#THREAD
@YouGov's May 2022 survey looked at 'The British public’s attitude to the #monarchy: past, present & future.'
Headline: just 62% of Britons think Britain should continue to have a monarchy in the future. 👑🇬🇧
yougov.co.uk/topics/society…
@YouGov's May 2022 survey looked at 'The British public’s attitude to the #monarchy: past, present & future.'
Headline: just 62% of Britons think Britain should continue to have a monarchy in the future. 👑🇬🇧
yougov.co.uk/topics/society…
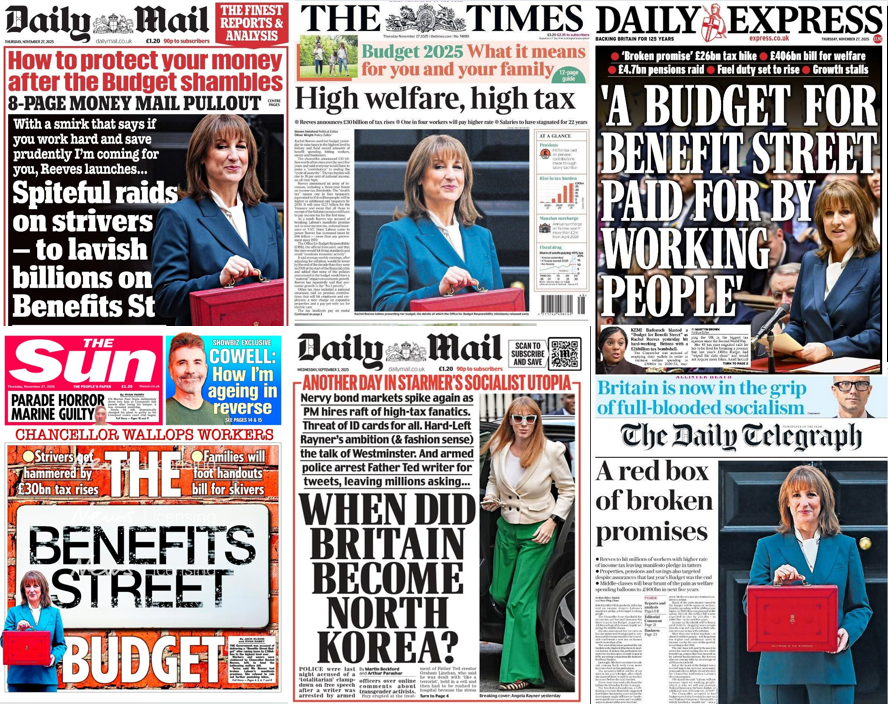
Should Britain continue to have a monarchy?
62% of Britons think Britain should continue to have a monarchy in the future, with 22% saying the country should move to having an elected head of state instead.
62% of Britons think Britain should continue to have a monarchy in the future, with 22% saying the country should move to having an elected head of state instead.

84% of Conservative voters say the monarchy should continue & 9% say we should have an elected head of state.
Labour voters are 48% in favour of a monarchy and 37% in favour of a head of state.
33% of 18 to 24-year-olds favour a monarchy & 31% a head of state.
Labour voters are 48% in favour of a monarchy and 37% in favour of a head of state.
33% of 18 to 24-year-olds favour a monarchy & 31% a head of state.
While the majority of Britons have consistently been in favour of continuing the monarchy, there has been a decline over the last decade, from a high of 75% in favour of a monarchy in July 2012, to 62% in May 2022. 

Young people have lost favour in a monarchical system over the last decade.
In 2011, when YouGov first started tracking the issue, 59% of 18 to 24-year-olds thought the monarchy should continue in Britain, compared to just 33% in May 2022.
In 2011, when YouGov first started tracking the issue, 59% of 18 to 24-year-olds thought the monarchy should continue in Britain, compared to just 33% in May 2022.

Is the institution of the monarchy good or bad for Britain?
56% of Britons feel that the institution of the monarchy is good for Britain, although this percentage has also fallen since December 2012, when 73% of the public saw the monarchy as a good thing for the country.
56% of Britons feel that the institution of the monarchy is good for Britain, although this percentage has also fallen since December 2012, when 73% of the public saw the monarchy as a good thing for the country.

Eight in 10 Conservative voters (80%) see the monarchy as being good for Britain, compared to 44% of Labour voters.
Three-quarters of Britons aged 65 and older (74%) say the same, compared to just 24% of 18 to 24-year-olds.
Three-quarters of Britons aged 65 and older (74%) say the same, compared to just 24% of 18 to 24-year-olds.

Will Britain still have a monarchy in 100 years’ time?
Over the past decade, there has been a shift in opinion about what the monarchy will look like in the future.
Britons are now split on whether the country will still have a monarchy in 100 years’ time.
Over the past decade, there has been a shift in opinion about what the monarchy will look like in the future.
Britons are now split on whether the country will still have a monarchy in 100 years’ time.
In 2011, two-thirds of Britons said they thought there would still be a monarch in 100 years’ time, while just 24% said there would not be one.
In May 2022, 39% say the institution will still be around in a century, & 41% say it will not.
In May 2022, 39% say the institution will still be around in a century, & 41% say it will not.

The British public’s perception of the importance of the monarchy may be affected by proximity to a Jubilee: in 2011, 71% saw the monarchy as being less important to Britain than they were in 1952; in May 2022, 56% of Britons thought the royal family has become less important. 

Even those who feel that the monarchy should continue in Britain are agreed that the royal family play less of an important role today than they did 70 years ago (50%), while just 16% see them as more important and 27% think there has been no change. 

Are Britons still proud of the monarchy?
Britons have become more embarrassed of the monarchy over the last decade: 18% now say they are embarrassed of the Crown, compared to just 8% in 2012.
47% say they are proud of the monarchy today - a drop from 57% in 2012.
Britons have become more embarrassed of the monarchy over the last decade: 18% now say they are embarrassed of the Crown, compared to just 8% in 2012.
47% say they are proud of the monarchy today - a drop from 57% in 2012.

70% of Conservative voters say they are proud of the monarchy.
34% of Labour voters say they are proud of the monarchy, 28% embarrassed, & 35% neither.
61% of Britons aged 65+ are proud.
23% of Britons aged 18-24 are proud, 28% embarrassed & 30% neither proud nor embarrassed.
34% of Labour voters say they are proud of the monarchy, 28% embarrassed, & 35% neither.
61% of Britons aged 65+ are proud.
23% of Britons aged 18-24 are proud, 28% embarrassed & 30% neither proud nor embarrassed.

Is the royal family good value for money?
The royal family is funded by the ‘Sovereign Grant’ (formerly ‘Civil List’), with the Queen normally receiving 15% of the Crown Estate profits & the rest going to the government. In 2020/21, the Crown Estate generated £269m in profit.
The royal family is funded by the ‘Sovereign Grant’ (formerly ‘Civil List’), with the Queen normally receiving 15% of the Crown Estate profits & the rest going to the government. In 2020/21, the Crown Estate generated £269m in profit.
A majority of the public (55%) think that the royal family are good value for money, with 30% saying they are bad value for money.
This figure has declined since the Diamond Jubilee, however, when close to two-thirds (64%) saw the royal family as being good value for money.
This figure has declined since the Diamond Jubilee, however, when close to two-thirds (64%) saw the royal family as being good value for money.

75% of Conservative voters see the royal family as good value for money.
41% of Labour voters say they are good value, & 44% see them as bad value.
69% of Britons aged 65+ say they're good value.
34% of 18 to 24-year-olds say they're good value & 36% say they are not.
41% of Labour voters say they are good value, & 44% see them as bad value.
69% of Britons aged 65+ say they're good value.
34% of 18 to 24-year-olds say they're good value & 36% say they are not.

80% of those who think the monarchy should continue in Britain think the royal family are good value for money, 10% say they are bad value.
13% of those who think the country should have a head of state think the royal family are good value for money, 79% say they're bad value.
13% of those who think the country should have a head of state think the royal family are good value for money, 79% say they're bad value.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh