1/”Now your mouth will drop when you see the cord compression we caused,” I said to my fellow looking at our targeted #bloodpatch CT, “But take a deep breath—that’s actually what we want.”
A #tweetorial about CSF leaks & blood patches! #medtwitter #CSFleak #neurotwitter #neurorad
A #tweetorial about CSF leaks & blood patches! #medtwitter #CSFleak #neurotwitter #neurorad

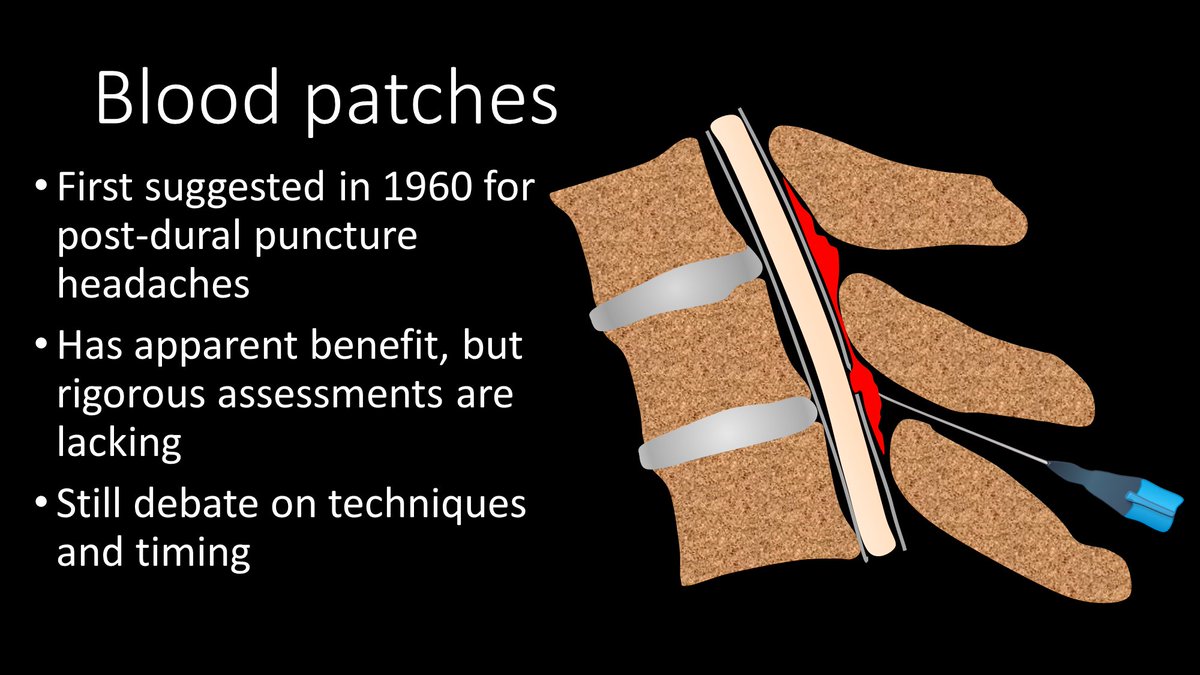
2/Epidural blood patches (EBPs) have been around since the 60s. Blood was first injected in the epidural space to try to plug the leak in post-dural puncture HA. It has now been expanded to other CSF leaks. However, controlled studies are lacking & therefore methods vary greatly 
3/No one is sure of how EBPs work. Some believe blood directly plugs the leak site. Other believe it’s a pressure effect--injected blood increases epidural pressure, squeezing the thecal sac like a stress ball, elevating subarachnoid CSF pressure to relieve low pressure HA. 
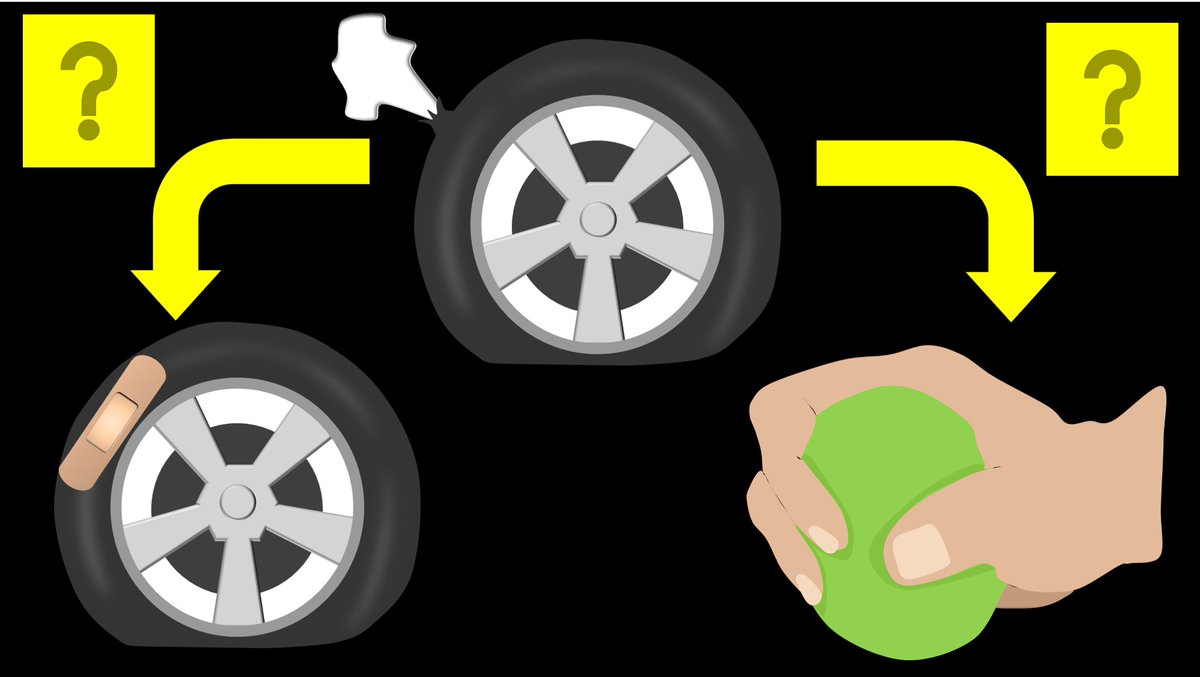
4/In reality, it is probably both mechanisms. The pressure effect is likely what provides the immediate relief from the low pressure HA but the direct plug of the leak is likely what provides the long lasting effectiveness. 

5/Since direct plugging likely gives long term relief, it’s important to patch the leak site, to increase the likelihood the blood will reach the defect. Finding the leak site could fill a whole other tweetorial. Today we will focus on how to treat the site after it’s found. 

6/Leaks occur at 3 main sites: (1) Ventrally, usually from an osteophyte spike tearing the dura (2) At the nerve root sleeve, likely related to a leak from a leaking/torn nerve root sleeve diverticulum (3) Dorsally, usually related to a lumbar puncture or spinal intervention 

7/To get a targeted patch for a ventral leak, a transforaminal approach w/a 22g spinal needle is used to access the ventral epidural space. Care should be taken to avoid the nerve root in the foramen. Both fibrin glue & blood are given to maximize the chance of plugging the leak 

8/For a leak at the nerve root sleeve, a similar approach for a targeted patch is used, except the needle is stopped short in the foramen and blood/fibrin is given in this region. 

9/For a nerve root sleeve leak targeted patch, one should see epidural reflux of contrast, to indicate the whole nerve root sleeve has been coated by the patch. For ventral leaks, it is important to confirm that blood has spread across the ventral epidural space to cover the leak 

10/For a dorsal leak, the traditional interlaminar approach to the epidural space is used. This can be achieved using either fluoroscopy or CT depending on the site.
Choice of injection material/volume can and do vary for all these EBPs depending on the proceduralist
Choice of injection material/volume can and do vary for all these EBPs depending on the proceduralist

11/A significant volume should be given—bc the patch will shrink. I give at least 4cc fibrin & 5-10cc blood—depending on pt tolerance--this guides you. So cord compression is fine, as long as the toes can move. Patch will shrink—like this patch imaged on myelography 3 days later 

12/Here is a 3D rendering of targeted EBPs/fibrin at 2 levels punctured during spinal stimulator insertion. You can see that over half the canal is filled by the patch. I always tell my fellows a little rhyme: Remember thecal sac compression will lead to symptom regression! 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















