Operational CATOBAR Aircraft Carriers and their Air Wing (late 2010s). Let’s look at the air wing composition of the Nimitz Class and Charles de Gaulle and see how they compare.
#USNavy #Aircraft #Military #Jets
#USNavy #Aircraft #Military #Jets

But first, we will look at the role and capabilities of each aircraft. We will take the Nimitz Class’s air wing as an example.
Quick note: The next infographic will cover the evolution of these carriers, their air wings and China’s arrival to the club
Quick note: The next infographic will cover the evolution of these carriers, their air wings and China’s arrival to the club
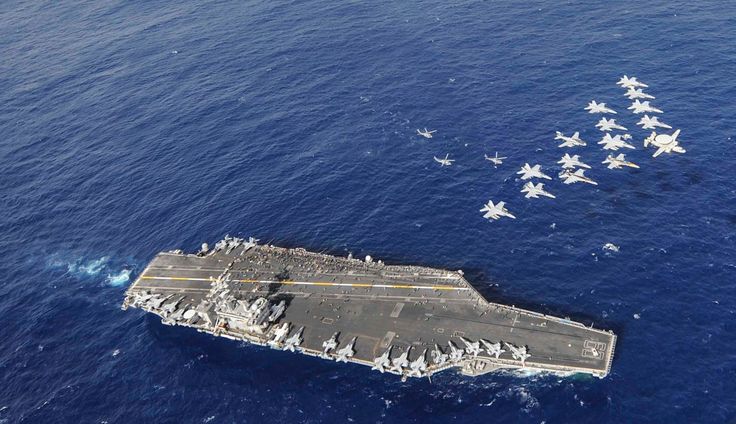

The US Carrier Air Wing (CVW) has x44 F/A-18 Super Hornet multirole fighter. Meaning it can do almost any mission an aircraft could do: Air to Air engagements, Ground strikes, Anti-Ship, Suppression of Air defence… They are the main weapon of the carrier 
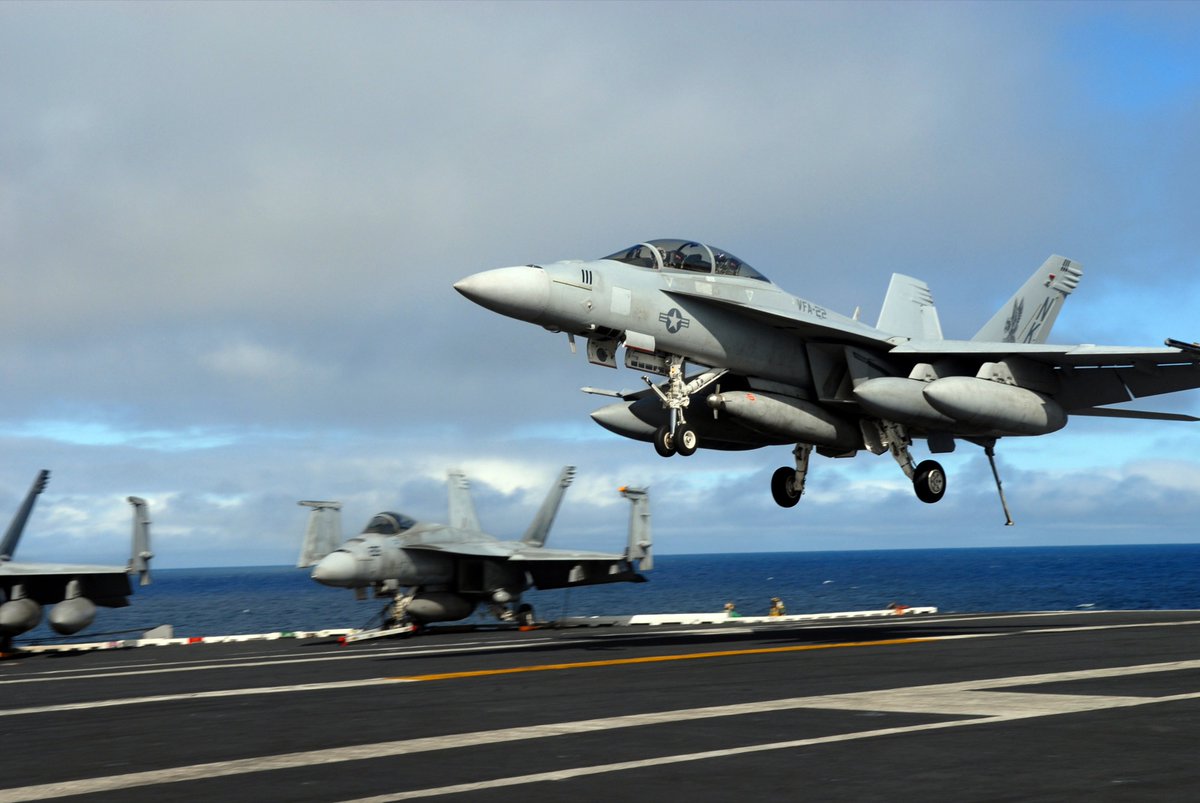

Various specialised aircraft also support those fighters: x5 EA-18G Growlers provide dedicated electronic warfare capability. In short, the Growler can disrupt the enemy’s communication or radar by interfering with the radio waves it uses 

This gives an extra layer of passive protection to attacking aircraft that need to approach a target that has the range to defend itself
The CVW also has x4 E-2C Hawkeyes. These planes with powerful radars enable them to detect threats from far away and transmit the info to any friendly units around. They are the eyes of the carrier group 

The helicopters on board support the carrier directly. They offer a dedicated anti-submarine capability, S&R, transport cargo or personnel, or provide ISR. There is also the possibility of carrying x2 C-2A Greyhounds for transport and logistics. 



So how do the two air wings compare? The major difference is in numbers. The CDG being smaller, can carry fewer aircraft: x36 Rafales against x44 F/A 18s. However, the difference is principally reflected in the number of supporting aircraft 



The CDG has x2 E-2C Hawkeyes, and this is a significant difference. For example, the CDG can cover one zone with two rotating Hawkeyes, whereas the US CVW can cover two zones simultaneously. The CDG also has x2 helicopters compared to the 19 available to the US carrier. 

This means that the CDG relies more on its escorts for protection against submarines than the Nimitz Class carriers. We can also note the lack of a dedicated EW aircraft. 

Having more numbers enables you to take more punches before getting knocked out of the fight. With such a massive number of embarked aircraft and aircraft carriers, the US Navy has a better ability to sustain losses than the French Navy. 

However, it is important to put this comparison back into perspective. Having an aircraft carrier with catapults in the first place is in itself a considerable capability boosts for a navy. Catapults enable to launch heavier aircraft and extend the range of lighter ones. 

Carriers with ski jumps, like those in the Royal Navy, PLAN, or the Marina Militare, are limited in terms of strike range and cannot launch Airborne Early Warning aircraft 







By having the Charles de Gaulle, the French hold a major tool for force projection around the world while having a much more limited budget than the US. For example, in 2019, the US spent 732 billion$ on its defence budget while France spent 50.1 billion$. 

Finally, a Nimitz class carrier displaces 100,000t compared to Charles de Gaulle’s 42,500t. With less than half of the displacement, the CDG still holds a powerful embarked air wing. 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh