@peterktodd @aantonop @lopp @adam3us
Each of you claim to understand bitcoin's White Paper. You claim expertise in the system I created. You claim that I'm a fraud because I say something contrary to what you promote. Yet, you are promoting a system that is modified vs bitcoin
Each of you claim to understand bitcoin's White Paper. You claim expertise in the system I created. You claim that I'm a fraud because I say something contrary to what you promote. Yet, you are promoting a system that is modified vs bitcoin
You falsely claim to believe in a system that decentralises power and does not have intermediaries and yet act to control the network and to introduce a system such as the lightning network that creates a series of intermediaries
@Blockstream
@Blockstream

You actively deceive people into believing that their home node is not merely a Sybil designed to give you power and control over the fate of BTC and all who use it.
This is your grab for ultimate #power!
This is your grab for ultimate #power!
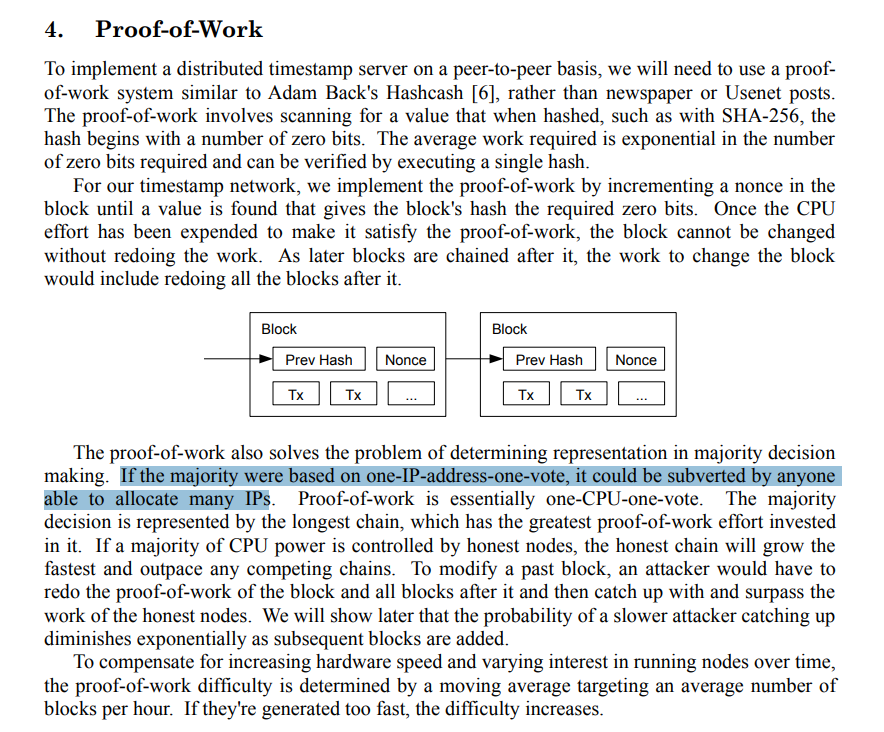
You drive people away from my paper so that they don't read it and listen to your lies and deceptions.
Yet, I called out your lies before I even launched bitcoin in 2009.
Home nodes have no say in the network and make no difference whether they exist or not.
Yet, I called out your lies before I even launched bitcoin in 2009.
Home nodes have no say in the network and make no difference whether they exist or not.

It is defined in the whitepaper that they do not have any power to determine anything and may be easily subverted.
These nodes use the most deceptive aspects of BTC to be controlled despite the will and desire of their owners. That is a soft fork.
These nodes use the most deceptive aspects of BTC to be controlled despite the will and desire of their owners. That is a soft fork.
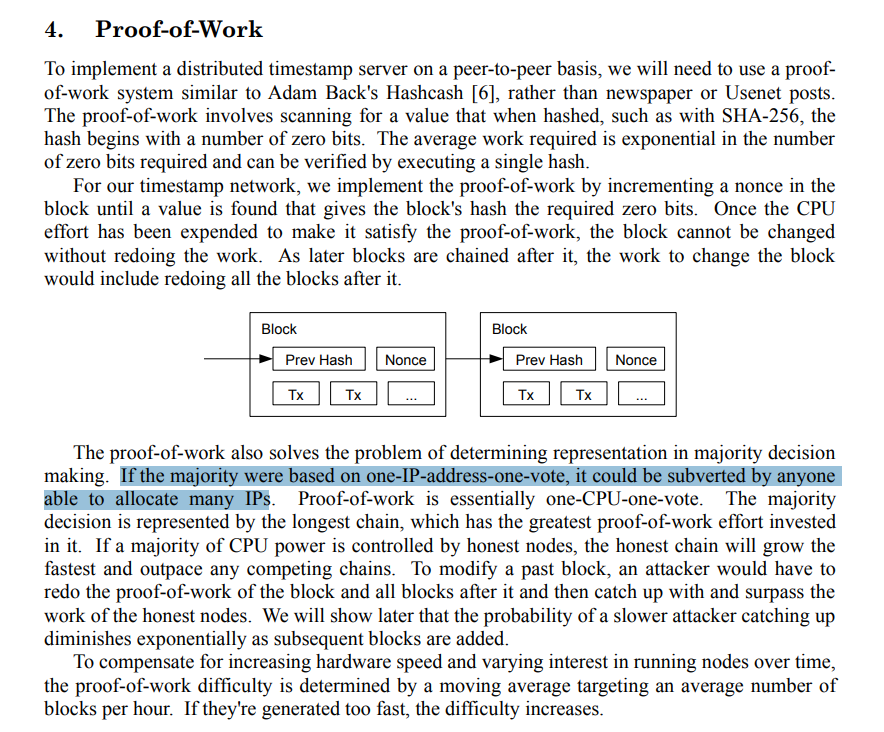
The soft fork is a means for the people controlling the code in BTC who will tell you that they have no control though they sign off everything personally, that your node makes a difference.
7,200 of the 11,000 public nodes are controlled by three entities.
Three!
Read
7,200 of the 11,000 public nodes are controlled by three entities.
Three!
Read
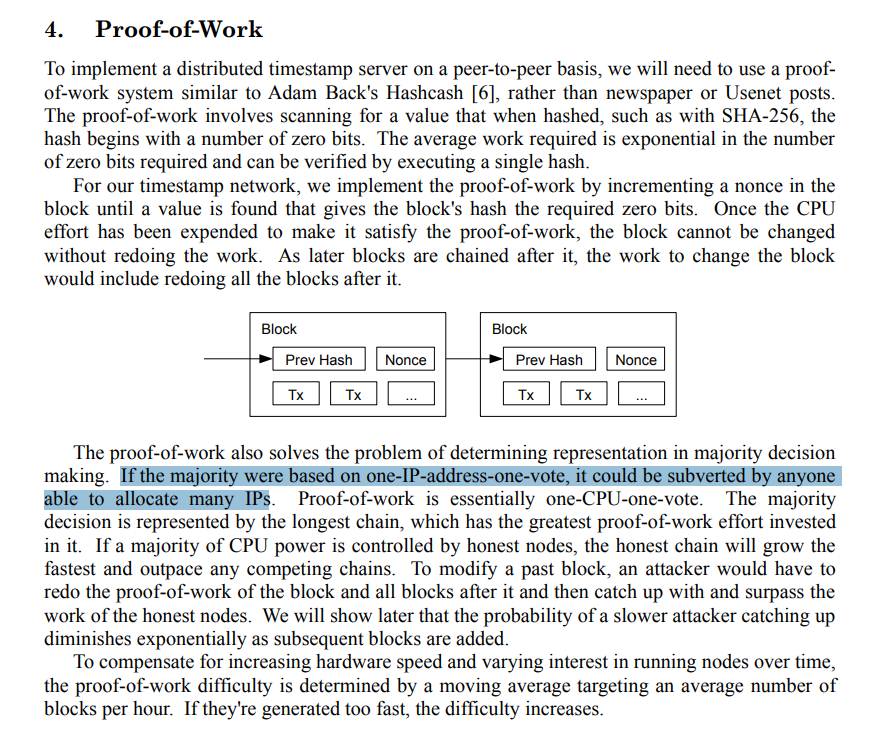
I warned you all.
Before I left to work privately, I had already warned you and did not need to give you this lesson. I told you in my paper to watch out for this type of deception and subversion.
Wake UP.
Before I left to work privately, I had already warned you and did not need to give you this lesson. I told you in my paper to watch out for this type of deception and subversion.
Wake UP.

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh




