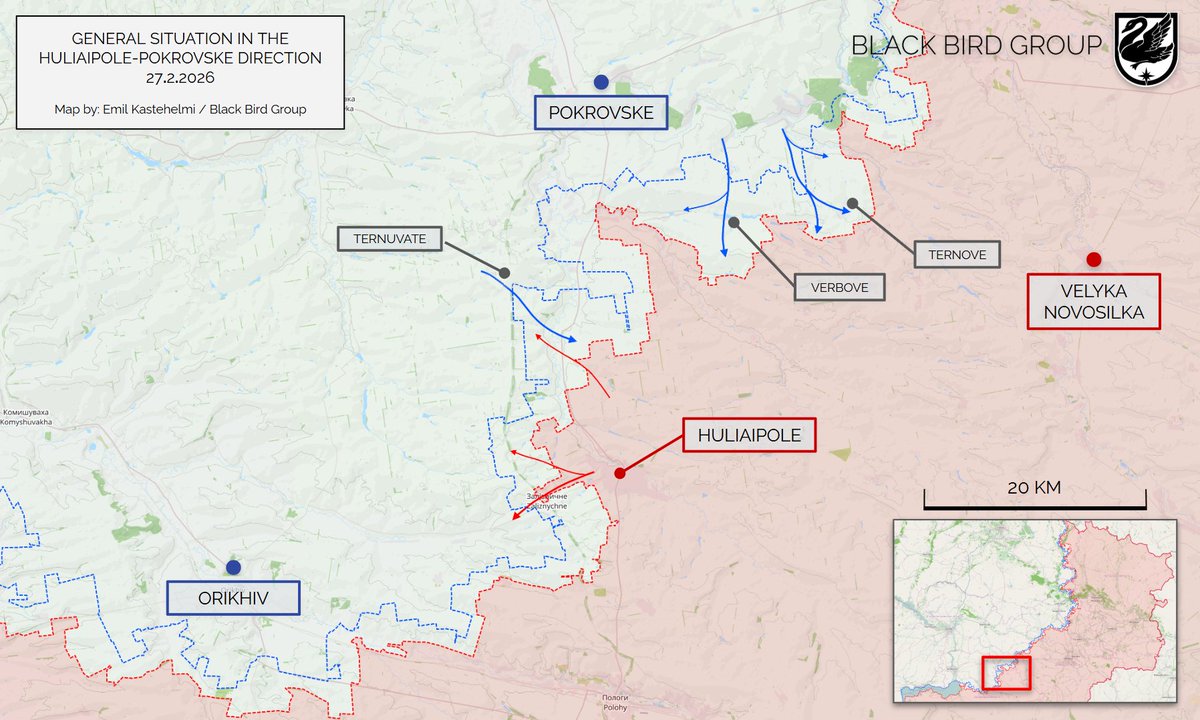
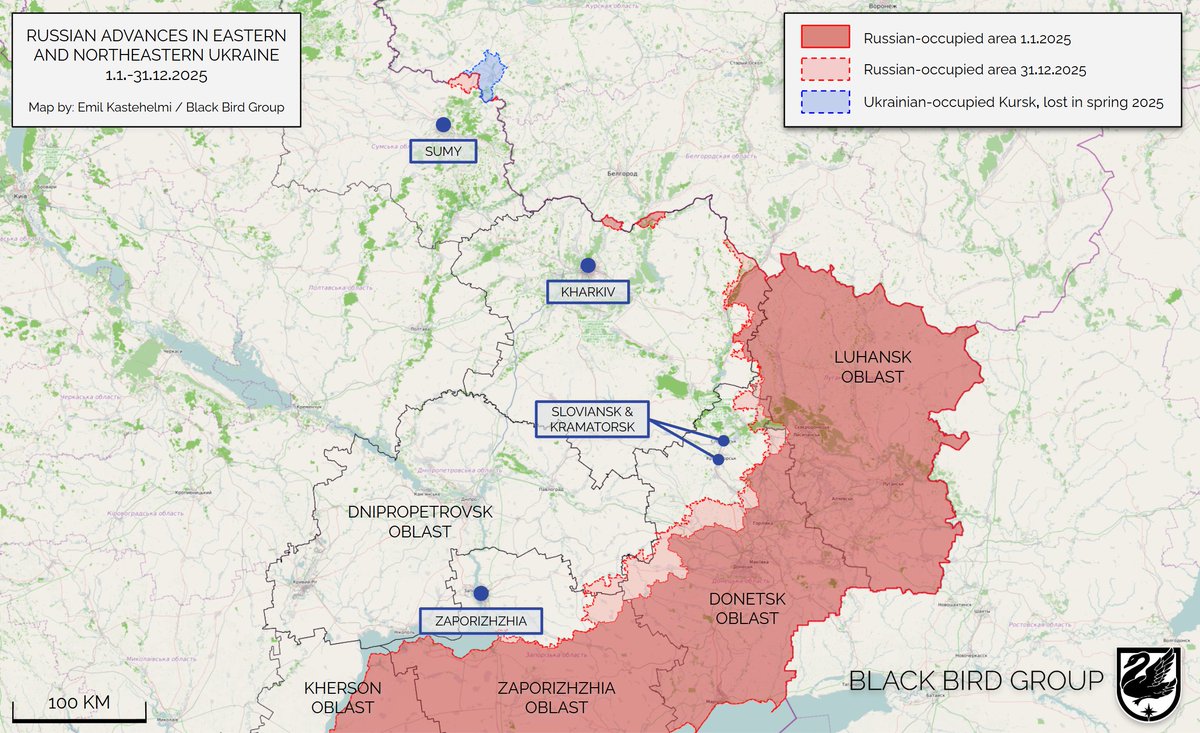
Ukraina on oman ilmoituksensa mukaan vapauttanut kymmeniä kyliä Hersonin alueella. Myös Suomen mediassa lukua on toisteltu melko tiuhaan. Paljon puhuttu vastahyökkäys ei ole kuitenkaan tosiasiassa edennyt juuri lainkaan.
Eli mikä homma? Ketju Hersonin vastahyökkäyksestä 1/🧵
Eli mikä homma? Ketju Hersonin vastahyökkäyksestä 1/🧵
Viime kuukausien aikana Hersonissa on taisteltu aktiivisesti. Ukraina on hiljalleen vapauttanut kyliä toisensa jälkeen pysäytettyään Venähän hyökkäyksen. Venäjä on työnnetty hitaasti kauemmas Kryvyi Rihistä ja Mykolaivista, ja rintaman keskiosa on vakiintunut Inhulets-joelle 2/
Ukrainalaiset ovat siis vapauttaneet kyliä pitkällä aikavälillä. Ukraina on myös viime viikkoina implikoinut, että uusi, suurempi vastahyökkäys olisi toteutumassa. Villeimmät näkemykset Ukrainasta kertovat, että Herson olisi vapaa syyskuuhun mennessä, eli tämän kuun lopussa. 3/
On kuitenkin huomionarvoista, että tämä mediassa paljon puhuttu vastahyökkäys ei vielä näy vapautettuina kylinä. Ukraina viestii siis käytännössä vanhemmilla saavutuksillaan. Esimerkiksi viimeisen kahden viikon aikana ei todellakaan ole vapautettu kymmeniä kyliä. 4/
Jos Herson halutaan vapauttaa syyskuuhun mennessä, on Ukrainalla äärimmäinen kiire. Venäjä on eri tietojen perusteella linnoittanut asemiaan Hersonin suunnalla, eivätkä ukrainalaiset ole välttämättä kohdanneet edes vielä alueen raskaampia puolustusasemia. 5/
On myös epäselvää, mitä Hersonin vapauttaminen tarkoittaa. Puhutaanko pelkästään Hersonin kaupungista vai koko oblastista, joka jatkuu Krimille saakka? Itse uskon tavoitteen olevan rintaman siirto Dnepr-joelle. Sekin vaatii jo hyvin raskaita taisteluita. 6/
Epäilen myös Ukrainalla olevan sisäisiä haasteita vastahyökkäyksen aloittamisen kanssa. Ukraina onnistui tuhoamaan parin viikon sisällä Dneprin ja Inhulets-joen yli meneviä tärkeitä siltoja. Tämä sekoitti venäläisten logistiikkaa, kun tärkeimmät huoltoyhteydet ottovat osumaa. 7/
Vaikuttaa kuitenkin siltä, että Ukraina ei ole onnistunut kunnolla hyödyntämään tätä sekaannusta. Nyt venäläiset ovat saaneet korjailtua tilannetta - lautat kulkevat jokien yli, ponttoonisiltoja on pystytelty ja siltoja korjailtu. Hersoniin on myös tuotu paljon lisäjoukkoja. 8/
Ukrainalla on siis vastassaan merkittävästi vahvennettu vihollinen, joka pystyy myös vastaamaan huoltoyhteyksien vahingoittamiseen. Jos vastahyökkäys todella lähtee täydellä voimalla käyntiin, siitä ei tule helppoa Ukrainalle. Venäjä ei halua luopua Hersonista. 9/
Sotaa on pian käyty jo puoli vuotta. #OSINT-tiimimme tuottaa edelleen yhtä internetin aktiivisimmista tilannekarttapalveluista. Annan myös yhä mielelläni aiheesta haastatteluja medialle. Yhteystiedot löytyvät profiilista. 10/10
scribblemaps.com/maps/view/The-…
scribblemaps.com/maps/view/The-…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh