1/ In the last few weeks, we have investigated various infections with the malware dubbed "Raspberry Robin" by RedCanary.
As described by Microsoft and observed in our own investigations, the infections lead to further malware, in our case, Agent Tesla. 🧵
As described by Microsoft and observed in our own investigations, the infections lead to further malware, in our case, Agent Tesla. 🧵
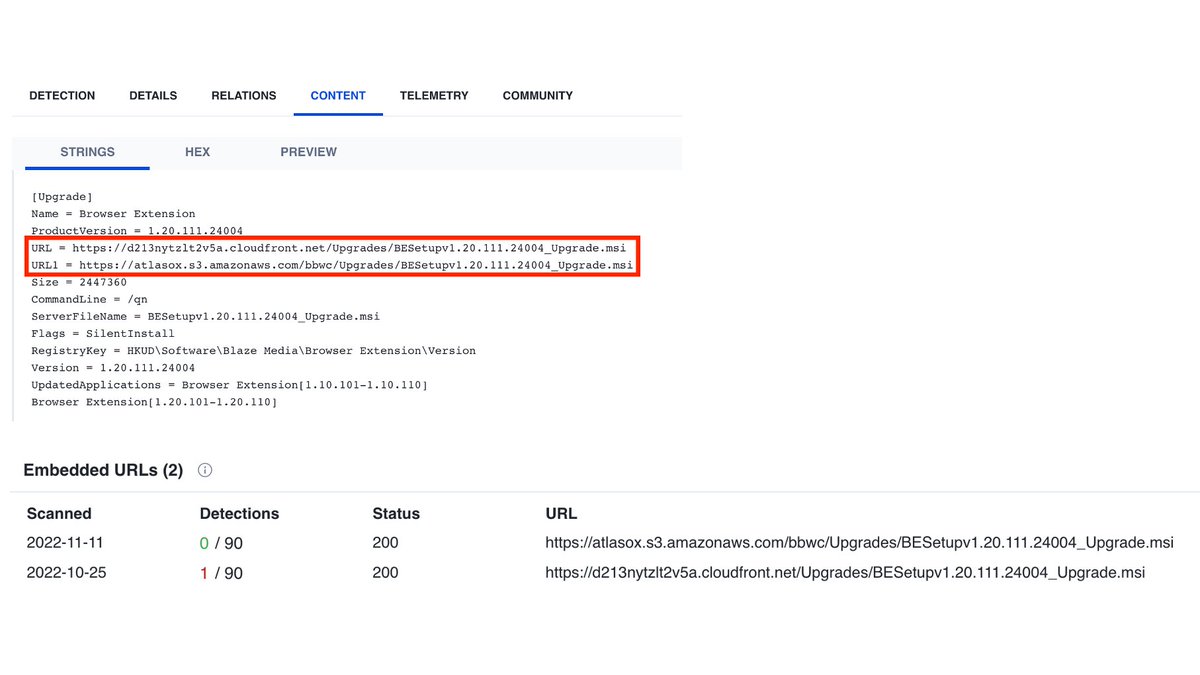
2/ Raspberry Robin uses msiexec.exe to download a malicious MSI package, using short domain names, as described in [1].
In addition, we observed port 8080 in the corresponding network request in all infections examined - a good indicator for #hunting in the firewall logs.
In addition, we observed port 8080 in the corresponding network request in all infections examined - a good indicator for #hunting in the firewall logs.

3/ @Kostastsale tweeted a regex for hunting these C2 requests and @felixaime a link to a repository consisting of Raspberry Robin domains (also called QNAP Worm). [3][4]
The domains contacted by our infected machines are also listed on the IOC inventory 👌 (passive DNS, anyone?)
The domains contacted by our infected machines are also listed on the IOC inventory 👌 (passive DNS, anyone?)

4/ "Inclusion of a string of random alphanumeric characters as the URL subdirectory, frequently followed by the victim's hostname and username" [1]. 

5/ In all our incidents, the network request over msiexec used unencrypted HTTP, and the hostname and username were always part of the GET request.
If your company assigns the hostnames according to a specific pattern, search for hostnames in the proxy logs using a regex.
If your company assigns the hostnames according to a specific pattern, search for hostnames in the proxy logs using a regex.
6/ Further, dllhost.exe, rundll32.exe, and regsvr32.exe have established (unencrypted) connections to TOR sites. Example:
rundll32.exe has initiated a HTTP connection to 212.186.71[.]38/tor/server/fp/ece1073ca9f22e30b024fc3bebc901b39a4552a5
Again, check your proxy logs. 🕵️♀️
rundll32.exe has initiated a HTTP connection to 212.186.71[.]38/tor/server/fp/ece1073ca9f22e30b024fc3bebc901b39a4552a5
Again, check your proxy logs. 🕵️♀️
7/ In some cases, we have also seen that the infection wrote a DLL in a random ProgramData directory and setup a persistence via scheduled task - the same behavior described by Microsoft [2].
Example:
Example:
8/ msiexec.exe created a scheduled task:
Name:
'Microsoft\Windows\RemoteApp and Desktop Connections Update\odbcaReady'.
Payload:
C:\ProgramData\ImportNotes\ThumbPuoh\IOSCsxft_wPFRT.dll
Name:
'Microsoft\Windows\RemoteApp and Desktop Connections Update\odbcaReady'.
Payload:
C:\ProgramData\ImportNotes\ThumbPuoh\IOSCsxft_wPFRT.dll
9/ Red Canary has published various Atomic Red team tests to simulate the detections for Rasperry Robin.
The tactic "Emulating Command Prompt reading and executing the contents of a CMD file" has changed in our cases and would probably no longer work. 🤔
The tactic "Emulating Command Prompt reading and executing the contents of a CMD file" has changed in our cases and would probably no longer work. 🤔
10/ This atomic was developed specifically to emulate Raspberry Robin. It uses the "standard-in" command prompt feature (cmd /R <) to read and execute a file via cmd.exe.
cmd /r cmd<C:\AtomicRedTeam\atomics\T1059.003\src\t1059.003_cmd.cmd
From [1]
cmd /r cmd<C:\AtomicRedTeam\atomics\T1059.003\src\t1059.003_cmd.cmd
From [1]
11/ In our cases, we observed the following command line:
cmd.exe /Q /C TyPe IEgl.LOG|CMD
On my system, the AtomicRedTeam payload also opens calc, but without using "cmd /R <".
cmd.exe /Q /C TyPe IEgl.LOG|CMD
On my system, the AtomicRedTeam payload also opens calc, but without using "cmd /R <".

12/ Raspberry Robin has become a critical finding due to further code reloading, which must be analyzed promptly and thoroughly.
For older infections, it is imperative to check for post-infection activity. Good luck 🍀
For older infections, it is imperative to check for post-infection activity. Good luck 🍀
13/ References:
[1] redcanary.com/blog/raspberry…
[2] microsoft.com/en-us/security…
[3]
[4] github.com/SEKOIA-IO/Comm…
[1] redcanary.com/blog/raspberry…
[2] microsoft.com/en-us/security…
[3]
https://twitter.com/Kostastsale/status/1602321123823058945
[4] github.com/SEKOIA-IO/Comm…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh