Here is another episode of the never ending launch price/cost saga, starring @momentusspace: I am surprised that I have not yet seen any commentary on their appreciation of the price of access to orbit as shown in the May 2022 investor presentation. static.seekingalpha.com/uploads/sa_pre… 1/ 

Beyond the fact that I don't know what is their basis for calculations, in particular how they allocate the cost of "own propulsion" to the launch, considering that the propulsion systems serves other functions, I gather from this that 15k$/kg is their price tag? 2/
So the "last mile" service actually applies a factor 3 to the baseline rideshare price on #SpaceX? I fail to see the viability of this model, but maybe it is still too early (also considering that #Vigoride didn't do very well so far: spacenews.com/momentus-attem…) 3/
Just for the sake of the discussion, here is my own appreciation of launch prices/costs. (hairsplitters, please note that I consider launch cost from the customer perspective, so it is the equivalent of price) - this slide is from my lecture on the space economy 4/ 

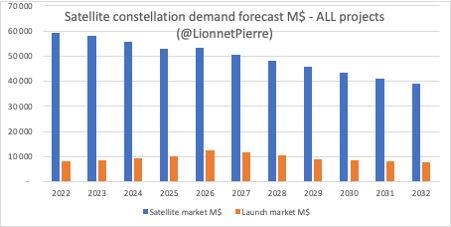
And BTW, the infamous #Stratistics did it again: a very creative assessment of the space transportation market. I don't know where these guys source their data from, but come on... 2020 TAM >15B$? And MEO>GEO? Here are my own values for comparison. 5/end 



• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh