1/I always say you can tell a bad read on a spine MR if it doesn’t talk about the lateral recess
What will I think when I see your read? What do you say about lateral recesses?
Here’s a #tweetorial on lateral recess #anatomy & grading stenosis
#medtwitter #neurorad #spine
What will I think when I see your read? What do you say about lateral recesses?
Here’s a #tweetorial on lateral recess #anatomy & grading stenosis
#medtwitter #neurorad #spine

2/First anatomy.
Thecal sac is like a highway, carrying the nerve roots down the lumbar spine.
Lateral recess is part of the lateral lumbar canal, which is essentially the exit for spinal nerve roots to get off the thecal sac highway & head out into the rest of the body
Thecal sac is like a highway, carrying the nerve roots down the lumbar spine.
Lateral recess is part of the lateral lumbar canal, which is essentially the exit for spinal nerve roots to get off the thecal sac highway & head out into the rest of the body

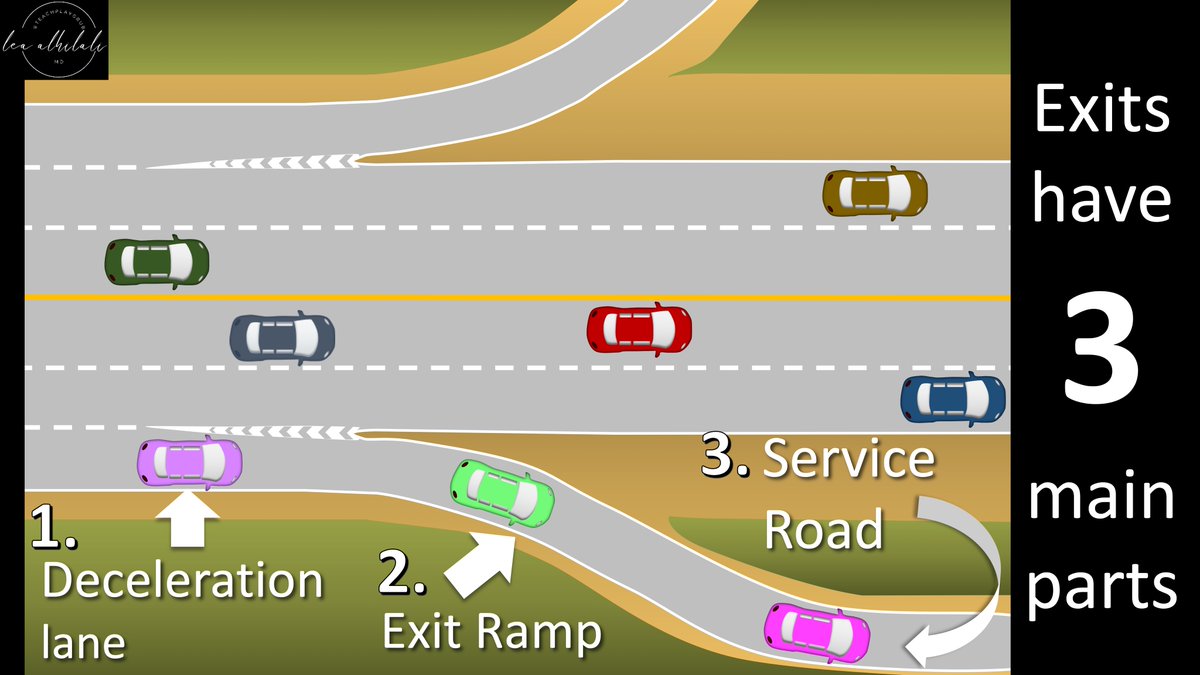
3/Exits have 3 main parts.
First is the deceleration lane, where the car slows down as it starts the process of exiting.
Then there is the off ramp itself.
The off ramp leads into the service road, which takes the car to the roads that it needs to get to its destination
First is the deceleration lane, where the car slows down as it starts the process of exiting.
Then there is the off ramp itself.
The off ramp leads into the service road, which takes the car to the roads that it needs to get to its destination
4/Lateral canal also has 3 parts like the parts of a freeway exit
Entrance to the lateral canal is like a deceleration lane & is called the entrance zone
Next is the middle zone, acts like an off ramp
Finally, is the exit zone, which is like the service road along the side
Entrance to the lateral canal is like a deceleration lane & is called the entrance zone
Next is the middle zone, acts like an off ramp
Finally, is the exit zone, which is like the service road along the side

5/The deceleration lane/entrance zone is called the “lateral recess” or “subarticular recess”
It's right behind the superior articular process (SAP) of the facet
On axial images, it is the lateral most part of the canal, right behind the vertebral body & anterior to the facet
It's right behind the superior articular process (SAP) of the facet
On axial images, it is the lateral most part of the canal, right behind the vertebral body & anterior to the facet

6/Deceleration lane leads to the exit ramp, which is the middle or foraminal zone
This is the portion that goes down under the pedicle, just like exit ramps often go down after exiting the highway
On axials, this is the region just lateral to the thecal sac, under the pedicle
This is the portion that goes down under the pedicle, just like exit ramps often go down after exiting the highway
On axials, this is the region just lateral to the thecal sac, under the pedicle

7/Finally is the exit or extraforaminal zone. It's the portion after the pedicle, running over the SAP of the lower vertebra
Like a service road, it is the last part of the exit before the nerve heads out towards its road that leads to its final destination in the body
Like a service road, it is the last part of the exit before the nerve heads out towards its road that leads to its final destination in the body

8/Now getting through this lateral canal is like an obstacle course for the nerve root!
First, the subarticular recess is located between the superior articular process & disc. These form a tunnel that the nerve root must pass through. It needs enough room in the tunnel to fit
First, the subarticular recess is located between the superior articular process & disc. These form a tunnel that the nerve root must pass through. It needs enough room in the tunnel to fit

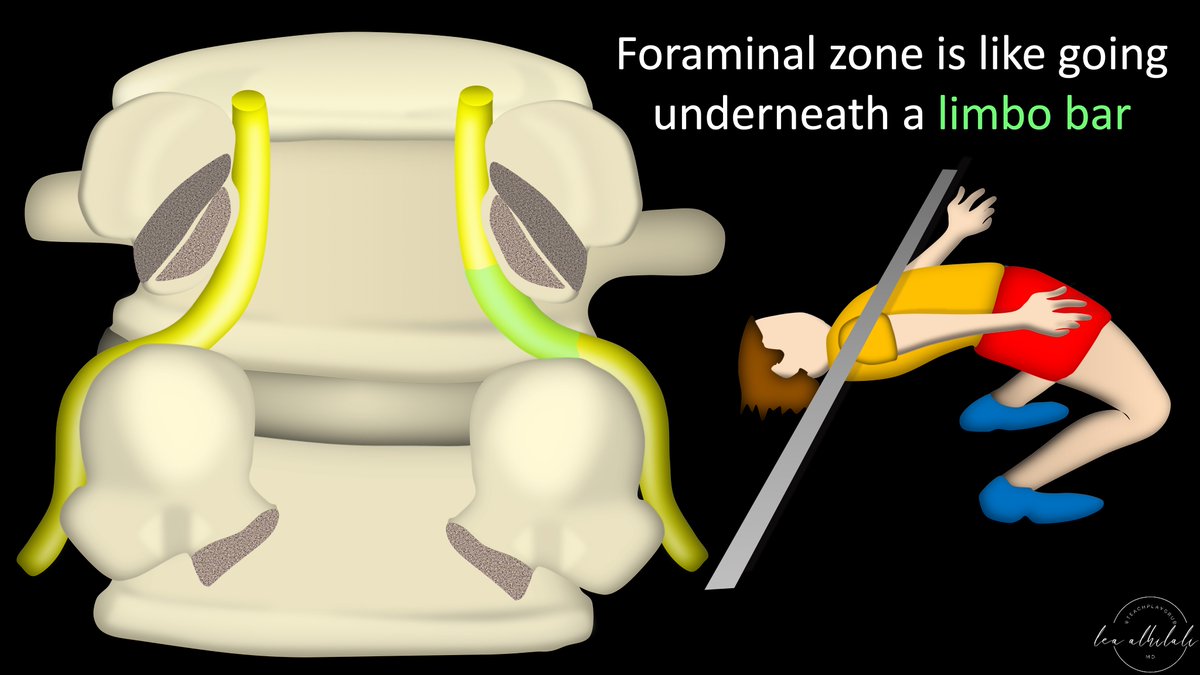
9/Next, it needs pass under the pedicle like someone doing limbo under a pole.
It needs the pole/pedicle to be high enough so it can pass under it & fit.
It needs the pole/pedicle to be high enough so it can pass under it & fit.
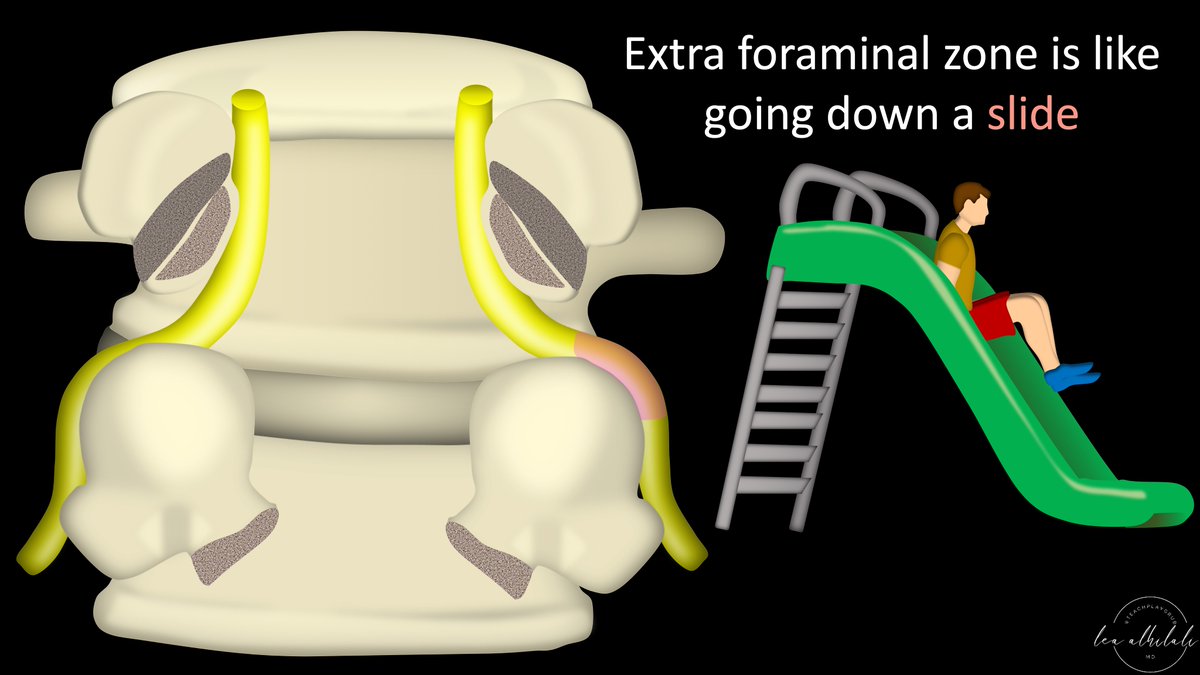
10/Finally, passing over the superior articular process of the lower lumbar vertebra is like riding down a slide—anything bumps that get in the way will make it difficult or painful to get down 
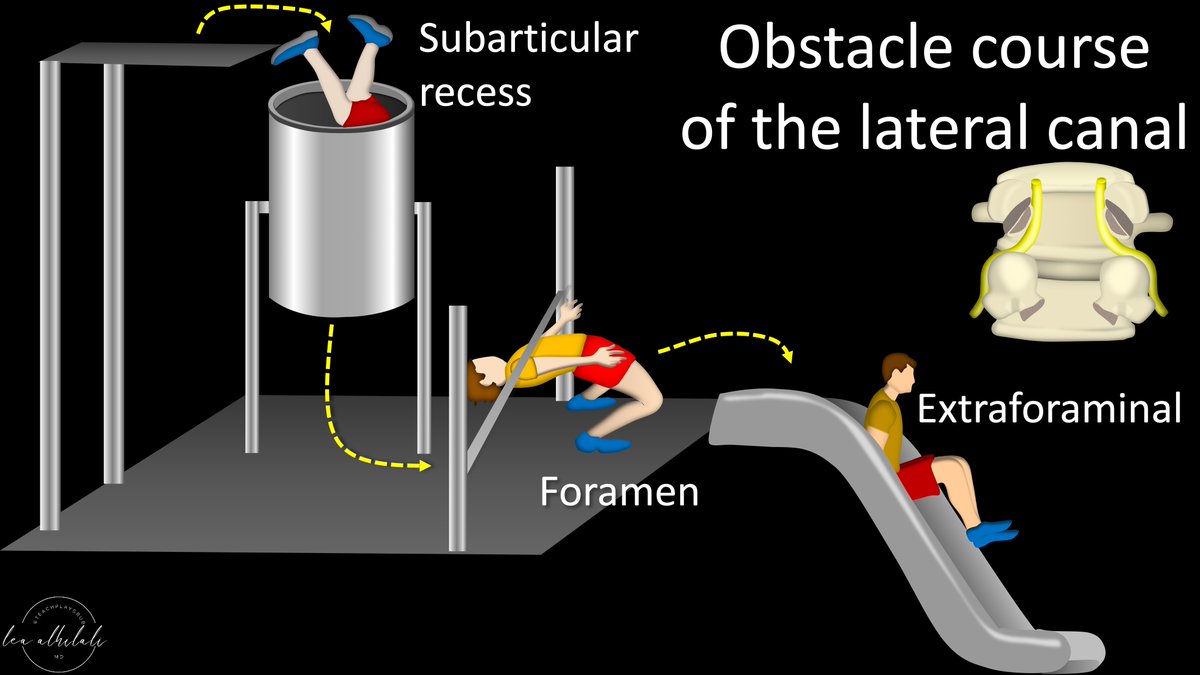
11/So here is the obstacle course of the lateral lumbar canal:
First, you must pass through the subarticular recess/lateral recess tunnel, next limbo under the pedicle in the foraminal region, & finally slide down the superior articular process of the lower lumbar vertebra.
First, you must pass through the subarticular recess/lateral recess tunnel, next limbo under the pedicle in the foraminal region, & finally slide down the superior articular process of the lower lumbar vertebra.
12/And there can be trouble along the way.
Let’s start in the subarticular/lateral recess.
This tunnel is commonly narrowed by osteophytes off of the superior articular process or even the disc
This can make the tunnel too narrow & the nerve root will be compressed!
Let’s start in the subarticular/lateral recess.
This tunnel is commonly narrowed by osteophytes off of the superior articular process or even the disc
This can make the tunnel too narrow & the nerve root will be compressed!

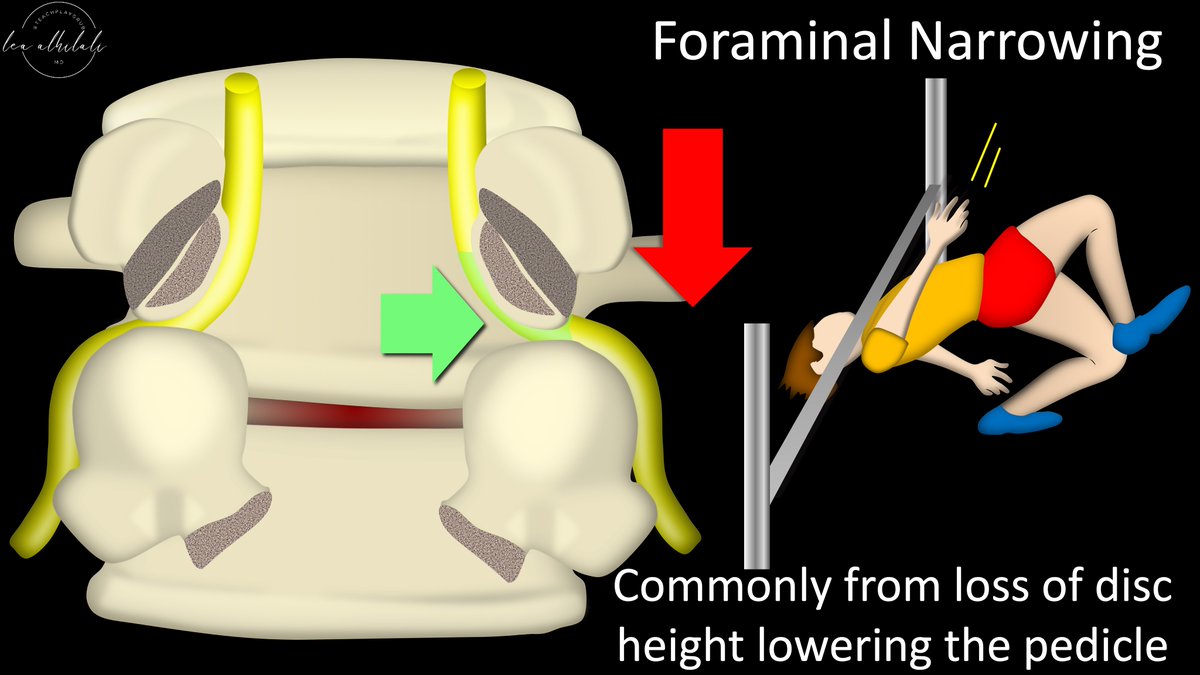
13/In the foraminal zone, the limbo bar of the pedicle is often lowered by decreased disc height, making it hard for the nerve root to pass under.
Herniations & osteophytes here can lower the bar or raise the floor so that it is impossible for the nerve root to limbo under
Herniations & osteophytes here can lower the bar or raise the floor so that it is impossible for the nerve root to limbo under
14/Finally, in the exit or extraforaminal zone, the slide down the superior articular process can be bumpy from osteophytes from the superior articular process itself.
It's like trying to go down a slide & finding a big boulder in the middle—you’ll hit it & it will hurt!
It's like trying to go down a slide & finding a big boulder in the middle—you’ll hit it & it will hurt!

15/So how do we grade lateral/subarticular recess narrowing?
Normally the nerve root sits in the subarticular recess like a pea in a pod. Just the right amount of space or CSF surrounds it.
Normally the nerve root sits in the subarticular recess like a pea in a pod. Just the right amount of space or CSF surrounds it.

16/However, these peas sit precariously positioned between the disc & superior articular process, like a pea pod between a pincer grasp.
And like a pincer grasp, the disc & superior articular process can begin to squeeze down on the nerve in the subarticular/lateral recess
And like a pincer grasp, the disc & superior articular process can begin to squeeze down on the nerve in the subarticular/lateral recess

17/Splettstober et al. came up with a rating system to describe the degree of squeeze. Grade 0 is no squeeze. No impingement on the lateral recess. Happy pea in a pod 

18/Grade 1 or MILD narrowing is when you start to squeeze it just a tiny bit.
This means the space around the peas narrow, but the peas themselves aren’t compressed or moved.
The CSF in the subarticular/lateral recess is attenuated, but nerve root is not impinged
This means the space around the peas narrow, but the peas themselves aren’t compressed or moved.
The CSF in the subarticular/lateral recess is attenuated, but nerve root is not impinged

19/Grade 2 or MODERATE narrowing is when you squeeze even harder. Bc of the increased pressure, the peas begin to move more medially in the pod
Grade 2 is when you have medialization of the nerve root bc there isn’t enough room for it in the lateral recess bc of the narrowing
Grade 2 is when you have medialization of the nerve root bc there isn’t enough room for it in the lateral recess bc of the narrowing

20/Grade 3 or SEVERE narrowing is when you really pinch down & crush the peas.
Here, the nerve root itself is compressed—it can’t even go medial to escape.
This rating system has been found to correlate with symptoms/radiculopathy referrable to the lateral recess
Here, the nerve root itself is compressed—it can’t even go medial to escape.
This rating system has been found to correlate with symptoms/radiculopathy referrable to the lateral recess

21/So now you know the anatomy of the lateral lumbar canal, its lateral/subarticular recess, and how to rate the narrowing in this region.
I know now that when I see one of your reads, I will be sure to be impressed!
I know now that when I see one of your reads, I will be sure to be impressed!

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















