1/Talk about twisting your back! Do spine vascular lesions make your brain feel tangled like the dilated vessels you see?
Here’s a #tweetorial on #spine vascular #anatomy & dural arteriovenous fistulas (dAVF)
#medtwitter #meded #FOAMed #neurotwitter #neurosurgery #neurorad
Here’s a #tweetorial on #spine vascular #anatomy & dural arteriovenous fistulas (dAVF)
#medtwitter #meded #FOAMed #neurotwitter #neurosurgery #neurorad

2/To understand spinal dural AVFs, you need to understand basic spinal vascular anatomy.
The spine is LONG—to get blood from the top of the cord to the bottom is like going through the length of a marathon course
The spine is LONG—to get blood from the top of the cord to the bottom is like going through the length of a marathon course

3/So we will need to tackle it like you tackle running a marathon.
When you run a marathon, you replenish yourself at aid/water stations along the way so you can make it all the way through.
Same w/spinal arterial vasculature—it needs to be replenished on the way down.
When you run a marathon, you replenish yourself at aid/water stations along the way so you can make it all the way through.
Same w/spinal arterial vasculature—it needs to be replenished on the way down.

4/The aid stations that replenish the spinal arteries on the way down are the radiculomedullary arteries. They arise from the radicular arteries (radiculo-) and go to the cord (-medullary). They give a boost to the anterior & posterior spinal arteries on their way down the spine 

5/Initially, in the fetus, the spinal arteries are replenished at every level.
But slowly, some radiculomedullary arteries regress, leaving only the radicular arteries from which they came.
Other hypertrophy to compensate, so there’s only replenishment at certain levels
But slowly, some radiculomedullary arteries regress, leaving only the radicular arteries from which they came.
Other hypertrophy to compensate, so there’s only replenishment at certain levels
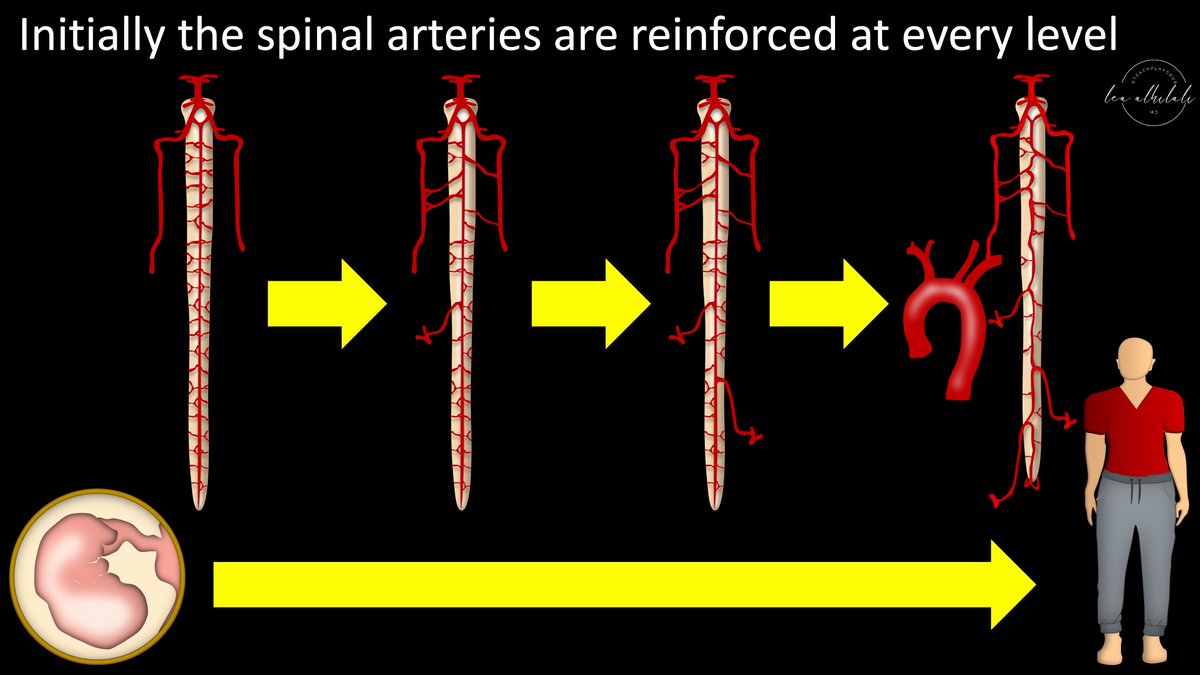
6/It is kind of like training for a marathon.
Early, you need to stop at every water station to replenish.
But as you grow & get stronger, you learn how to get more out of every aid station & you only have to use a few to replenish
Early, you need to stop at every water station to replenish.
But as you grow & get stronger, you learn how to get more out of every aid station & you only have to use a few to replenish

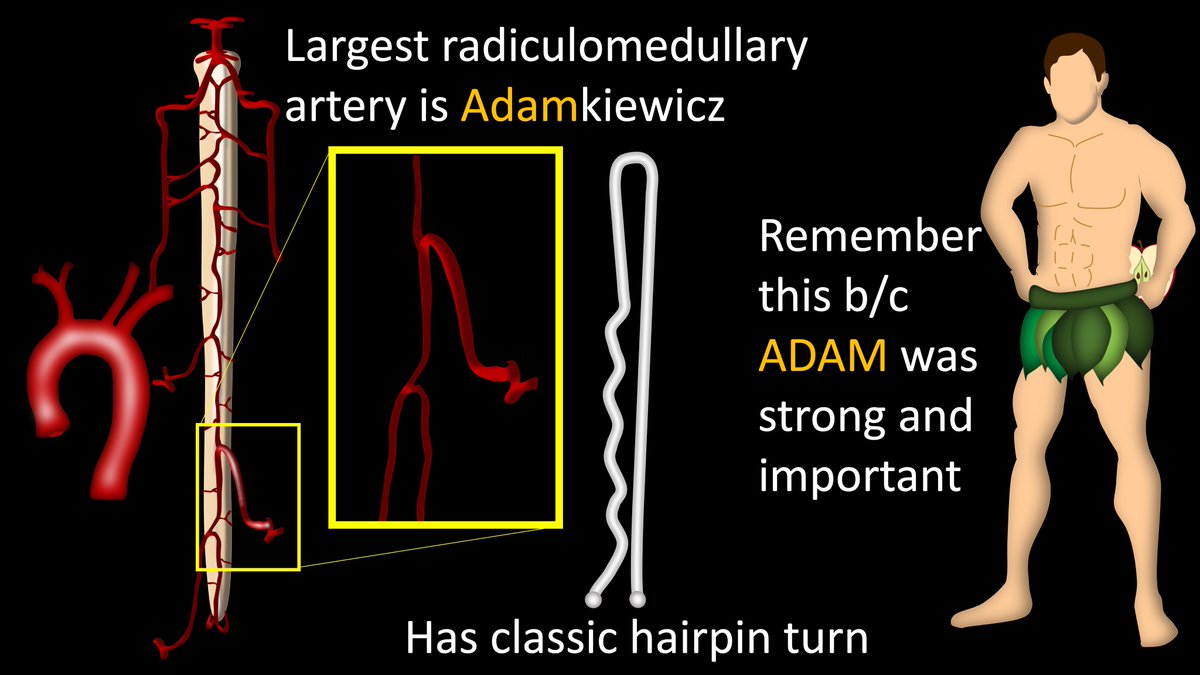
7/Largest of the radiculomedullary arteries that hypertrophied & remains is called the Artery of Adamkiewcz. It has a classic “hairpin” turn.
Other radiculomedullary arteries also can have such a turn, but Adamkiewcz will be the largest. Remember Adam was important & strong!
Other radiculomedullary arteries also can have such a turn, but Adamkiewcz will be the largest. Remember Adam was important & strong!
8/Radicular arteries supplying the radiculomedullary vessels live in the dura of the nerve root sleeve (nerves give you RADICULAR pain--so by the nerves is RADICULAR artery)
Radicular veins are here too, draining this region into the perimedullary venous plexus along the cord
Radicular veins are here too, draining this region into the perimedullary venous plexus along the cord

9/In addition to giving off branches that supply or drain to the cord, radicular arteries and veins also supply/drain the adjacent pedicle and nerve root in this region 

10/The fistula forms in the nerve root sleeve. No one knows exactly why. Some think the Glomerulus of Manelfe, which regulates venous pressures here, causes fistulas.
Regardless, increased pressure in the arterialized radicular vein backs up into the perimedullary plexus
Regardless, increased pressure in the arterialized radicular vein backs up into the perimedullary plexus

11/So the dilated vessels you see on MR & angiograms IN THE CANAL, are NOT the fistula
Rather, these are the dilated perimedullary plexus--resulting from high arterial flow in the radicular vein backing up into the perimedullary plexus
Rather, these are the dilated perimedullary plexus--resulting from high arterial flow in the radicular vein backing up into the perimedullary plexus

12/The fistula itself is not in the canal, but in the nerve root sleeve
But it is connected to all of the dilated perimedullary venous plexus vessels in the canal we see on imaging and associate with spinal dural AVFs
But it is connected to all of the dilated perimedullary venous plexus vessels in the canal we see on imaging and associate with spinal dural AVFs

13/On an MRA for spinal dAVF, you won’t usually see the fistula—it’s too small. But you'll see the dilated, arterialized radicular vein draining into the dilated perimedullary plexus.
So it’s your job to find the level of the dilated radicular vein—b/c that’s the fistula level!
So it’s your job to find the level of the dilated radicular vein—b/c that’s the fistula level!

14/The fistula causes damage b/c the perimedullary plexus isn’t made to carry arterial volume. It’s like drinking from a slow faucet & then suddenly having it turned on all the way—you’ll choke!
Fistulas cause veins to be overloaded, get wall thickening, & eventually shut down
Fistulas cause veins to be overloaded, get wall thickening, & eventually shut down

15/Arterialized venous pressure & veins shutting down from overload causes venous congestion in the cord.
Even though the radicular vein itself doesn’t drain the cord, it drains to the perimedullary plexus, which drains the cord
So perimedullary hypertension affects the cord
Even though the radicular vein itself doesn’t drain the cord, it drains to the perimedullary plexus, which drains the cord
So perimedullary hypertension affects the cord

16/It’s like an accident on a freeway exit ramp. Even if you aren’t on the exit ramp, the exit ramp backup eventually backs onto the highway—so even cars not using that exit are affected
Even though the cord doesn’t drain through the radicular vein, the venous backup affects it
Even though the cord doesn’t drain through the radicular vein, the venous backup affects it

17/ B/c there is a pressure gradient in the upright position & the cspine has better venous drainage, congestion is most pronounced caudally, even if the fistula is higher.
So you cannot use the location of veins or cord edema to localize the fistula!
So you cannot use the location of veins or cord edema to localize the fistula!

18/Venous cord congestion causes the classic Foix-Alajounine syndrome. Venous hypertension from the fistula causes veins to overload & shut down. This causes more HTN & more shutdown.
This feed forward loop causes slowly greater venous cord edema & slowly progressive myelopathy
This feed forward loop causes slowly greater venous cord edema & slowly progressive myelopathy

19/So now you understand the anatomy and pathology behind spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas!
Hopefully, this tweetorial didn’t overload you & cause some information hypertension!
Hopefully, this tweetorial didn’t overload you & cause some information hypertension!

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















