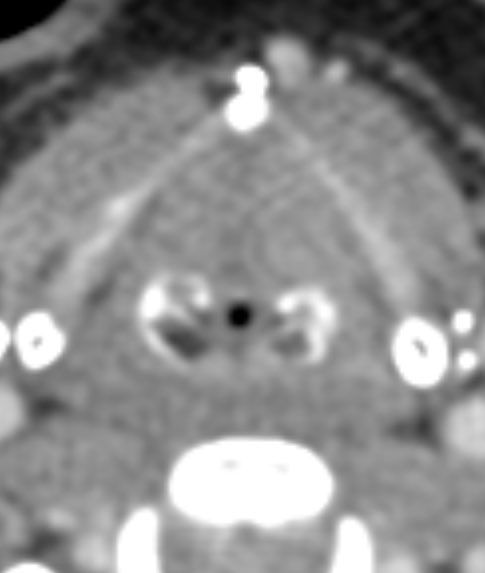
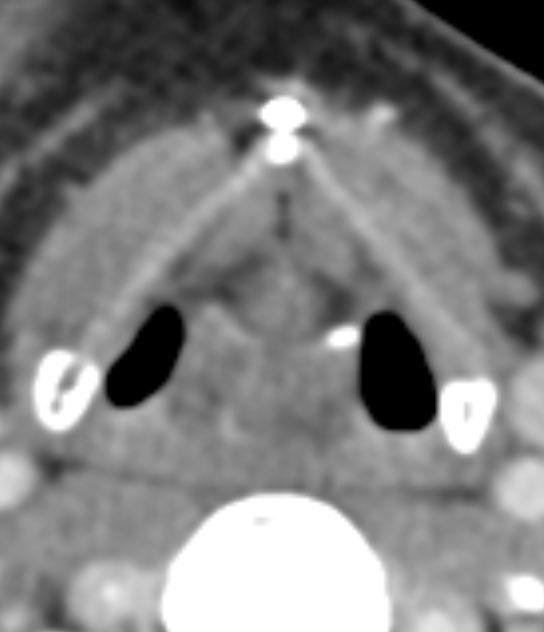
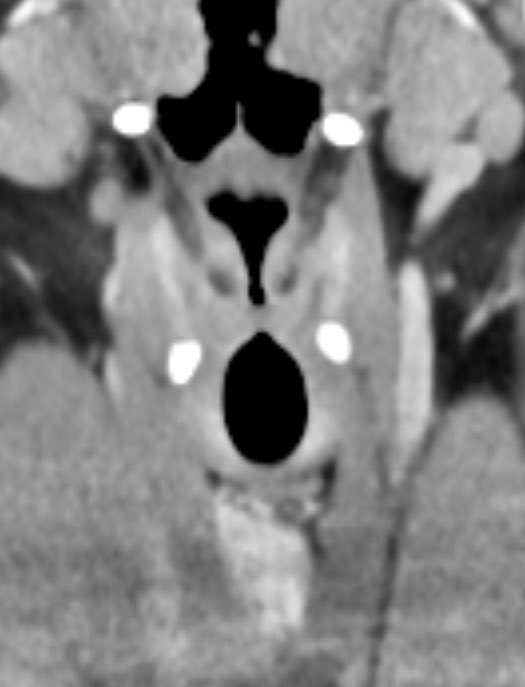
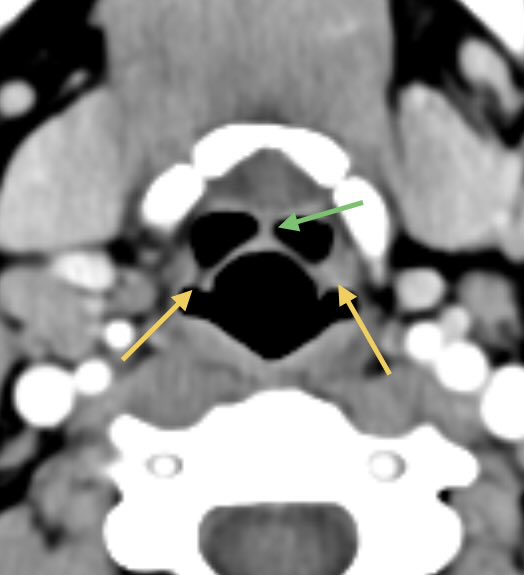
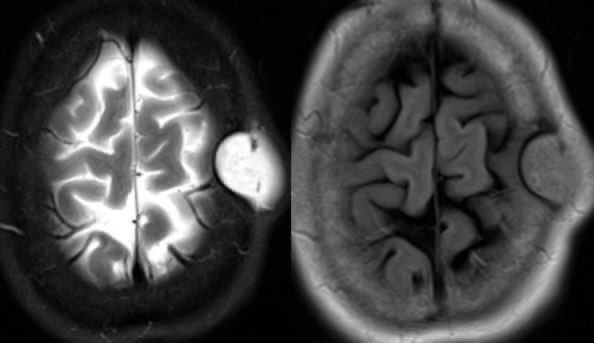
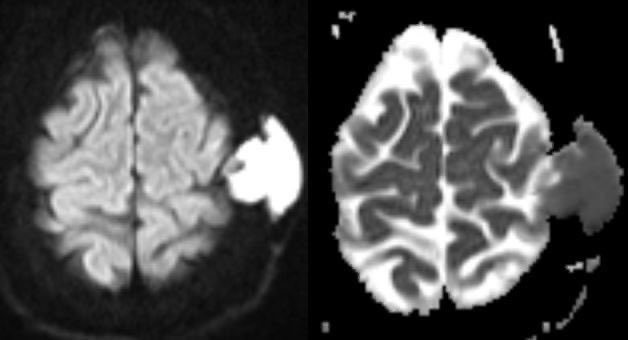
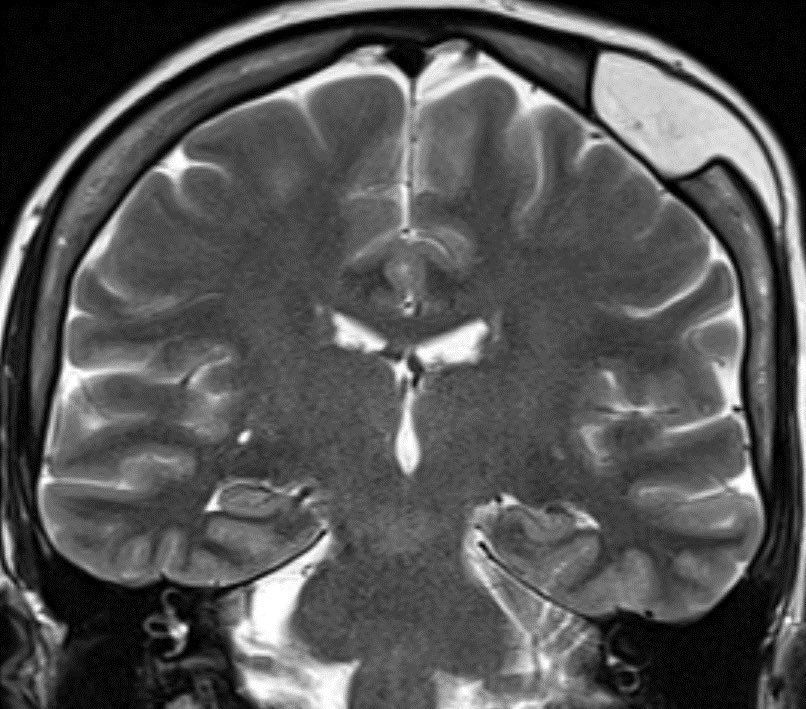
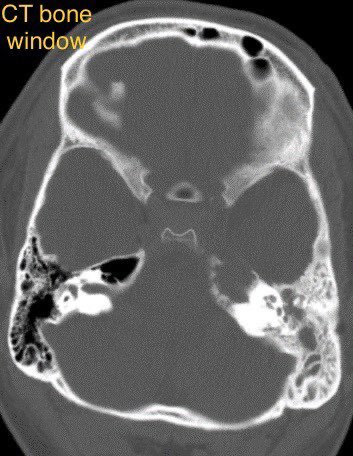
Dacryocystitis in this patient with painful swelling in the region of the right medial canthus
Etiology: obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct leads to proximal dilatation and superimposed infection of the nasolacrimal duct sac
#ophthalmology #ent #radres @ASHNRSociety

Etiology: obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct leads to proximal dilatation and superimposed infection of the nasolacrimal duct sac
#ophthalmology #ent #radres @ASHNRSociety


May be congenital or acquired
Congenital: imperforate membrane, incomplete canalization, or atresia leads to tears and mucus accumulation causing a dacryocystocele, if infected/inflamed, use the term dacryocystitis
Adults: acquired from any cause of obstruction
Congenital: imperforate membrane, incomplete canalization, or atresia leads to tears and mucus accumulation causing a dacryocystocele, if infected/inflamed, use the term dacryocystitis
Adults: acquired from any cause of obstruction
Imaging: often obtained to evaluate for orbital cellulitis
Look for a well defined cystic lesion at the medial canthus with continuity with the nasolacrimal duct
When reporting, discuss the extent of the lesion, laterality, and if there are signs of infection 🧠
Look for a well defined cystic lesion at the medial canthus with continuity with the nasolacrimal duct
When reporting, discuss the extent of the lesion, laterality, and if there are signs of infection 🧠
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh