Non Fungible Token Design: The Structure of Yield Generating Tokens.
My Tutor, @SamuelXeus always said to his community "Never research a tree, but rather, research what makes the tree stand"
Lately, NFT Yield tokens have been mooning, how do they exist to moon?
Follow up 👇
My Tutor, @SamuelXeus always said to his community "Never research a tree, but rather, research what makes the tree stand"
Lately, NFT Yield tokens have been mooning, how do they exist to moon?
Follow up 👇

1/ Projects are building fully sustainable economies around NFTs. Services have been extended beyond Arts, and so, utilities are embedded to ensure holders keep their asset and mitigate downward sell pressure and illiquidity problems. 

2/ The Economic Design NFT collection remains the same as the economic design of Tokens. That is;
• The Market Design,
• The The Mechanism Design and,
• The Token Design.
All of these three are needed to maintain a project's sustainability.
• The Market Design,
• The The Mechanism Design and,
• The Token Design.
All of these three are needed to maintain a project's sustainability.

3/ The Token Design of an NFT Project begins with the formation of a Decentralized Autonomous Organisation after the mint process. Within the DAO, lies the treasury, for DAO management, governance is integrated, and for stable governance, a native token is required. 
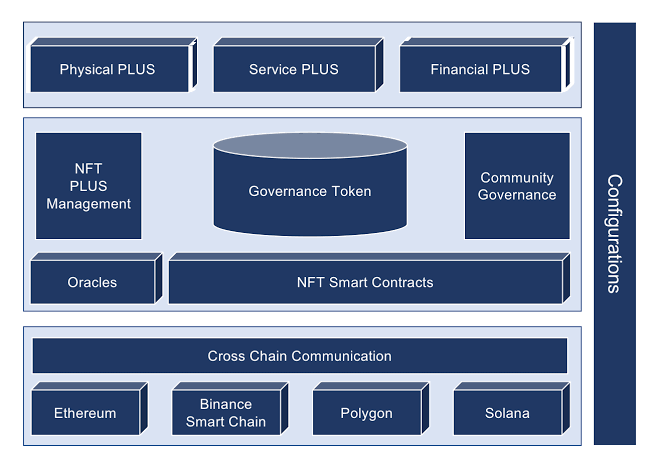
4/ As displayed above, the token design of the economic framework of NFT collection includes;
A. Supply and Inflation Rate.
B. Rarity and Desirability.
C. Revenue Generation Mechanisms
These three factors are important to both the NFT collector and the project itself
A. Supply and Inflation Rate.
B. Rarity and Desirability.
C. Revenue Generation Mechanisms
These three factors are important to both the NFT collector and the project itself

5/ The above Token Design factors creates three basic elements for yield generating token sustainability as related to NFTs. They are
1. The Tokenomics.
2. The Token Utility.
The Tokenomics is simply the factors that impacts a token use and value.
1. The Tokenomics.
2. The Token Utility.
The Tokenomics is simply the factors that impacts a token use and value.

6/ These factors include;
1. Operating Revenue.
2. Effect of Network Growth.
3. Cost of Services.
4. Desiring Value from Utility.
5. Operating Cost.
Within the above, three elements of NFT tokenomics are derived. They are:
• Supply
• Monetary Policy
• Token Distribution
1. Operating Revenue.
2. Effect of Network Growth.
3. Cost of Services.
4. Desiring Value from Utility.
5. Operating Cost.
Within the above, three elements of NFT tokenomics are derived. They are:
• Supply
• Monetary Policy
• Token Distribution

7/ In NFTs, both for the art and the token, supply and monetary are attached together. This is because the supply of NFT yield tokens are discretionary. That is, they are created and distributed with no predefined schedule, but according to the will, or need, of the token issuer.
8/ Therefore, the supply of NFT yield tokens answers the question of how many of that token are existing at present and how many will be existing in the future. Thus, inflation is inclined, meaning, they will both determine the collection of the NFTs. That is why they are bonded.
9/ Inflation, in a simple term, is the reduction or decrease in the purchasing power of the Token. The major cause of token inflation is EMISSION, afterwards, staking is involved. It is almost related to a DeFi token inflation. Check my article: medium.com/@RubiksWeb3/to…
10/ For Token Distribution, there is no Token Generation Event, neither is there a burning schedule, only emissions. The emission involves the rate at which the tokens are produced and issued. It is issued on a daily basis, which is minted per day as a revenue stream for holders
11/ Yield tokens also have a supply cap, that is, the total number of years at which the whole tokens will be released. For example, $Banana token of @CyberKongz has 10 years emission over 10 $Banana daily production. Meaning that, 3,650,000 $Banana will be emitted in 10 years. 

12/ @coolcatsnft is another great example, it yields a baseline of 1000 $Milk per day, with some generating more depending on the NFT tier at highest daily yield of 450 $Milk.
@CetsOnCreck has a 4.2 $Creck daily yield and 5.25 $creck for am upgraded Cet, based on staking.
@CetsOnCreck has a 4.2 $Creck daily yield and 5.25 $creck for am upgraded Cet, based on staking.

13/ Token Utility, which is the second element of designing yield generating NFT tokens, is a Demand function. It is highly necessary and important. It answers the question of why people should hold the token. Therefore, it involves activities beyond staking and emissions. 

14/ Attached to the demand mechanism, which binds the token utility is the Network Value. The underlying value is captured in the token behavior, and it is the representation of the level of trust towards the network itself and the utility the token can provide to it's holders. 

15/ This Implies that, price fluctuations are driven by the supply and demand equilibrium. Network driven demand may arise, for example, from the token usage to access services, and in the case of fixed supply, leads to increase in price.
16/ The token supply, can also be adjusted by the token issuer to create inflationary or deflationary trends with direct consequences on the token value.
17/ Overflowing Importance of NFT Yield Generating Tokens
1. Access: The token grants access to services and activities within a DAO. Tokens are used as a raffle base to get whitelists from other projects. @VandalCityCorp was raflled to some people with the @DeGodsNFT $dust token
1. Access: The token grants access to services and activities within a DAO. Tokens are used as a raffle base to get whitelists from other projects. @VandalCityCorp was raflled to some people with the @DeGodsNFT $dust token
18/
2. Revenue: The token acts as a substitute for fiat currencies in the intermediation of economic transactions within and outside the DAO. It is therefore used to collect payments for services and contents.
A very good example is @droidcapital. They engage in DAO trading.
2. Revenue: The token acts as a substitute for fiat currencies in the intermediation of economic transactions within and outside the DAO. It is therefore used to collect payments for services and contents.
A very good example is @droidcapital. They engage in DAO trading.

19/
3. Discounts: Discount on services are attached to the NFT holders with the token. The partnership mechanism for @droidcapital show this feature.
4. Governance: Tokens are used to shape the DAO rules, influencing it's evolution and being actively occupied with voting rights.
3. Discounts: Discount on services are attached to the NFT holders with the token. The partnership mechanism for @droidcapital show this feature.
4. Governance: Tokens are used to shape the DAO rules, influencing it's evolution and being actively occupied with voting rights.

20/
5. Reputation: The token is a way to quantify and account for the project's reputation in the NFT Space as well as within the ecosystem. This is a fundamental fact to help reinforce widespread trust among the DAO members and emerging utilizers. $dust of DeGods is an example.
5. Reputation: The token is a way to quantify and account for the project's reputation in the NFT Space as well as within the ecosystem. This is a fundamental fact to help reinforce widespread trust among the DAO members and emerging utilizers. $dust of DeGods is an example.
Lately, there had been a surge in the demand for NFT yield tokens. This is based on the activities of the project in building the value attached to the token via utility. It is a pleasure to give a detailed write-up on the structure of the outlook. Read with pleasure and enjoy.
Also, do not hesitate to like, retweet, follow, and share.
Click on the medium link I'm my bio to read articles related to Token Economics.
#NFTs #Web3 #NFTProjects #token #Tokenomics #tokendesign #yields
Click on the medium link I'm my bio to read articles related to Token Economics.
#NFTs #Web3 #NFTProjects #token #Tokenomics #tokendesign #yields
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh



















