Is there a role for Local Tx of the Primary Tumor for Patients with Metastatic Cancer?
🚫Many studies demonstrate no benefit.
📌We performed a MetaAnalysis to evaluate the average effect of Local Tx across various tumors.
A thread🧵#AMSM #PRIMETX
redjournal.org/article/S0360-…
1/25

🚫Many studies demonstrate no benefit.
📌We performed a MetaAnalysis to evaluate the average effect of Local Tx across various tumors.
A thread🧵#AMSM #PRIMETX
redjournal.org/article/S0360-…
1/25

Critics of Local Tx to the Primary Tumor
📌 Many providers think local control of the primary tumor in the setting of M1 dz is akin to “closing the barn door after the horse has bolted”
📌 Ian Tannock wrote a fantastic article on this back in 2000.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11759650/
2/
📌 Many providers think local control of the primary tumor in the setting of M1 dz is akin to “closing the barn door after the horse has bolted”
📌 Ian Tannock wrote a fantastic article on this back in 2000.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11759650/
2/
Supporters of Local Tx
📌Some support aggressive ablation of all sites due to the enhanced ability to detect occult disease with improved imaging technologies and 📉 toxicities with complete ablation.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35831494/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31182289/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34742582/
3/


📌Some support aggressive ablation of all sites due to the enhanced ability to detect occult disease with improved imaging technologies and 📉 toxicities with complete ablation.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35831494/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31182289/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34742582/
3/



To date,
📌Some trials have demonstrated an OS benefit with Local Tx, while many others have shown no benefit.
📌As a recent meta-analysis investigated the utility of ablation of metastasis, the focus of thiswork is Local Tx to the primary tumor.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33237270/
4/
📌Some trials have demonstrated an OS benefit with Local Tx, while many others have shown no benefit.
📌As a recent meta-analysis investigated the utility of ablation of metastasis, the focus of thiswork is Local Tx to the primary tumor.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33237270/
4/

Methods
📌 Comprehensive search on PubMed/MEDLINE and Cochrane Review.
📌 Primary outcome measures of OS and PFS.
📌 RCTs that included simultaneous local consolidative Tx to the primary tumor and metastases (e.g., Gomez for NSCLC) were excluded.
bit.ly/PRIME-TX_Liter…
5/


📌 Comprehensive search on PubMed/MEDLINE and Cochrane Review.
📌 Primary outcome measures of OS and PFS.
📌 RCTs that included simultaneous local consolidative Tx to the primary tumor and metastases (e.g., Gomez for NSCLC) were excluded.
bit.ly/PRIME-TX_Liter…
5/


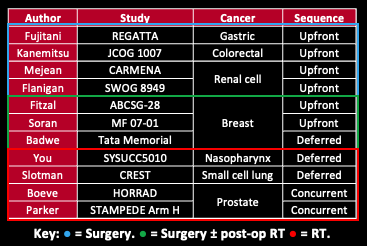
Results
📌 Literature search revealed 11 studies from 2001-2021, comprising 4,952 patients who underwent systemic therapy +/- local treatment to the primary tumor.
📌 Bookmark these Tables and view the different sheets to follow these tweets.
bit.ly/PRIME-TX_Tables
6/
📌 Literature search revealed 11 studies from 2001-2021, comprising 4,952 patients who underwent systemic therapy +/- local treatment to the primary tumor.
📌 Bookmark these Tables and view the different sheets to follow these tweets.
bit.ly/PRIME-TX_Tables
6/
Results: Efficacy
📌 OS and PFS were not significantly improved with Tx of the primary tumor.
📌 There was a significant difference in summary effect size on PFS between trials that used surgery and the trials that used RT as the primary local Tx modality.
7/
📌 OS and PFS were not significantly improved with Tx of the primary tumor.
📌 There was a significant difference in summary effect size on PFS between trials that used surgery and the trials that used RT as the primary local Tx modality.
7/

Results: Palliative treatment to the primary tumor in the no local treatment (control) arms
📌 Rates of palliative treatment to the primary tumor for symptoms or progression in the no local treatment (control) arms ranged from 6-18% (Table 2, post 6)
8/
📌 Rates of palliative treatment to the primary tumor for symptoms or progression in the no local treatment (control) arms ranged from 6-18% (Table 2, post 6)
8/
Results: Physician-Graded Toxicity and QoL
📌 Only 4 studies reported QoL (3 of which were for breast cancer; Table 3, post 6)
📌More robust QoL data is needed, with particular attention to later stages where symptomatic progression and palliative needs are often more common
9/
📌 Only 4 studies reported QoL (3 of which were for breast cancer; Table 3, post 6)
📌More robust QoL data is needed, with particular attention to later stages where symptomatic progression and palliative needs are often more common
9/
Results: The Upfront Surgery trials (n=6/7)
📌 Typically large, locally advanced tumors.
📌 MTT initiation of systemic therapy ranged from 19 to 34d after surgery.
📌 Twice as many patients (4.4→ 8.9%) failed to initiate systemic therapy in the local therapy arms.
10/
📌 Typically large, locally advanced tumors.
📌 MTT initiation of systemic therapy ranged from 19 to 34d after surgery.
📌 Twice as many patients (4.4→ 8.9%) failed to initiate systemic therapy in the local therapy arms.
10/

Discussion: RT trials
📌 The two primary tumor types driving the OS benefit in the low M1 population treated with RT include prostate ca (n=2 trials; #STAMPEDEArmH, #HORRAD) and NPC (n=1 trial; SYSUCC5010).
📌 Surgery trials investigated very different populations!
11/

📌 The two primary tumor types driving the OS benefit in the low M1 population treated with RT include prostate ca (n=2 trials; #STAMPEDEArmH, #HORRAD) and NPC (n=1 trial; SYSUCC5010).
📌 Surgery trials investigated very different populations!
11/


Discussion: Surgery trials
📌 Most surgical studies were dominated by large locally advanced or initially unresectable tumors. What about smaller, more easily resectable tumors?
📌 Most surgical studies investigated upfront surgery (n=6/7). What about deferred surgery?
12/
📌 Most surgical studies were dominated by large locally advanced or initially unresectable tumors. What about smaller, more easily resectable tumors?
📌 Most surgical studies investigated upfront surgery (n=6/7). What about deferred surgery?
12/
Discussion: #stcsm
📌 #REGATTA: Gastric cancer. Upfront Surgery. S-1/Cisplatin until progression or toxicity.
📌 Trend to 📉PFS/OS.
📌 Tumors involving upper 1/3 of stomach may have 📈 compliance issues with chemo.
📌 Deferred surgery 🔜#RENAISSANCE?
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26822397/
13/

📌 #REGATTA: Gastric cancer. Upfront Surgery. S-1/Cisplatin until progression or toxicity.
📌 Trend to 📉PFS/OS.
📌 Tumors involving upper 1/3 of stomach may have 📈 compliance issues with chemo.
📌 Deferred surgery 🔜#RENAISSANCE?
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26822397/
13/


Discussion: #CRCSM
📌#JCOG1007: 1-3 unresectable mets. Upfront surgery. FOLFOX6 or CapeOX-Bev.
📌Trend to 📉 PFS/OS.
📌60d mortality 11% on #CAIRO4.
📌Should regular endoscopic surveillance guide potential role of deferred primary tumor surgery?
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33560877/
14/



📌#JCOG1007: 1-3 unresectable mets. Upfront surgery. FOLFOX6 or CapeOX-Bev.
📌Trend to 📉 PFS/OS.
📌60d mortality 11% on #CAIRO4.
📌Should regular endoscopic surveillance guide potential role of deferred primary tumor surgery?
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33560877/
14/




Discussion: #kcsm 1/2
📌 Upfront surgery. 1) SWOG: 📈 OS (outdated IFN era). 2) #CARMENA: 🚫 OS benefit (TKI era)
📌 Deferred nephrectomy may be preferred to select for patients who respond to systemic Tx (#SURTIME)
📌 Reserve for 1 IMDC risk factor?
lists.papersapp.com/Lt7VWzrOoPuN15…
15/



📌 Upfront surgery. 1) SWOG: 📈 OS (outdated IFN era). 2) #CARMENA: 🚫 OS benefit (TKI era)
📌 Deferred nephrectomy may be preferred to select for patients who respond to systemic Tx (#SURTIME)
📌 Reserve for 1 IMDC risk factor?
lists.papersapp.com/Lt7VWzrOoPuN15…
15/




Discussion: #kcsm 2/2
Cytoreductive Nephrectomy (CN) in 2022: Where are we now?
📌 CN: Still Necessary, Obsolete, or Obselete but Necessary?
📌 2022 ASCO and EAU Guidelines support CN in select patients.
sciencedirect.com/science/articl…
sciencedirect.com/science/articl…
sciencedirect.com/science/articl…
16/


Cytoreductive Nephrectomy (CN) in 2022: Where are we now?
📌 CN: Still Necessary, Obsolete, or Obselete but Necessary?
📌 2022 ASCO and EAU Guidelines support CN in select patients.
sciencedirect.com/science/articl…
sciencedirect.com/science/articl…
sciencedirect.com/science/articl…
16/



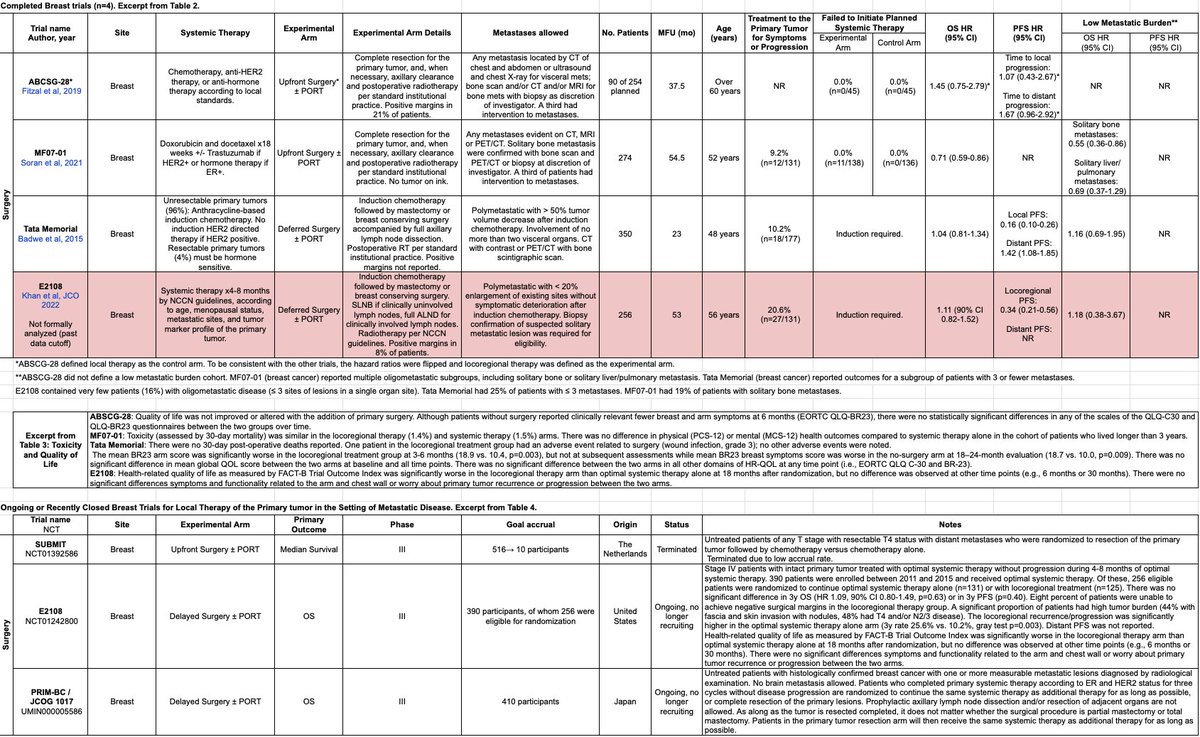
Discussion: #BCSM 1/2
📌 Upfront surgery: #ABSCG28, #MF0701.
📌 Deferred surgery: #TataMemorial, #E2108.
📌 Only one trial (MF07-01, positive margins in 0%) suggests 📈 OS with local therapy in an enriched population of HR+ solitary bone metastases.
lists.papersapp.com/Lt7VWzrOoPuN
17/



📌 Upfront surgery: #ABSCG28, #MF0701.
📌 Deferred surgery: #TataMemorial, #E2108.
📌 Only one trial (MF07-01, positive margins in 0%) suggests 📈 OS with local therapy in an enriched population of HR+ solitary bone metastases.
lists.papersapp.com/Lt7VWzrOoPuN
17/




Discussion: #BCSM 2/2
📌 Overall PFS is not reported in all 4 breast studies. There appears to be a distant PFS detriment with surgery (Cochrane review PMID 29542106; Tata memorial), further supported by ABSCG-28.
📌 Fantastic review here: pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35578060/
18/


📌 Overall PFS is not reported in all 4 breast studies. There appears to be a distant PFS detriment with surgery (Cochrane review PMID 29542106; Tata memorial), further supported by ABSCG-28.
📌 Fantastic review here: pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35578060/
18/


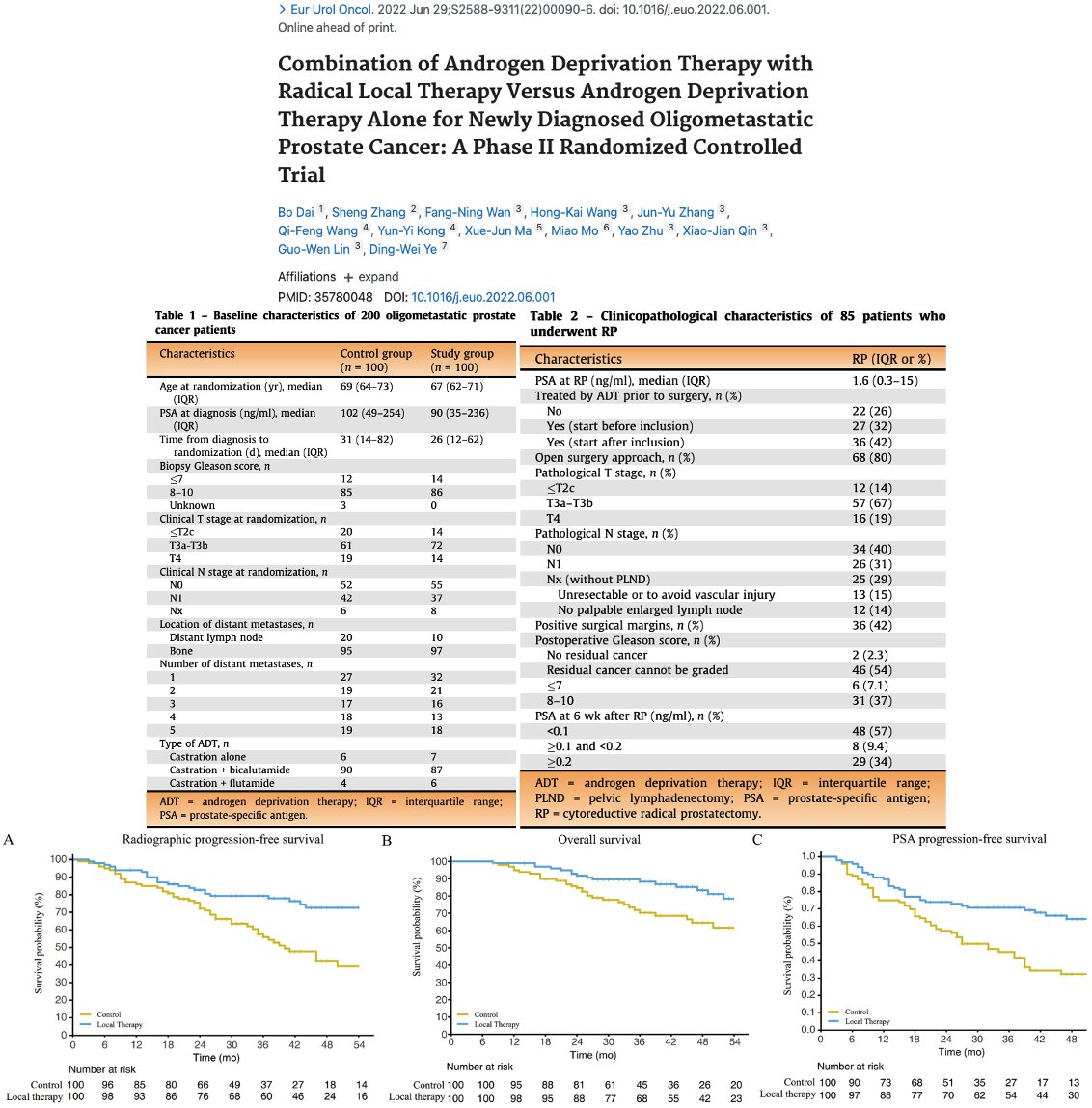
Discussion: #PCSM
📌 There is an OS benefit with prostate RT for < 5 bone mets (#HORRAD) or per #CHAARTED definition (#STAMPEDEArmH).
📌 Q: Does prostate RT provide benefit the setting of docetaxel ± abi? A: Awaiting the #PEACE1 RT publication.
📌 Role for prostatectomy?
19/



📌 There is an OS benefit with prostate RT for < 5 bone mets (#HORRAD) or per #CHAARTED definition (#STAMPEDEArmH).
📌 Q: Does prostate RT provide benefit the setting of docetaxel ± abi? A: Awaiting the #PEACE1 RT publication.
📌 Role for prostatectomy?
19/



Discussion: #NPXSM
📌 For some tumor locations (e.g., NPX), an uncontrolled primary tumor may cause substantial morbidity and even mortality. Therefore, the attainment of local control could easily impact survival.
📌 Fantastic prognostic model here: pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32853711/
20/


📌 For some tumor locations (e.g., NPX), an uncontrolled primary tumor may cause substantial morbidity and even mortality. Therefore, the attainment of local control could easily impact survival.
📌 Fantastic prognostic model here: pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32853711/
20/



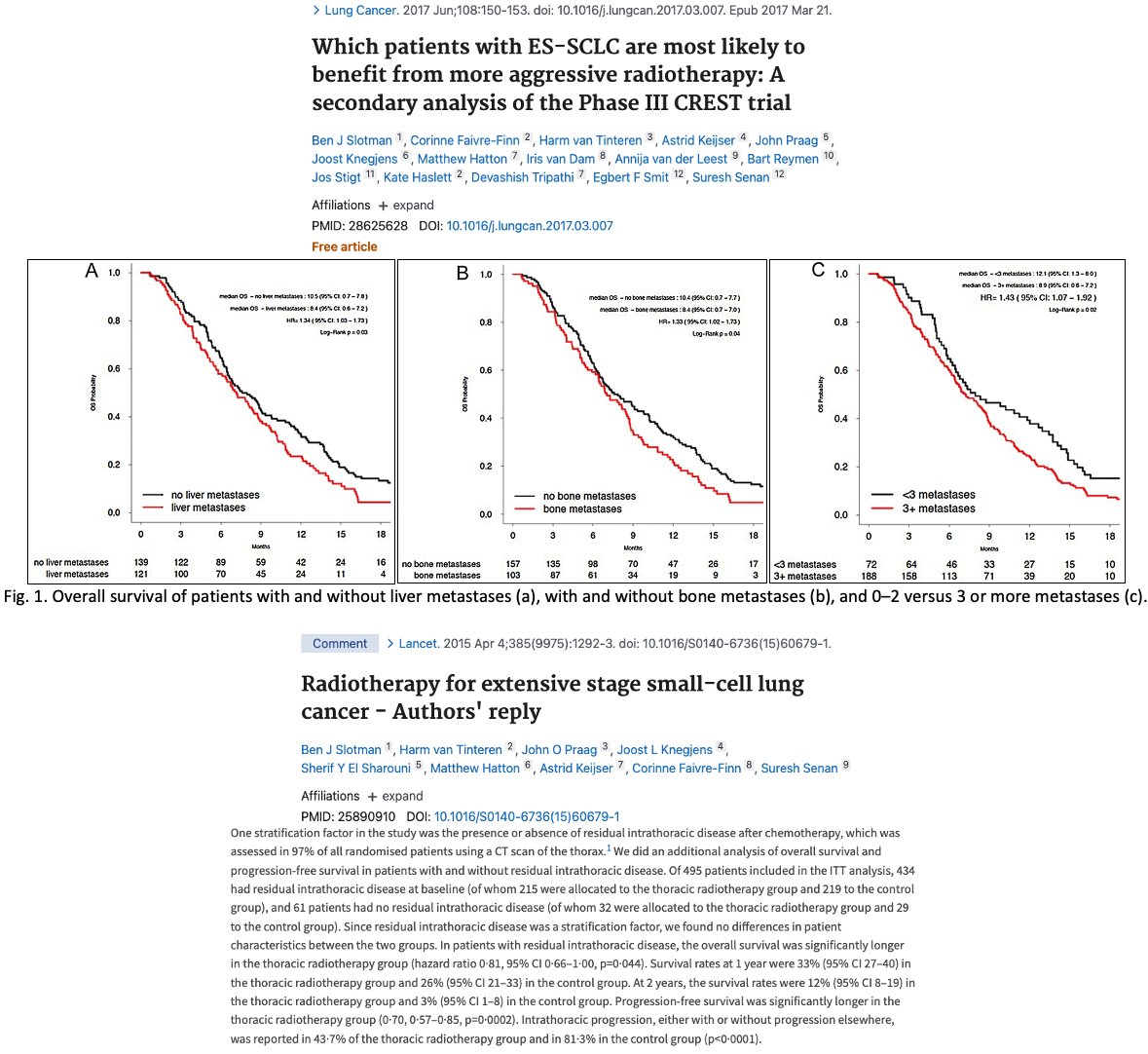
Discussion: #SCLC
📌#CREST (pre-IO era) delivered lower doses of thoracic consolidation (30Gy/10Fx).
📌 OS benefit most pronounced when only patients with residual thoracic dz were included.
📌 Is the role for thoracic RT for ES-SCLC in the IO-era? pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31673520/
21/



📌#CREST (pre-IO era) delivered lower doses of thoracic consolidation (30Gy/10Fx).
📌 OS benefit most pronounced when only patients with residual thoracic dz were included.
📌 Is the role for thoracic RT for ES-SCLC in the IO-era? pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31673520/
21/



Discussion: #NSCLC
📌 No trials of which we are aware randomized to local Tx to primary tumor alone (e.g., Gomez also treated metastases).
📌 PRIME-LUNG is investigating upfront SABR to the primary tumor.
📌 PI @ShankarSiva from @PeterMacCC
clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05…
22/
📌 No trials of which we are aware randomized to local Tx to primary tumor alone (e.g., Gomez also treated metastases).
📌 PRIME-LUNG is investigating upfront SABR to the primary tumor.
📌 PI @ShankarSiva from @PeterMacCC
clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05…
22/

I want to use this moment to highlight the utility of a BCC for such a large co-author group as this to avoid email fatigue.
HT @NicholasZaorsky for his fantastic mentorship 🙏
23/
HT @NicholasZaorsky for his fantastic mentorship 🙏
https://twitter.com/NicholasZaorsky/status/1479581406435102722?s=20&t=s5G70hTZYn5M6KwxVNzk2A
23/
Conclusion
📌 No consistent PFS/OS benefit in the overall population.
📌 PFS differed significantly between trials utilizing surgery vs. trials utilizing RT.
📌 More data needed to determine differences in subgroups (e.g., type/sequencing of Tx w/i each primary tumor type).
24/
📌 No consistent PFS/OS benefit in the overall population.
📌 PFS differed significantly between trials utilizing surgery vs. trials utilizing RT.
📌 More data needed to determine differences in subgroups (e.g., type/sequencing of Tx w/i each primary tumor type).
24/

Special thanks to all co-authors for their support!🙏
Please, be mindful: Site-specific discussions for each primary tumor type in this Tweetorial are the tip of the iceburg (read: hopelessly oversimplifed). When in doubt, discuss at tumor board.
Thanks for stopping by!
25/25
Please, be mindful: Site-specific discussions for each primary tumor type in this Tweetorial are the tip of the iceburg (read: hopelessly oversimplifed). When in doubt, discuss at tumor board.
Thanks for stopping by!
25/25
Here is the working link for the cited papers: lists.papersapp.com/Lt7VWzrOoPuN
What might explain 📉distant PFS with breast surgery as suggested by Tata Memorial and ABSCG-28?
Here is my stab at it (HT @_ShankarSiva). Surgery may be immunosuppressive? But this hypothesis doesn't explain the clear benefit of surgery in #MF0701 & RCC
Here is my stab at it (HT @_ShankarSiva). Surgery may be immunosuppressive? But this hypothesis doesn't explain the clear benefit of surgery in #MF0701 & RCC
https://twitter.com/jryckman3/status/1542886019435008001?s=20&t=Eug7zeJkKMdkA_-rfWqXPA
@Docace911 - any thoughts on the curves separating after 3y on MF07-01? Also, any thoughts on the theory as to why distant PFS might be worse w breast surgery?
Huge fan of your work! Obviously, this is a different Q than MDT. Please DM if you feel these are controversial topics.

Huge fan of your work! Obviously, this is a different Q than MDT. Please DM if you feel these are controversial topics.


• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh





























