How does Netflix scale push messaging for millions of devices?
This post draws from an article published on Netflix’s engineering blog. Here’s my understanding of how the online streaming giant’s system works.
This post draws from an article published on Netflix’s engineering blog. Here’s my understanding of how the online streaming giant’s system works.

𝐑𝐞𝐪𝐮𝐢𝐫𝐞𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐬 & 𝐬𝐜𝐚𝐥𝐞
- 220 million users
- Near real-time
- Backend systems need to send notifications to various clients
- Supported clients: iOS, Android, smart TVs, Roku, Amazon FireStick, web browser
- 220 million users
- Near real-time
- Backend systems need to send notifications to various clients
- Supported clients: iOS, Android, smart TVs, Roku, Amazon FireStick, web browser
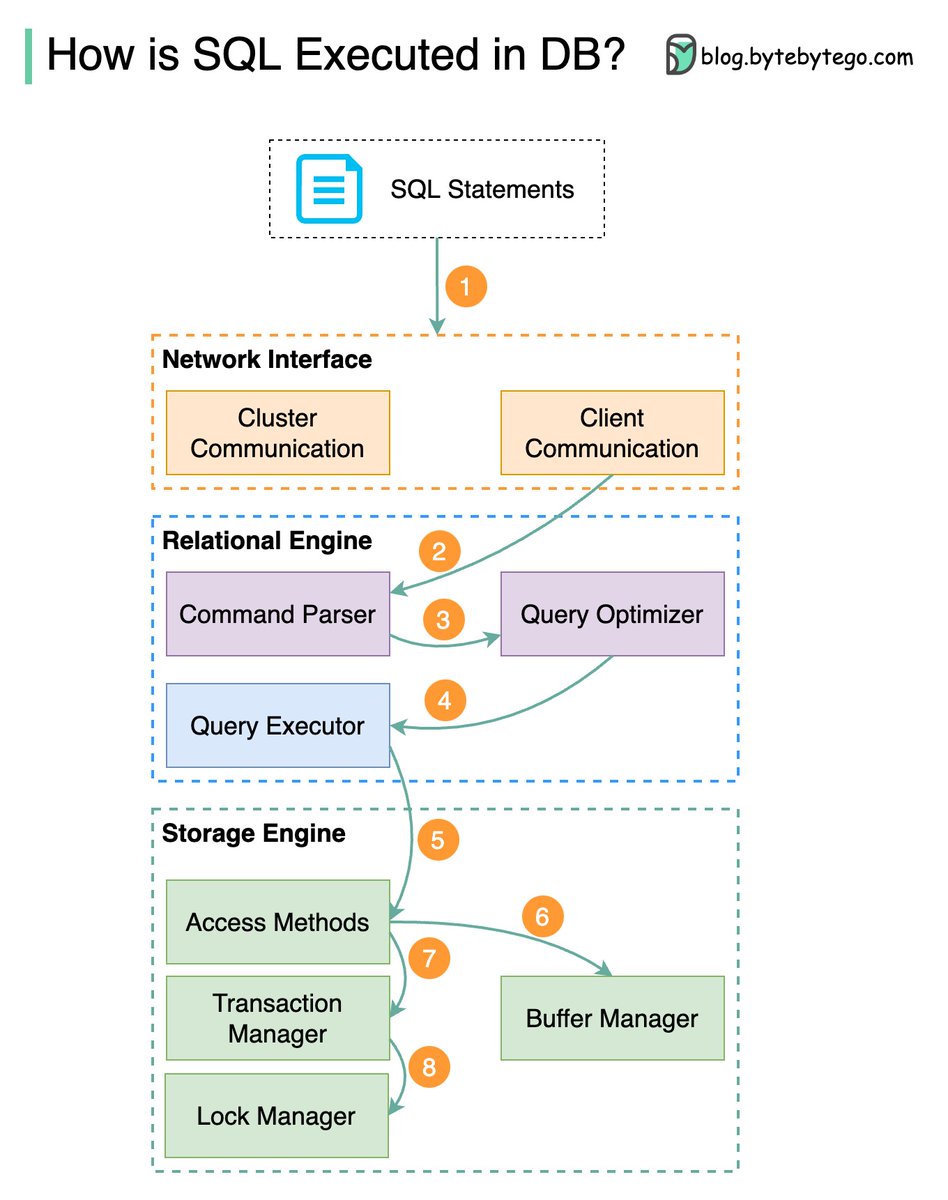
𝐓𝐡𝐞 𝐥𝐢𝐟𝐞 𝐨𝐟 𝐚 𝐩𝐮𝐬𝐡 𝐧𝐨𝐭𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧
1. Push notification events are triggered by the clock, user actions, or by systems.
2. Events are sent to the event management engine.
1. Push notification events are triggered by the clock, user actions, or by systems.
2. Events are sent to the event management engine.

3. The event management engine listens to specific events and forward events to different queues. The queues are populated by priority-based event forwarding rules
4. The “event priority-based processing cluster” processes events and generates push notifications data for devices
4. The “event priority-based processing cluster” processes events and generates push notifications data for devices

5. A Cassandra database is used to store the notification data.
6. A push notification is sent to outbound messaging systems.
6. A push notification is sent to outbound messaging systems.

7. For Android, FCM is used to send push notifications. For Apple devices, APNs are used. For web, TV, and other streaming devices, Netflix’s homegrown solution called ‘Zuul Push’ is used. 

Over to you: if you wanted to support every kind of device, which delivery model would work better, push or pull-based notifications?
Subscribe to our weekly newsletter to learn something new every week ⇩:
bit.ly/3ysfTqW
#systemdesign #coding #interviewtips
bit.ly/3ysfTqW
#systemdesign #coding #interviewtips
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh