So new EU #Russia #sanctions package just dropped yesterday. You're curious what's in it, but don't have the time go through it!
Lucky for you: I've got you covered. I just spend the entire night dissecting every line. Here is what's in it.
Lucky for you: I've got you covered. I just spend the entire night dissecting every line. Here is what's in it.
EU changed 3 areas of law:
1/ Asset freezes/visa bans, adding new 30 individuals and 7 entities (incl. Alexander Dugin);
2/ Major Russia sanctions law, by adding new restrictions, incl. oil price cap; and
3/ Embargo on Donetsk/Luhansk.
I will analyze these in turn.
1/ Asset freezes/visa bans, adding new 30 individuals and 7 entities (incl. Alexander Dugin);
2/ Major Russia sanctions law, by adding new restrictions, incl. oil price cap; and
3/ Embargo on Donetsk/Luhansk.
I will analyze these in turn.
As for individuals designations (asset freezes/entry bans), the EU listed additional 30 individuals and 7 entities. The total number is now at 1262 individuals and 118 entities. 3/
Among new individuals we have:
-10 persons involved in conducting illegal referenda in Zaporizhzhia, Kherson, Donetsk & Luhansk (2 from Russian Central Election Commission - Chair & Deputy, 2 from the State Council, 6 from local structures at Zaporizhzhia, Kherson & Donetsk);
4/
-10 persons involved in conducting illegal referenda in Zaporizhzhia, Kherson, Donetsk & Luhansk (2 from Russian Central Election Commission - Chair & Deputy, 2 from the State Council, 6 from local structures at Zaporizhzhia, Kherson & Donetsk);
4/
- 4 persons from local pseudo-governmental structures in Donetsk & Luhansk;
- 6 Deputy Ministers of Defence (how many do they have in total? 😏);
- 2 from Russian Army (Gen. Ryzhkov & G. Zhidko);
5/
- 6 Deputy Ministers of Defence (how many do they have in total? 😏);
- 2 from Russian Army (Gen. Ryzhkov & G. Zhidko);
5/
- 1 from FSB (V Kulishov - Head of RUS Border Service listed for systemic "filtration operations" & forced deportations of Ukrainians from occupied territories)
- 1 from Federal Service for Military Technical Cooperation FSVTS which controls military coop w/ 3rd countries;
6/
- 1 from Federal Service for Military Technical Cooperation FSVTS which controls military coop w/ 3rd countries;
6/
- 2 businessmen (Lushnikov - largest shareholder of Kalashnikov Concern & Kochkin - Executive Director of Tecmash - key designer of missiles and munitions used by the Russian army)
7/
7/
- 3 singers/musicians (Yulia Chicherina,Nikolay Rastorguev, Oleg Gazmanov) for participating in pro-war and anti-Ukraine rallies and concerts for soldiers);
8/
8/
- and - last but not least - ALEXANDER DUGIN for promoting ideas that justified annexation of Crimea and attack on Ukraine.
It's just not his year, is it. 😏
The full justification for listing Dugin is below. 👇
9/
It's just not his year, is it. 😏
The full justification for listing Dugin is below. 👇
9/

EU also listed 7 new entities, incl. 5 defence manufacturers (eg. S300/400 & TOR missile system designer MKB Fakel, manufacturer MMZ Avangard & aircraft manufacturer Irkut), secure documents (passports, banknotes) manufacturer Goznak & Russian Central Election Commission.
10/
10/
Second, related to assess freezes: the EU also created a new grounds for listing (e.g. subjecting to sanctions) of foreign companies and individuals that facilitate EU persons violation of EU sanctions.
11/
11/

There are no specific foreign companies sanctioned yet, but this signals that EU now can - if it decides to - sanction non-EU companies if they are engaged in helping EU entities engage in forbidden transactions.
/12
/12
This is quite a U-turn for EU, which has until recently been complaining abt US applying its sanctions to non-US companies extraterritorially. It now appears EU is discovering it too needs to have a weapon against 3rd country entities entangled in EU sanctions circumvention
/13
/13
Third, EU has also relaxed two asset freeze provisions related to Kamaz and to National Settlement Depository, allowing EU parties to terminate their relationships with these entities. The details are unclear, but I'll take a guess.
/14
/14
With Kamaz, it seems that someone in the EU may have a JV with one of these guys 👇(may be Kamaz, or someone else) & needs to cash out, but can't find a buyer. So they'll most likely sell to Kamaz, but for this they need an exemption to make the payment.
/15
/15

The other exemption is for Nat'l Settlement Depository, Russia's largest securities depository owned by Moscow Exchange. It functions as RU's domestic paying agent (like Euroclear/Clearstream). It was sanctioned in June 2022 and its challenging these sanctions in EU courts.
/17
/17
The exemption allows unfreezing of frozen assets or payments to NSD necessary for termination, before 7/1/23 of operations, contracts or other agreements concluded before 3/6/22.
So some EU party has three months to wrap things up with NSD.
/18
So some EU party has three months to wrap things up with NSD.
/18
So now we move to amendments to the big sanctions regulation, Reg. 833, the consolidated version of which now has over 200 pp.
/19
/19
The first big one is the infamous oil price cap. Once a price is established, EU introduces a complete ban on transport, including ship-to-ship transfers, to third countries, of Russian crude oil (from 4/12/22) and petroleum products (from 5/2/23), unless the cap is met.
/20
/20
The cap itself is established by the G7 "Price Cap Coalition" (not defined in EU law) and introduced into the EU legal system unanimously by a Council Decision inserting the price cap into the Annex to the sanctions law.
/21
/21
The EU hasn't introduced a cap yet, but it has already exempted shipments to Japan of crude oil for the Sakhalin-2 project in Russia from any future price cap. 👇
/22
/22

When once-stablished price cap is changed, a 90 day grace period will continue in effect to cover deliveries under pre-existing contracts that meet the previous cap.
/23
/23
Finally, the cap will not extend to shipments of non-Russian crude and petroleum products that were only transshipped through Russia.
/24
/24
The second - minor - is a correction made to ban on assistance and brokering related to petroleum products.
The original ban on imports of crude oil enters into force on 5/12/22, and the ban on imports of petroleum products enters into force on 5/2/23.
/25
The original ban on imports of crude oil enters into force on 5/12/22, and the ban on imports of petroleum products enters into force on 5/2/23.
/25
But when the EU introduced a ban on technical assistance, brokering services, financing and financing assistance to transport of crude oil and petroleum products to 3rd countries, the ban entered into force on one date: 5/12/22. There was no delay for petroleum products.
/26
/26
So now the EU separated both dates and the ban on technical assistence, financing, etc for crude oil enters on 5/12/22, but for petroleum products it enters on the same date as the EU's own import embargo on petroleum products: 5/2/23.
/27
/27
(that was too technical maybe, sorry)
/28
/28
The EU also allowed the paying out of insurance claims after the embargo on crude oil and petroleum products enters into force. This is necessary, as it could be deemed prohibited as "financing" or "financial assistance".
(but this too, is minor)
/29
(but this too, is minor)
/29
The second big new sanction is - in my view - MONUMENTAL. This is the extension of the steel import embargo, to products "processed in third countries", but incorporating Russian iron and steel products.
/30
/30
I cannot stress this enough. This is BIG. Essentially, under Russian sanctions, the EU is banning imports of certain steel and iron products from ANY COUNTRY, if they are made from Russian steel and iron.
These are secondary sanctions, in a way. Extraterritorial.
/31
These are secondary sanctions, in a way. Extraterritorial.
/31
For example, a Turkish or Chinese steel product will not be able to enter into the EU, if its made from Russian input. Mentally, the EU just completely reversed years of its sanctions policy.
If extended to other products (oil, gas), this could have MASSIVE implications.
/32
If extended to other products (oil, gas), this could have MASSIVE implications.
/32
It could close the EU market to any foreign products (Chinese, Indian, Turkish, etc) if made from Russian components. Essentially, the EU is exporting its import ban on Russia to other countries.
/33
/33
If you are a Chinese producer targetting the EU market, will you risk buying from the Russians? I don't think you will.
/34
/34
(need to take a short break, I'll be back with this shortly)
Regarding the timing, this new embargo on third country steel & iron products incorporating Russian input is introduced with a significant delay: most products are banned as from 30 Sept. 2023 (so one year), while others from 1 April 2024 or 1 October 2024.
/35
/35
Regarding the scope, this new embargo covers all 3rd country products, which would be banned if coming from Russia, and if they use Russian inputs which are also banned. So...
/36
/36
... it may be thus perceived as an anti-circumvention measure of sorts, but given the language of the provision and long list of banned products Product A manufactured in China, if made from Russian Product B would be banned, if both products A & B are listed as banned.
/37
/37
So a Chinese steel product could be banned if made from a highly transformed Russian products.
We're moving into secondary sanctions territory.
/38
We're moving into secondary sanctions territory.
/38
The third interesting change with respect to steel embargo: the EU introduced import quotas for two products: CN 7207.12.10 (abt 3.7 mln t per year, for 2 years) & CN 7207.11 (decreasing in 3 steps, until April 2024).
Clearly, some steel users successfully fought back.
/39
Clearly, some steel users successfully fought back.
/39

Fourth import sanction: the list of products that "generate significant revenues for Russia" and their import is prohibited got significantly extended by 120 customs headings, including chemicals, paper products, textiles, semi-precious stones, machinery, etc.
/40


/40

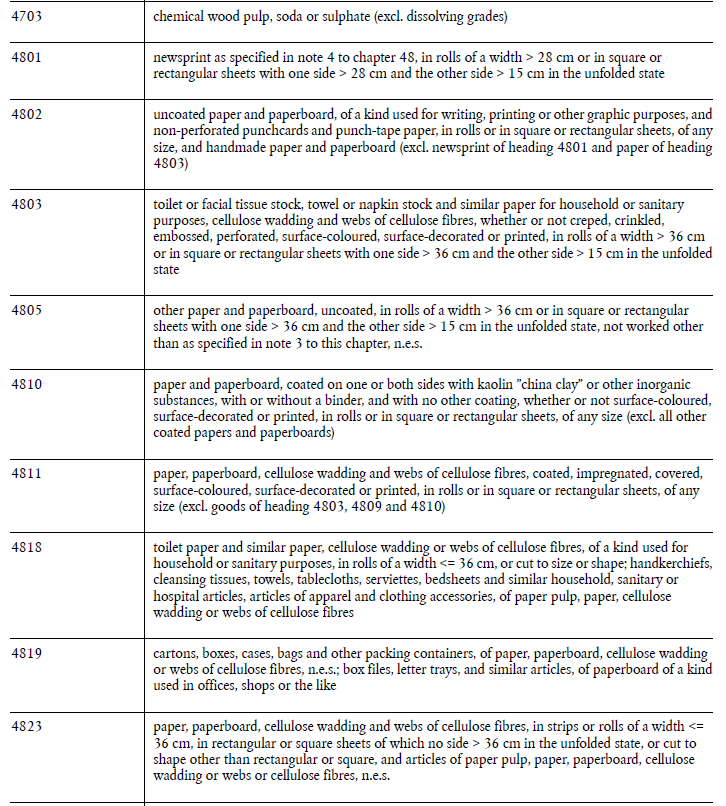

As usual, there is grandfathering clause allowing conclusion - until 8 January 2023 - of contracts for these products, entered before 7 October 2022 (today). 🗓️
/41
/41
The fifth change - I should have included this when discussing the steel embargo - is that the list of products got significantly extended. The EU added 40 full customs headings (4-digit) of steel products banned for import to the EU.
/42
/42
Some of them had already been banned earlier, as specific 8-digit products, but now entire headings are banned.
There is also a grandfathering clause for the newly banned steel products - must be imported by 8 January 2023, if based on a contract predating 7 Oct. 2022.
/43
There is also a grandfathering clause for the newly banned steel products - must be imported by 8 January 2023, if based on a contract predating 7 Oct. 2022.
/43
Sixth import/export change. The EU has previously banned exports to Russia or for use in Russia of goods and technology suited for use in aviation ✈️or space 🪐🚀industry.
This, until yesterday, included only "aircraft, spacecraft and parts thereof."
/44
This, until yesterday, included only "aircraft, spacecraft and parts thereof."
/44
So now EU extended this ban to also include some other items, including oils, tyres, brake parts, and some apparatus and instruments. 👇
/45
/45
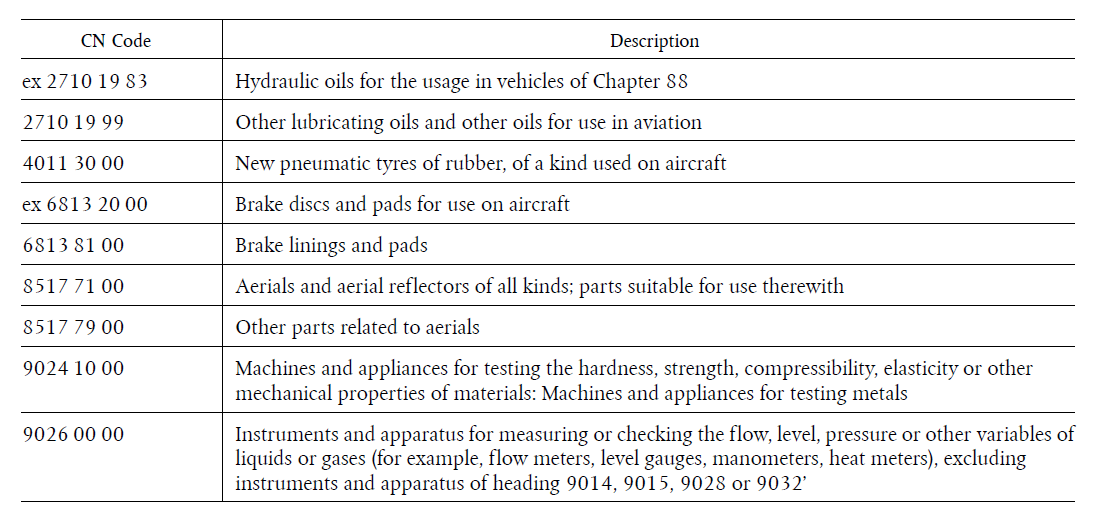
As usual, a grandfathering clause allows execution - until 6 November 2022 of contracts entered before 7 October 2022.
/46
/46
The final change among trade measures, is insertion of a grandfathering clause to EU ban on exporting to Russia or for use in Russia of items that "could contribute to the enhacement of Russian industrial capacities".
/47
/47
This list now includes almost 700 tariff subheadings (6-digit), ranging from gases (hydrogen, nitrogen), chemicals, dies, paints, oils, photographic equip, catalysts, plastics, rubbers, wood & paper products, fabrics, building components, ceramic items, glass equipment, ...
/48
/48
... iron, steel & metal products, machinery, electrical equipment, telecom items, tractors, special purpose vehicles and others.
Impressive list of industrial stuff you can't ship to Russia.
/49
Impressive list of industrial stuff you can't ship to Russia.
/49
The EU now added coal, lignite, peat, coke and... this 👇 machinery/equipment, whatever this it....🤓
As usual, a grandfathering clause was introduced for the first our items, allowing execution of previous entered into contracts, until 8 January 2022.
/50
As usual, a grandfathering clause was introduced for the first our items, allowing execution of previous entered into contracts, until 8 January 2022.
/50

This concludes the import/export part of the new sanctions package. Now we go to services, investment and others.
(Don't worry. Another 70 tweets and we'll get there). 😉
/51
(Don't worry. Another 70 tweets and we'll get there). 😉
/51
Previously, the EU banned provision of certain professional services, such as accounting, auditing, bookkeeping, tax consulting, business & management consulting as well as PR services to the Russian government and any persons in Russia.
/52
/52
This has now been extended to architectural, engineering, legal advisory and IT consultancy services.
For some reason, the EU did not decide to legally define what's what, but includes some non-binding clarification in the recitals. 👇
/53
For some reason, the EU did not decide to legally define what's what, but includes some non-binding clarification in the recitals. 👇
/53

There are numerous exceptions to this of course. The main ones - covered already by the definition - relate to keeping the right to defence and legal representation in judicial proceedings and necessary for access to arbitration, judicial and administrative proceedings.
/54
/54
Other exemptions are for Russian subsidiaries of EU-entities or for services necessary for health emergencies.
/55
/55
EU Member States can also authorize some transactions: humanitarian, civil society, diplomatic, consular context, but also to ensure critical energy supply, import of important inputs such as titanium, aluminium, copper, nickel, palladium or iron ore.
Wishful thinking! 😉
/56
Wishful thinking! 😉
/56
The second change related to services relates to the ban on providing crypto-asset wallet, account or custody services to Russian persons. Previously, this ban only applied when the total value of the crypto-assets acceded 10 000 €. Now this value limit has been removed.
/57
/57
The third - and possibly the most media-spectacular -change is the ban on any European to hold any post in the governing bodies of certain publicly owned Russian companies.
I would call this "the Schroeder clause". 😈
/58
I would call this "the Schroeder clause". 😈
/58
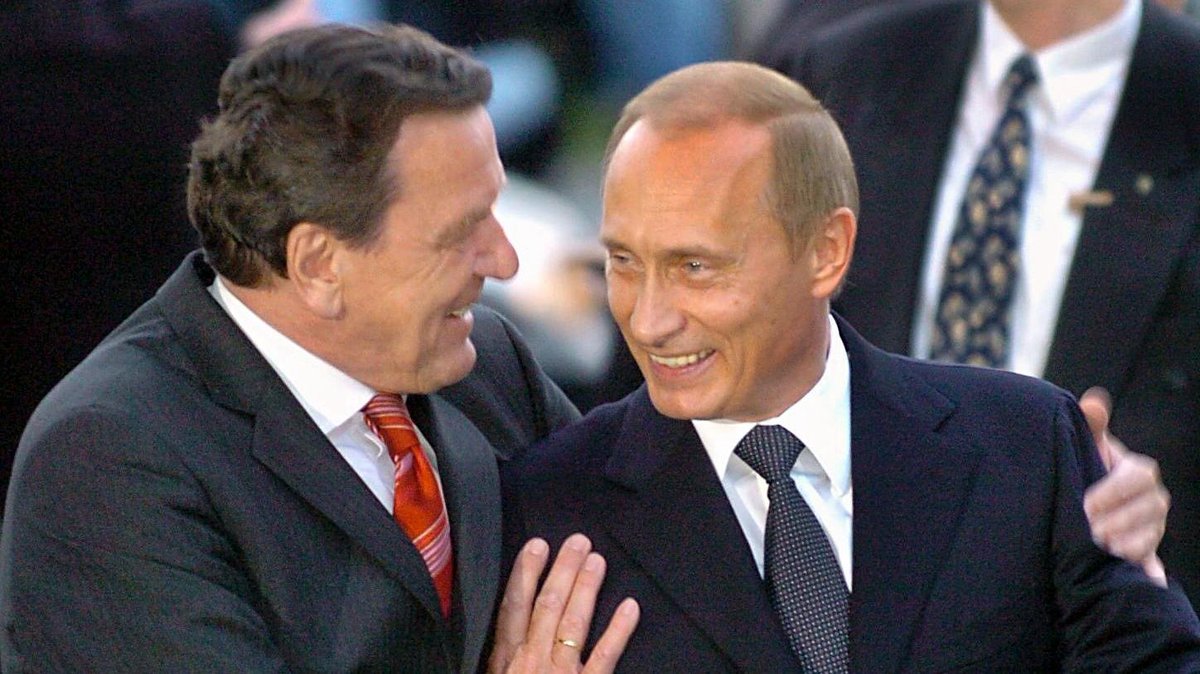

This will mostly apply to Russian companies, publicly controlled, or with over 50% public ownership or in which Russian government or its Central Bank has the right to participate in profits or has a significant economic stake.
/59
/59
These companies are listed in the Annex and include Rosneft, Gazprom Neft, TransNeft and so on. 👇
/60
/60

I'd say its sad that Gerhard S. quit the Rosneft board a few months ago as we'd have sanctions have an immediate impact on him.
/61
reuters.com/business/energ…
/61
reuters.com/business/energ…
I don't follow Russian corporate developments closely, so I am not aware if any of the above companies has any European board members, but it is probably a step in the right direction.
/62
/62
Moreover, given the obvious lack of self-restraint among Europeans in serving dubious Russian companies and the ongoing war, this restriction should probably be extended to private Russian companies as well for the time being.
/63
/63
Compare the situation of former German Chancellor Schroeder (Rosneft Board), former Austrian foreign minister Karin Kneissl (Rosneft Board) and former French Prime Minister Francois Fillon (Sibur Board).
/64
/64
Schroeder and Kneissl would be covered, but Fillon not, even though obviously Sibur, though not public, is extremely well-connected to Russian politics via its owners oligarchs Mikhelson and Timchenko.
/65
/65
One more thing: there was a discussion whether such a ban should extend to former EU leaders, government members of EU or EU Member State, former prime ministers, ministers, etc. I think that ultimately, legal reasons under EU law resulted in an overall ban.
/66
/66
The EU also decided to sanction in numerous ways the Russian Maritime Register of Shipping, which is involved in classification and inspection of Russian ships.
/67
/67
First, the EU added RMRS to the list of public companies (mentioned a few tweets above) which is covered by a ban for EU nationals to hold any post in their governing bodies.
/68
/68
These companies are also subject to a wide ban on any transactions (though there are some narrow exceptions in law and Member States can authorize some). So now that RMRS is added to this list, it is now also covered by this ban.
/69
/69
The EU has also decided a number of other sanctions on RMRS:
=> to withdraw the EU's recognition from the RMRS,
=> to withdraw authorizations granted to the RMRS by EU Member States, and
=> to extend port access and lock back to vessels certified by RMRS.
/70
=> to withdraw the EU's recognition from the RMRS,
=> to withdraw authorizations granted to the RMRS by EU Member States, and
=> to extend port access and lock back to vessels certified by RMRS.
/70
By way of background, in April this year the EU introduced a ban on access to EU ports and locks for vessels flying the Russian flag. The new sanction extends this ban also to non-Russian vessels, but certified by RMRS.
/71
/71
And this concludes the review of all new sanctions introduced into the main Russia sanctions package, mainly in Council Regulation 833/2014.
So now we are left with the third topic: Donbas/Luhansk sanctions.
/72
So now we are left with the third topic: Donbas/Luhansk sanctions.
/72
By way of background: after Russia's annexation of Crimea/Sevastopol in 2014, EU introduced in June 2014 an embargo on Crimea and Sevastopol. It consisted first of import ban on exports from there, but was later extended to an export ban in some sectors, investment ban, etc.
/73
/73
So when Russia decided to annex Luhansk and Donetsk in February 2014, the EU responded with a similar sanctions package, modelled on the Crimea example: total import ban, export ban in many sectors (telecom, transport, energy, raw materials), investment ban etc.
/74
/74
So now that Russia has conducted sham referenda in parts of Donetsk, Kherson, Luhansk and Zaprizhzhia and then annexed these territories, the EU decided to expand its already existing sanctions package to these new territories.
/75
/75
So in practical terms, the Donets/Luhansk embargo regulation & decision now have a new title & a new territorial scope:
"non-government controlled areas of Ukraine in the oblasts of Donetsk, Kherson, Luhansk, and Zaporozhzhia".
No other meaningful changes have been made.
/76
"non-government controlled areas of Ukraine in the oblasts of Donetsk, Kherson, Luhansk, and Zaporozhzhia".
No other meaningful changes have been made.
/76

And that's it! We have gone through the entire new sanctions package:
=> changes to the asset freeze/visa ban (mainly new listings);
=> various new sanctions in the major Russia economic sanctions law (Reg. 833/2014); and
=> update of the Donetsk/Luhansk embargo law.
/77
=> changes to the asset freeze/visa ban (mainly new listings);
=> various new sanctions in the major Russia economic sanctions law (Reg. 833/2014); and
=> update of the Donetsk/Luhansk embargo law.
/77
If you've made it this far, it means you may be a #sanctions wonk, you dont have a life, I may owe you a beer 🍺(or you owe me three), or all of the above!
Thank you for bearing with this loooong thread.
If you have any questions, ask here or DM me.
Until next time.
78/78
Thank you for bearing with this loooong thread.
If you have any questions, ask here or DM me.
Until next time.
78/78
. I need to come back to one issue which I should have pointed out when discussing the import/export bans. Thank you @damspleet for inquiring about this. /79/
The EU has in place a ban on exports to Russia of goods and technology which might contribute to RU military and technological enhancement or development of defence and security sector.👇 /80 

This was introduced immediately following the break out of the war (25-Feb-2022). The goods and technologies covered by the ban are listed in an Annex. This Annex has been expanded over time (March, April, June) and currently spans over 56 pages. /81
It includes electronics (microprocessors, circuits, converters, cells, electronic assemblies, etc. and equipment to manufacture & inspect them), computers (incl. software), telecom equipment, sensors & lasers, navigation, avionics & marine equipment (systems, software)...
/82
/82
.... aerospace/propulsion (engines, test equipment, tooling, software), others (equipment for oil production/explaration, cryogenic refrigeration), special materials (fingerprinting powders, special chemical compouds) & materials processing (explosives & detonation systems).
/83
/83
The above is just to give you a taste. Its very long and very detailed.
/84
/84
Anyway, the EU now expanded this list by adding:
=> weapons and devices for riot control & self protection, incl. items to disseminate toxic gases;
=> poisons used in executions;
=> certain chemicals (mercury, sulphuric acid);
=> semiconductors items;
..
/85
=> weapons and devices for riot control & self protection, incl. items to disseminate toxic gases;
=> poisons used in executions;
=> certain chemicals (mercury, sulphuric acid);
=> semiconductors items;
..
/85
=> integrated circuits, and
=> special cameras for underwater use, aerial survey, medical or surgical use, or for forensic or criminological purposes.
/86
=> special cameras for underwater use, aerial survey, medical or surgical use, or for forensic or criminological purposes.
/86
All these items cannot now be exported to RUS or for use in RUS, regardless whether they are EU origin. Various types of assistance (technical, financial, brokering) related to these goods, as well as to their provision, manufacture, maintenance or use are also prohibited.
/87
/87
So hopefully this now concludes this thread. Thanks again to @damspleet for inquiring abt Annex VII.
88/88
88/88
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh







