1/I always tell my fellows, “Anyone can see the bright spot on diffusion—what sets you apart is if you can tell them why it’s there!”
Can you tell a stroke’s etiology from its appearance on MRI?
Here’s a #tweetorial to show you how!
#medtwitter #neurotwitter #stroke #neurorad
Can you tell a stroke’s etiology from its appearance on MRI?
Here’s a #tweetorial to show you how!
#medtwitter #neurotwitter #stroke #neurorad
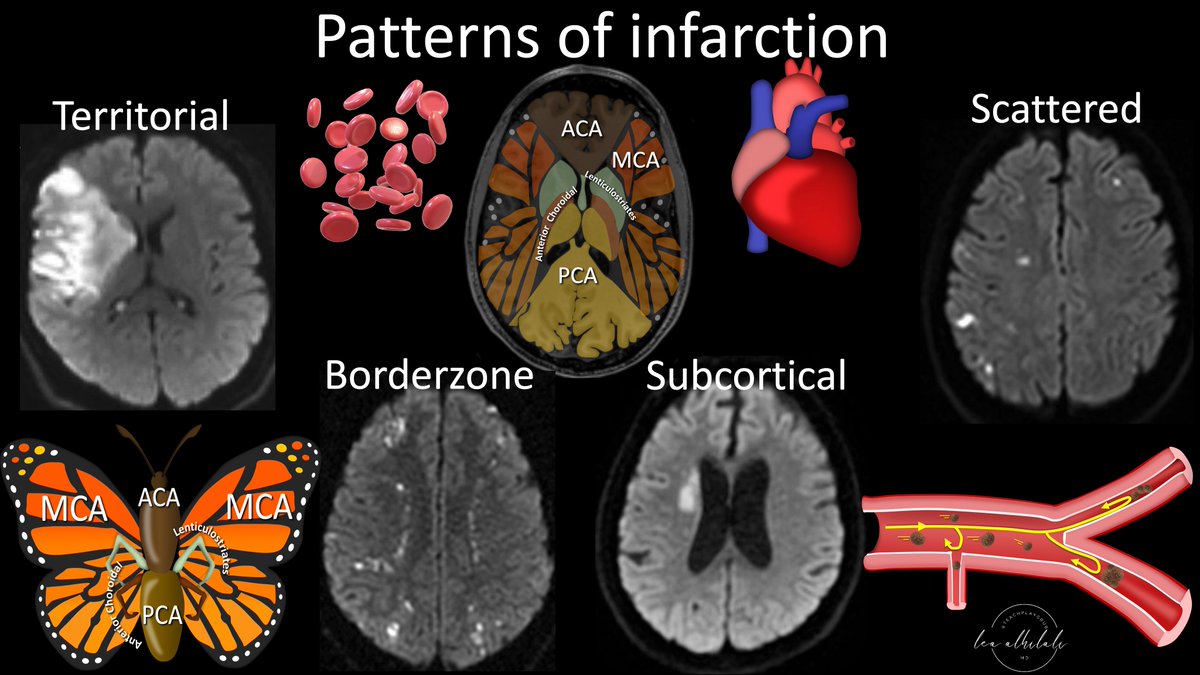
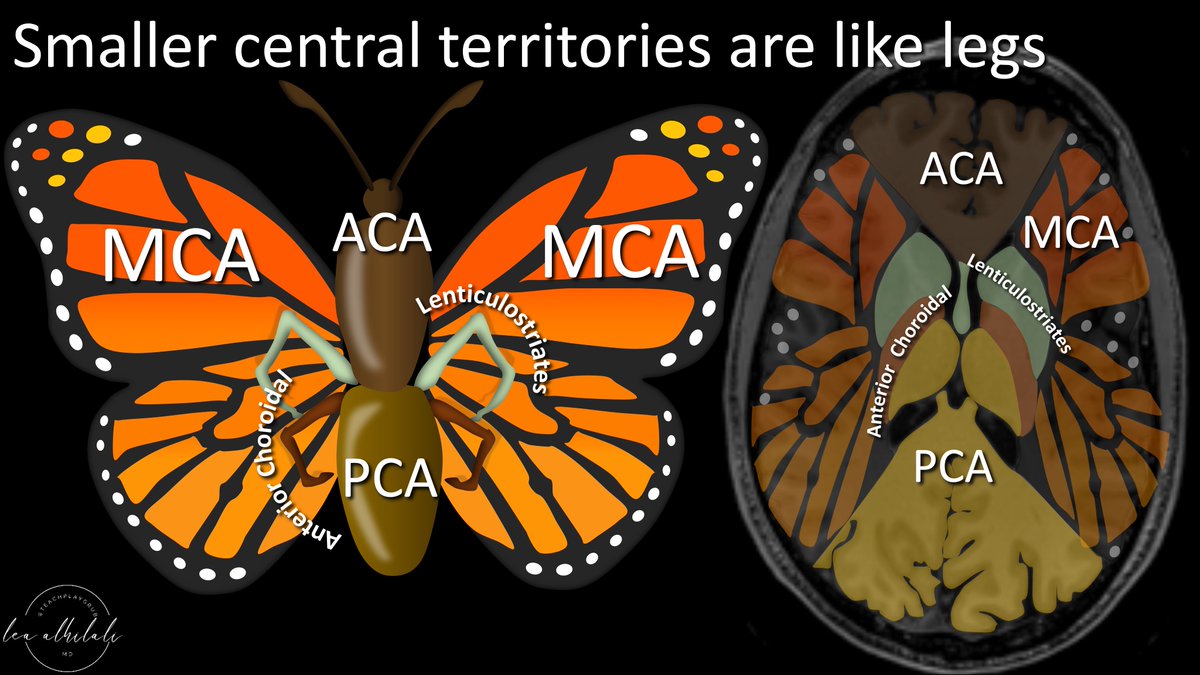
2/First a review of the vascular territories.
I think the vascular territories look a butterfly—w/the ACA as the head/body, PCA as the butt/tail, and MCA territories spreading out like a butterfly wings.
I think the vascular territories look a butterfly—w/the ACA as the head/body, PCA as the butt/tail, and MCA territories spreading out like a butterfly wings.

3/Of course, it’s more complicated than that.
Medially, there are also small vessel territories—the lenticulostriates & anterior choroidal.
I think they look like little legs, coming out from between the ACA body & PCA tail.
Medially, there are also small vessel territories—the lenticulostriates & anterior choroidal.
I think they look like little legs, coming out from between the ACA body & PCA tail.
4/Brain arterial system is like a road system transporting blood/oxygen to all over the brain via different sized roads.
Large vessels are the interstates, branch vessels are state highways, & perforators are county roads. But they are interconnected—just like a road system
Large vessels are the interstates, branch vessels are state highways, & perforators are county roads. But they are interconnected—just like a road system

5/When trying to remember the etiologies of stroke, it's helpful to think of the arteries like a road system
The same road problems that keep traffic from getting to their destination are analogous to the problems that keep blood from reaching where it needs to go in the brain
The same road problems that keep traffic from getting to their destination are analogous to the problems that keep blood from reaching where it needs to go in the brain

6/The first stroke etiology is thromboembolism. This occurs when a vulnerable plaque ruptures & causes local platelet aggregation & clot formation. This occludes the artery and prevents distal blood flow 

7/Rupture of the plaque is like a multicar accident that completely blocks the road. Nothing can past the giant pile up—just like nothing can get past the clot formation at the site of plaque rupture 

8/If this happens on a highway—& there is no other road serving that area, then no one can reach that whole territory
This is the way it is for northern Arizona & the I 17—if it is blocked, no one is getting to Flagstaff in the north. Thromboembolism causes territorial infarcts
This is the way it is for northern Arizona & the I 17—if it is blocked, no one is getting to Flagstaff in the north. Thromboembolism causes territorial infarcts

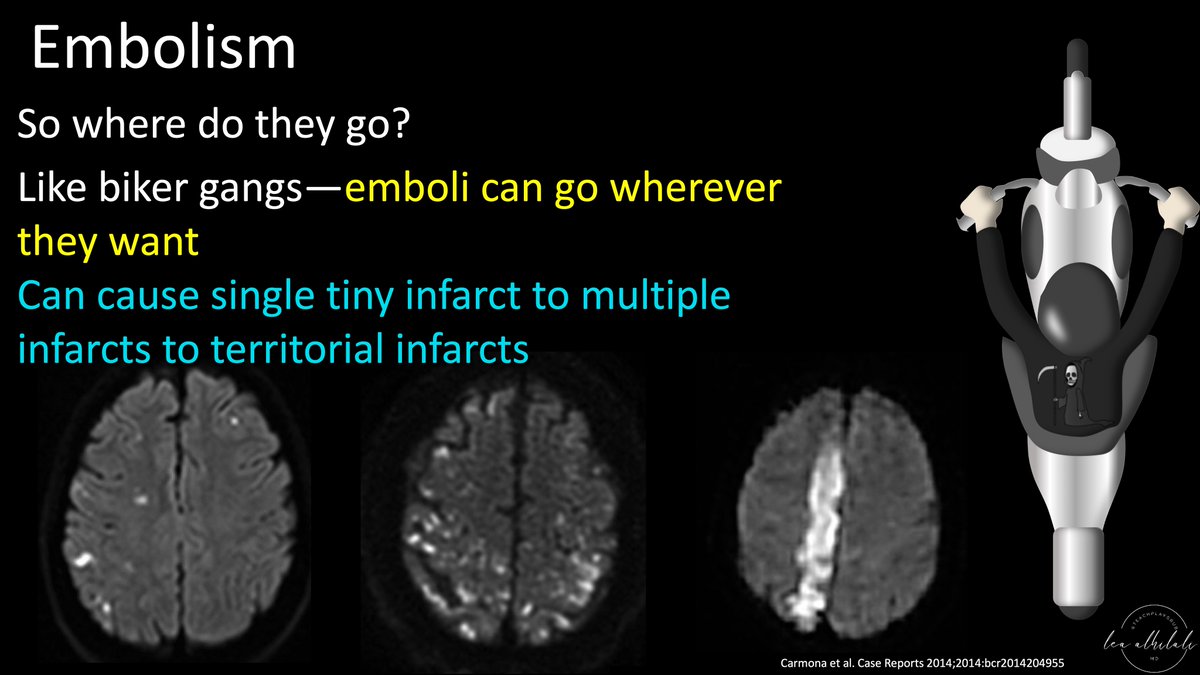
9/Next etiology is embolism.
Emboli can come either from a plaque that ruptures or breaks—but instead of occluding the artery, it spits out emboli downstream.
Alternatively, it can come from the heart, from stasis (Afib, CHF) or vegetations
Emboli can come either from a plaque that ruptures or breaks—but instead of occluding the artery, it spits out emboli downstream.
Alternatively, it can come from the heart, from stasis (Afib, CHF) or vegetations

10/I think of emboli as trouble from out of town. Thrombus from elsewhere invading an innocent artery.
It’s like motorcycle biker gangs from out of town—coming in & disrupting traffic in an innocent city
It’s like motorcycle biker gangs from out of town—coming in & disrupting traffic in an innocent city

11/So where do emboli go?
Like biker gangs, emboli go wherever they want. If they end up in large vessels, you get a territorial infarct, or they can block smaller vessels & give smaller infarcts.
They can even give you just one tiny infarct if you catch it soon enough
Like biker gangs, emboli go wherever they want. If they end up in large vessels, you get a territorial infarct, or they can block smaller vessels & give smaller infarcts.
They can even give you just one tiny infarct if you catch it soon enough
12/Next etiology is distal hypoperfusion. This is where the plaque is not so large that it occludes the vessel entirely, but large enough that it attenuates the flow distally—and tissue distal to the stenosis does not get enough blood as a result 

13/Hypoperfusion is like bad traffic.
You can get through, but waste so much gas sitting in traffic that you end up having to stop before your final destination.
As a result, no one gets to the distal cities on the highway—and certainly not all the way to the BORDER.
You can get through, but waste so much gas sitting in traffic that you end up having to stop before your final destination.
As a result, no one gets to the distal cities on the highway—and certainly not all the way to the BORDER.

14/These are called BORDERZONE infarcts, as blood flow runs out like gas & doesn’t make it to the distal borders between the territories
How to remember the borders? They’re the border between the butterfly parts. So picture the butterfly & you’ll always remember the borderzones
How to remember the borders? They’re the border between the butterfly parts. So picture the butterfly & you’ll always remember the borderzones

15/A common borderzone infarct is between the butterfly body (ACA) & wing (MCA). This borderzone infarct commonly has several small infarcts along the border.
It is sometimes called the string of pearl signs, b/c this row of small round infarcts looks like a string of pearls
It is sometimes called the string of pearl signs, b/c this row of small round infarcts looks like a string of pearls

16/I remember that a string of pearls is worn around the NECK.
So if I see a string of pearls on diffusion imaging, I immediately check the NECK, b/c this border zone infarct is commonly from a carotid stenosis in the neck
So if I see a string of pearls on diffusion imaging, I immediately check the NECK, b/c this border zone infarct is commonly from a carotid stenosis in the neck

17/Next etiology is impingement on perforators. This is when the plaque in a large vessel covers up the opening of a small perforator emerging from its wall. This obstructs flow to the perforator 

18/This is like when traffic is bad on the highway & blocks your exit. There’s no traffic on your exit—but you just can’t get to it b/c of traffic on the main highway.
There’s nothing more frustrating than seeing no traffic on your home exit—but being unable to reach it
There’s nothing more frustrating than seeing no traffic on your home exit—but being unable to reach it

19/These perforator infarcts usually result in subcortical infarcts.
I remember this b/c a single exit is being blocked. Like your exit to the street leading to your neighborhood or SUBDIVISION.
SUBdivision block means SUBcortical infarct.
I remember this b/c a single exit is being blocked. Like your exit to the street leading to your neighborhood or SUBDIVISION.
SUBdivision block means SUBcortical infarct.

20/Next etiology is vasculitis.
Vasculitis is an inflammatory condition of the vessel wall, that could be idiopathic, autoimmune, or infectious.
Regardless of the reason, the inflammation leads to vessel wall damage, stenosis, & focal occlusions or thrombosis
Vasculitis is an inflammatory condition of the vessel wall, that could be idiopathic, autoimmune, or infectious.
Regardless of the reason, the inflammation leads to vessel wall damage, stenosis, & focal occlusions or thrombosis

21/Vasculitis is like poor road conditions. It is like having potholes everywhere. These potholes cause car accidents wherever they may appear & result in traffic back up. 

22/Usually potholes are on smaller roads—b/c the government always takes care to make sure highways are maintained first, so they’re usually less like to have potholes than smaller streets. Similarly, infarcts are usually from smaller rather than larger vessels in vasculitis 

23/Last, but certainly not least, is small vessel disease.
This is a kind of wastebasket that encompasses many different pathologies that all have in common that they cause damage to & occlusion of small, unnamed vessels in the brain
This is a kind of wastebasket that encompasses many different pathologies that all have in common that they cause damage to & occlusion of small, unnamed vessels in the brain

24/You can remember this bc unnamed vessels are like the unnamed country roads that go to places larger roads don’t go to
These are usually dirt roads, so they’re very vulnerable to slow traffic, potholes, mud, etc
They are tiny, so their infarcts are usually tiny as well
These are usually dirt roads, so they’re very vulnerable to slow traffic, potholes, mud, etc
They are tiny, so their infarcts are usually tiny as well

25/So now you understand the different etiologies of stroke & how different etiologies have different distributions on MRI.
Remember, catching the stroke on the diffusion imaging isn’t the end of your job—it’s the beginning!
Remember, catching the stroke on the diffusion imaging isn’t the end of your job—it’s the beginning!

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















