1/ Interesting things appear to be happening currently on the Kinburn Peninsula (often erroneously called the Kinburn Spit), south-west of Kherson. Although exactly what is still uncertain, it's worth taking a look at why Kinburn matters.
2/ The Kinburn Peninsula is the hook-shaped peninsula at the mouth of the Dnieper Estuary. It's about 40 km (25 mi) long and about 9 km (6 mi) wide. The Kinburn Spit is the narrow curving 'tail', 8.5 km long, that extends into the estuary at the far west end of the peninsula. 

3/ The peninsula is flat and sandy, with many small lakes and salt marshes. It's partly wooded with oaks and pines. There are only four small villages on the peninsula with about 850 pre-war inhabitants. Oddly, the border between Mykolaiv and Kherson oblasts runs between them. 

4/ Most of the peninsula is uninhabited. It's the site of a number of rare natural habitats, protected by the National Park "Biloberezhia Sviatoslava". Before the war, it was a popular place for hydrofoil trips from Kherson, beach holidays, camping and wilderness hiking. 

5/ Sadly the peninsula has been badly affected by the current war. Large areas of forest have been burned, and fragile habitats are likely to have been badly damaged by military vehicles.
6/ The peninsula has always had strategic importance. Herodotus visited it in the 5th century BC, when it was known as Gilea ("Forest"). Its modern name comes from the 15th century Turkish fortress of Kilburun ("Beautiful Pole"), which was located on the spit. 

7/ Kilburun/Kinburn Fort was fought over several times in the 17th century before it was captured by Russia in 1774. The Anglo-French fleet attacked and captured it in October 1855 during the Crimean War, and it was demolished under the terms of the subsequent peace agreement. 

8/ Why is Kinburn so important? The strait between the spit and the north shore at Ochakiv is only 4km wide. As this map shows, it overlooks the entrances to both the Dnieper and to the Southern Bug river. It therefore controls access to Mykolaiv and Kherson ports. 
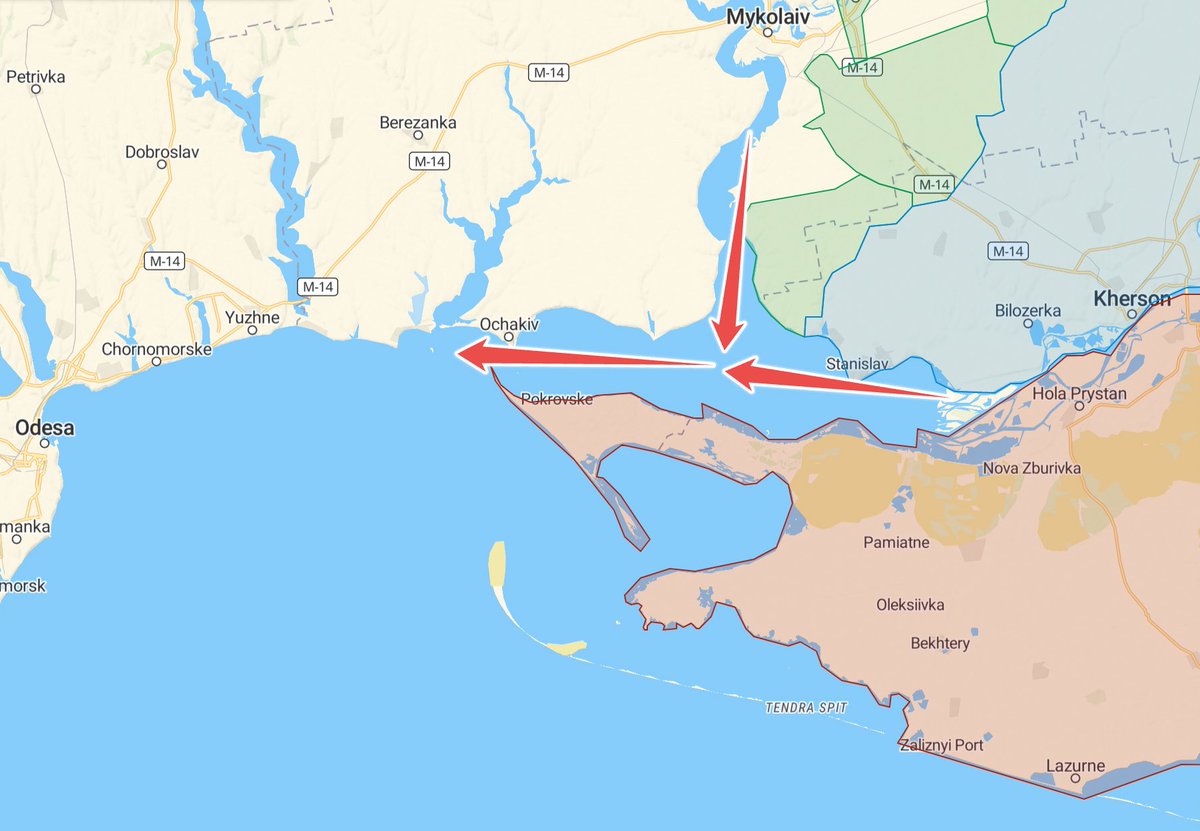
9/ Another important factor is that the peninsula is the most westerly mainland point Russia has reached in its invasion of Ukraine. It's the nearest occupied territory to Odesa, 60 km away, and overlooks most of Ukraine's remaining routes into the Black Sea. 

10/ For some reason Russia did not take control of the peninsula until around 10 June, three months after capturing the rest of Kherson oblast south of the Dnieper. It's not clear whether Ukraine had any forces there at the time.
11/ The Russian advance on Kinburn enabled it to launch missiles at Ochakiv port, capsizing the Ukrainian anti-submarine corvette Vinnytsia. The 81m landing ship Yury Olefirenko was filmed making a narrow escape under Russian bombardment.
12/ Russia soon turned Kinburn into a military base. Artillery, rockets and Iranian-made drones have all reportedly been fired from there. The peninsula and spit were fortified to blockade the strait and shell Ochakiv and the Ukrainian-held Pervomayskiy Island in the strait.
13/ The man in this propaganda video is mercenary commander Alexei Kondratyev, leader of the 'Don' Cossack Brigade of the Redut private military company. It appears that, at least in October-November 2022, Kinburn was held by Redut.
14/ Ukraine likely tried to probe Russian defences on Kinburn before the recent liberation of Kherson. Kirill Stremousov, the recently deceased head of the Russian administration in Kherson, claimed to have defeated a special forces raid in September.
15/ It's unclear what's been going on lately but unconfirmed reports and video appear to show amphibious armoured vehicles and/or boats crossing the Kinburn Strait at night, most likely from Ochakiv.
16/ Ukraine likely aims to stop Russia using the peninsula as a fire base. The fall of Kherson likely makes the peninsula untenable anyway, as it's now within artillery range from the Ukrainian-held north side of the Dnieper.
17/ What will happen next is not yet clear. Satellite images suggest that the Russians have set up new defensive lines at the neck of the peninsula.
https://twitter.com/NLwartracker/status/1592237134446198784
18/ As @NLwartracker points out, though, the new defences are also within artillery range and the restrictive terrain makes movement difficult. So I would not expect these defences to last long against a determined attacker.
https://twitter.com/NLwartracker/status/1592237142943887361
19/ It's possible, if the Ukrainians are feeling ambitious, that they could push further east to bypass the lines of defence that the Russians have set up in the rest of Kherson oblast. But that's speculation – we'll have to wait for official announcements. /end
A little more on why control of Kinburn is so important for the shipping lanes:
https://twitter.com/longwaves12/status/1594785634681778176?t=ZLjfYRuUOR-lxOZFyclRlQ&s=19
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh