract. So there is no need for third-party hosts
On-chain order books have the advantage of being entirely decentralized. Every order is stored within the smart contract. So there is no need for third-party hosts
22- The disadvantage: that every action requires a blockchain transaction. Therefore, it is a costly and slow process,
For this reason, many decentralized exchange protocols rely on off-chain order books and only use the blockchain as a settlement layer.
Disadv: centralization
For this reason, many decentralized exchange protocols rely on off-chain order books and only use the blockchain as a settlement layer.
Disadv: centralization
23- *Constant Function Market Maker(CFMM)
It is a smart contract-liquidity pool that holds (at least) two crypto assets in reserve and allows anyone to deposit tokens of one type and thereby to withdraw tokens of the other type.
It is a smart contract-liquidity pool that holds (at least) two crypto assets in reserve and allows anyone to deposit tokens of one type and thereby to withdraw tokens of the other type.
24- To determine the exchange rate, It uses variations of the constant product model, where the relative price is a function of the smart contract's token reserve ratio.
the constant product model can be expressed as xy= k, where x and y are the token reserves and k is a constant
the constant product model can be expressed as xy= k, where x and y are the token reserves and k is a constant
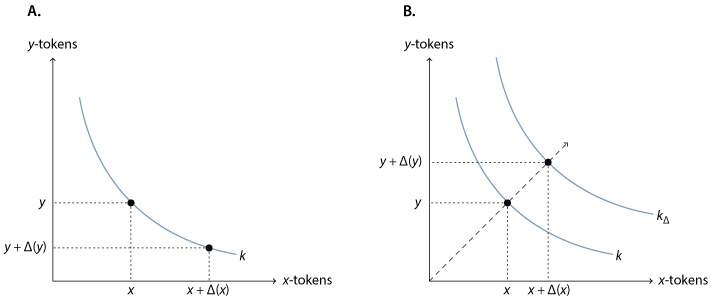
25- A liquidity pool using this model cannot be depleted, as tokens will get more expensive with lower reserves.
The implicit bid/ask spread of the constant product model (plus a small trading fee) may lead to the accumulation of additional funds. Anyone who provides liquidity-
The implicit bid/ask spread of the constant product model (plus a small trading fee) may lead to the accumulation of additional funds. Anyone who provides liquidity-
26- to the pool receives pool share tokens that allow them to participate in this accumulation and to redeem these tokens for their share of a potentially growing liquidity pool. Liquidity provision results in a growing k and is visualized in Figure above
the next part will be tomorrow, link to the full article which worth reading for sure: research.stlouisfed.org/publications/r… Thanks to professor: @chainomics and his contributions!
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh




